Photo: pixabay.com Updated: 03/27/2020
Are maternity benefits subject to taxation? No, payments related to maternity are exempt from all taxes. If the employer decides to pay the employee extra, then he will have to pay taxes, but not always. If the amount does not exceed 50,000 rubles, then the amount of the additional payment is not taxed.
- Who is paid for maternity leave?
- How long does maternity leave last?
- How to calculate the benefit amount?
- Who is granted parental leave for up to 1.5 years?
- What are personal income tax and insurance premiums, are they withheld from benefits related to maternity?
- How are personal income tax and insurance premiums withheld when maternity benefits are paid up to average earnings?
- How are maternity benefits reflected in 2-NDFL?
- Pilot project for direct payments from the Social Insurance Fund
Who is paid for maternity leave?
After issuing sick leave in connection with maternity, a woman can apply for maternity benefits. The hospital form is filled out by an obstetrician-gynecologist at the 30th week of pregnancy (clause 46 of Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 624n).
Recipient categories include:
- Officially employed
- Unemployed, if 12 months have not passed since the date of dismissal due to liquidation of the company
- Full-time students
- Military personnel under contract, and civilians in the military, outside the Russian Federation
- Adoptive mothers
Payment of benefits is made: at the place of work, service or study. Dismissed persons apply to the social protection authorities (SZN).
How long does maternity leave last?
After receiving a certificate of incapacity for work, the woman writes an application for maternity leave. Depending on how the pregnancy proceeds, the law (Article 10 of the Federal Law-255) provides for the duration of leave:
- 140 calendar days - for normal pregnancy (70 days before and 70 days after the baby is born)
- 156 days – if there is a difficult birth or pregnancy with complications (70 and 86 days)
- 194 days – for multiple pregnancies (84 and 110 days)
If pregnancy comes with complications, two certificates are issued for temporary disability. One for 140 days - by a doctor observing the pregnancy, the second for 16 days - upon discharge from the hospital with a newborn (clause 48 of Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 624n).
How to calculate the benefit amount?
Maternity benefit (M&B) is calculated based on the amount of wages for the pay period. The billing period is two full years preceding the vacation.
Amount of maternity payments in 2021
After calculating the average daily income, the resulting amount must be multiplied by the number of vacation days (140, 156 or 194 days).
The law establishes the maximum amount of benefit payments under the BiR, limited by the maximum insurance base.
The size of the minimum payment cannot be less than the minimum wage. With less than 6 months of experience, the B&R benefit cannot exceed the minimum wage (Clause 3, Article 11 of Federal Law No. 255-FZ of December 29, 2006).
The period for calculating benefits is up to 10 calendar days from the date of presentation of the certificate of incapacity for work. The employer transfers money per day at the nearest salary (Part 1, Article 15 of Federal Law-255). If the social security authorities are involved in the calculation, the transfer of funds occurs before the 26th of the next month, after the month of presentation of the certificate of incapacity for work (clause 18 of Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia No. 1012n).
Online maternity benefits calculator
Is income tax taken from the income of a working maternity leave and how to fill out a 2-NDFL certificate for her
As mentioned above, the question of whether income tax is withheld from maternity leave is important for accountants who issue 2-NDFL certificates. Indeed, what should this certificate be for a maternity leave?
IMPORTANT! If a woman is employed by several employers at the same time, she can receive maternity leave for all places of her work. An employer in a non-principal place of work is obliged to accrue maternity benefits in exactly the same order as for the main one.
After maternity leave, the employee has the right to parental leave:
- first up to 1.5 years, during which she (also at the expense of the Social Insurance Fund) is paid a monthly allowance;
- up to 3 years, during which she may not have any income, except for monthly compensation in the amount of 50 rubles, established by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of May 30, 1994 No. 1110 and applicable to all 3 years of parental leave.
Read more about these payments in the material “Art. 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: questions and answers.”
Since payments related to child care are also not subject to personal income tax, it may turn out that a woman has no income during the year for which she needs to submit a 2-NDFL certificate to the Federal Tax Service. That is, in such a situation, a certificate is not issued.
However, current legislation allows a woman on maternity leave to work (Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) with the condition that the work will be carried out part-time. In this case, the 2-NDFL certificate is issued in the general manner.
For information about the time frame for issuing a 2-NDFL certificate, read the article “The employee was not issued a 2-NDFL certificate? Wait for the trial .
Who is granted parental leave for up to 1.5 years?
After the end of the BiR leave and the closure of the certificate of incapacity for work, a woman has the right to take out maternity leave for up to 1.5 years.
The monthly child care benefit is 40% of average monthly earnings, and not 100% as the B&R benefit.
Amount of maternity payments in 2021
The same categories of recipients as recipients of BiR benefits can receive child care benefits. In addition to the mother of the child, the father or other relatives can take parental leave.
Parental leave is provided upon application. The start date of parental leave is the day after the end of sick leave. In addition to the application, it is necessary to provide a certificate from the second parent’s place of work stating that he did not apply for leave or benefits.
The procedure for calculating and transferring funds is the same as for the B&R benefit.
Payments when going on maternity leave in 2020
There is no concept of “maternity benefits” in current legislation. This is a collective term and includes all benefits transferred to an employee in connection with pregnancy, childbirth and subsequent child care. In 2021, maternity benefits include:
- One-time benefit when registering in the early stages of pregnancy.
It is paid to the employee upon registration at a medical institution up to 12 weeks of pregnancy inclusive. The amount of this benefit is fixed; it is not tied to income or length of service. The payment amount is set for each year, and in 2021 its value is 675.15 rubles. Read more in the article “Payment of benefits in the early stages of pregnancy.”
- Maternity benefit.
It is paid to the employee for the period of leave for labor and labor, which in general is 140 days (70 days before childbirth and 70 days after it). The amount of the benefit depends on the employee’s income for the last 2 years, the length of the insurance period and the labor and employment leave. The basis for issuing it is a sick leave certificate. To learn more about who is eligible for this benefit, see the article “Maternity Benefit 2021 for Working People.”
- One-time benefit for the birth of a child.
What are personal income tax and insurance premiums, are they withheld from benefits related to maternity?
Personal income tax (tax for individuals) or otherwise income tax is a mandatory fiscal fee in the amount of 13% of a citizen’s income, withheld monthly by the Employer in favor of the Federal budget (Article 208 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The employer pays monthly insurance contributions for compulsory social insurance (Article 419 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The object of taxation is income from labor activity.
All benefits received related to maternity are not subject to taxation. Articles 217, 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation list benefits that are not subject to insurance contributions, these benefits include:
- Maternity benefit (maternity benefit)
- Child care allowance
These payments are calculated from the Social Insurance Fund. Financing from an extra-budgetary fund is provided from the first day of temporary disability of the expectant mother.
Are maternity leave included in 2-NDFL and 6-NDFL?
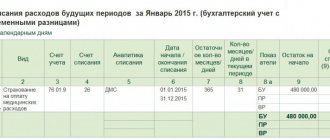
Since no income tax is paid to the budget on maternity payments, there is no need to include them in the 2-NDFL certificate and the 6-NDFL calculation. Additional payment subject to personal income tax must be made:
- in 2-NDFL - using code 4800 “Other income”;
- in 6-NDFL - indicating in lines 100 and 110 the date of actual payment of the additional payment, and in line 120 - the date of transfer of personal income tax to the budget (the day following the payment of the additional payment).
How are personal income tax and insurance premiums withheld when maternity benefits are paid up to average earnings?
In a standard situation, maternity benefits are calculated taking into account the maximum insurance base.
Example: With a salary of 100,000 rubles, income for 2 years will be 2,400,000 rubles, and the average daily income will be 3,283.17 rubles. To calculate the benefit, the maximum base for the 2 previous years is taken - 912,000 rubles for 2021, and 865,000 rubles for 2021, total 1,777,000 rubles. We find that the average daily earnings cannot be higher than 2,430.92 rubles. Taking into account the size of the insurance base, for 140 days of maternity leave, the maximum benefit amount will be 340,328.80 rubles. The employer may provide for additional payment of maternity benefits up to the actual average earnings. In this case, the additional payment of the difference is calculated at the expense of the organization, and not the Social Insurance Fund.
The Ministry of Finance believes that such additional payments cannot be classified as state benefits. They are not subject to Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and are subject to personal income tax and insurance contributions in the general manner (Letter dated February 12, 2009 No. 03-03-06/1/60).
This rule can be circumvented if you issue an additional payment as financial assistance. The payment is excluded from the tax base if the amount does not exceed 50,000 rubles. In the case where the amount of the surcharge is greater, tax must be paid on the difference (clause 8, part 1, article 217, clause 3, part 1, article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Additional payment to maternity benefits: do you need to pay personal income tax?
The B&R benefit is calculated based on average earnings for the 2 years preceding maternity leave. But the amount of the benefit is limited to a certain amount, which in 2021 is:
- RUR 322,191.80 - during pregnancy with one child and uncomplicated childbirth;
- RUB 359,013.72 - during pregnancy with one child and complicated childbirth;
- RUB 446,465.78 - during pregnancy with two or more children.
You can find out more about the procedure for calculating the maximum benefit amount in this article.
If the employee had no income or was very small, the employer is obliged to calculate her benefits based on the minimum wage. This benefit is called the minimum, and in 2020 its amount is:
- RUB 55,830.60 - during pregnancy with one child and uncomplicated childbirth;
- RUB 62,211.24 - during pregnancy with one child and complicated childbirth;
- RUB 77,365.26 - during pregnancy with two or more children.
Pilot project for direct payments from the Social Insurance Fund
Since 2012, a pilot project for direct payments from the Social Insurance Fund has been launched in two constituent entities of the Russian Federation. Since 2021, the number of participants has increased to 50. By July 2021, it is planned to transfer all regions of the Russian Federation to the new system.
The essence of the project is that the employer acts as an intermediary between the employee applying for maternity leave and the fund. The project helps a woman draw up an application for benefits using a special form and creates a package of documentation.
Then the employer contacts the Social Insurance Fund on behalf of the employee. The fund assigns benefits and independently transfers funds to the woman’s bank account. At the same time, the transactions are not reflected in the employer’s records, and the question of withholding personal income tax and insurance contributions does not arise.
Are maternity benefits subject to personal income tax?
The duration of maternity leave is generally 70 days. until the moment of birth and 70 days. immediately after. Registration of a period of incapacity for work is carried out in the presence and on the basis of a sick leave certificate, which is issued to the employee by the supervising doctor. The calculation procedure consists of determining the average earnings for the previous 2 years. The amount is paid by the employer if the region is not included in the FSS pilot project.
To find out whether maternity leavers are subject to personal income tax in 2021, let us turn to Art. 217 of the Tax Code, namely clause 1. This section clearly states that income tax is not levied on benefits under the BiR, in contrast to ordinary cases of disability. Working employees have the right to receive maternity benefits; conscripted military wives; female students; contract military personnel; as well as pregnant women dismissed due to the liquidation of the company.
As you can see, there have been no changes in legislation this year. And if the employer’s accountant reports that maternity benefits are subject to personal income tax, this indicates an incorrect interpretation of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Of course, the position of the employee when tax is withheld worsens, therefore, the company faces penalties for violations of labor laws. In addition, FSS specialists carefully check the accrued amounts of benefits and, if errors are identified, may refuse to reimburse the employer for the amounts of benefits issued.