The safety magazine, a sample download of which we will offer below, is used in a variety of areas. In production, at the factory, upon entering a job, even for students, similar instructions are provided. The document in question includes subsections - perhaps fire safety, rules for handling equipment and reagents (for example, in computer science, chemistry, physics lessons). In general terms, this is the name for a whole group of departmental documents that relate to the field of labor protection.
Legal norms
By law, the requirement to maintain a safety log applies to every employer. He is required to be present at production, in the office and when carrying out new work on other equipment. The fact that the employee is aware of the safety rules is indicated in the form, which is confirmed by his personal signature. The form of this form must comply with GOST.
Important! After filling out the log, it must be handed over to the archive, where it is stored permanently.
Particular attention is paid to maintaining, filling out and storing such a document in hazardous industries where there is a risk of injury and disfigurement. If an employee is not given introductory, repeated or other types of training, and he is injured or even killed, the employer will face a large fine and even criminal liability. Of course, it is important to register that the training has been completed; for this in 2021, as in previous years, a signature from the employee is required in the log. It is also important to observe the frequency of briefings and the rules for maintaining the journal itself.
Kinds
There are several types of instruction:
- Introductory. It is carried out with everyone who comes to work. The safety engineer or the manager directly is responsible for this if the company is small. Its essence is to conduct an explanatory conversation with a newcomer and familiarize himself with the instructions. It is carried out exclusively individually. The results of its implementation are entered into the journal.
- Repeated. The need for its implementation is prescribed by law. It is required to be carried out every 6 months, regardless of the company’s activity. This need arises to update the initial briefing data. It can be carried out unscheduled if it is necessary to familiarize employees with new data. This type of training is group in nature and is carried out only by an authorized person.
- Target. Such a study of instructions is narrowly focused. The main goal is to educate the employee about the specifics of implementing a particular task. They are carried out at construction sites, factories or when transferring to a new site. This instruction is required to avoid harm to health and life; it is individual.
- Unscheduled. Does not apply to the training plan that is recorded at the enterprise. It is practiced when introducing a new work scheme, introducing other equipment and when launching an additional technological process.
Important! In some cases, unscheduled training is associated with systematic violations of safety regulations or emergency situations at the enterprise. Sometimes it is carried out at the request of higher authorities.
Control over the lead
The head of the unit checks the safety log daily, regardless of whether there are new entries or not. This is the first degree of control. The head of the labor protection department is also responsible; he must check its registration. In his job description, this form of control is listed as monthly. Moreover, the journal must contain his visa regarding the presence or absence of violations of conduct. Even the CEO should check the log once a quarter. This is the last stage of control. If everyone responsible knows how the document should be filled out correctly and controls its maintenance, there will be no problems with inspection authorities and no penalties.
Rules for maintaining and storing a journal
Occupational health and safety (OHS) is controlled in three stages (variably depending on the complexity of the organization):
- The head of the unit in which the training is being conducted must monitor the availability of the journal on a daily basis, regardless of whether new entries are added there or not.
- A senior manager should review the logbook once a month or more frequently. A corresponding entry is made about this on the entire line. If any violations are discovered, the manager writes about them and indicates within what period they should be eliminated.
- Third-stage control is carried out in organizations with a complex structure - by the general director, chief engineer or HSE specialist - once a quarter or more often.
At small enterprises, control of the second and third stages is carried out by external authorized organizations. In practice, there are also cases when such control is not carried out at all or is carried out selectively.
The completed journal is handed over to the organization’s archives and must be stored until the expiration of the statute of limitations provided for by the organization’s regulations.
Responsible person: compilation and maintenance
Control is assigned to many levels, but only one is involved in compilation and maintenance. An example of a magazine can be found below and downloaded in Word format for free.
The forms, which are uniform for all structural divisions of the enterprise, are stored in one place and by one person - an occupational safety and health engineer. In small companies, such duties are assigned to any other employee, and a corresponding order is issued. The responsible person is obliged to keep a log in accordance with the following rules:
- numbering of all pages;
- firmware certified by management;
- presence of the signature and seal of the manager;
- A stationery book with an A4 format spread is used for maintenance;
- the working field consists of 12 line columns;
- if the entry is very long, then multiple lines are allowed;
- dashes are entered in empty columns;
- the cover and paper must be wear-resistant, since the document is designed for long-term use and permanent storage.
Important! Large enterprises most often order such forms from a printing house, although they can be printed according to the example given.
Basic Concepts
Occupational safety is a set of measures to ensure the safety of employees of an organization.
It includes:
- actions to ensure fire safety;
- sanitary maintenance of the enterprise;
- safety when using electrical equipment;
- measures to improve working conditions.
Safety precautions are an integral part of labor protection. It consists of measures aimed at reducing occupational injuries .
Safety consists not only of maintaining the good condition of industrial buildings and equipment, but also of instructing personnel on safe work practices.
At large enterprises, this is done by a labor protection specialist. Read more in this article.
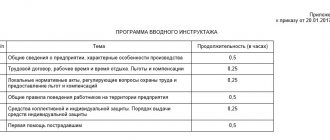
Contents of the safety magazine:
The log contains the following data in rows in order:
- record number;
- date of;
- FULL NAME. the employee who is being instructed;
- date and year of birth of the instructee;
- indication of profession and position. In some cases, instruction may be given to an employee of another organization. In this case, it is necessary to enter data regarding the details of the official ID or order, which is the basis for the employee’s presence at the briefing;
- type of training provided. If the purpose is repeated or extraordinary, the reason for the purpose should be indicated;
- FULL NAME. the one who conducts the training;
- signature of the person for whom the training was conducted and the person who carried it out. It is very important that the autograph of both one and the other be affixed with an indelible pen;
- If necessary, data on the number of shifts and the date of internship is entered.
Important! Based on the specifics of the enterprise’s activities, the structure of the journal may differ slightly. One general rule is that it requires filling out.
Form of maintaining and rules for filling out the journal
The general form according to which the journal is kept is approved by the State Standard number 12.0.004-90. Based on a single form, log templates are created that take into account safety instructions for any specific activity.
To familiarize yourself with the form, you can also see its title page.
The rules for filling out the journal are as follows:
- For maintenance, a spread of a stationery book and A4 sheets are used.
- Entries are entered into a work field consisting of 12 columns per line (for modified templates, the composition of the columns may change).
- A long entry can be written on two or more lines. In the empty spaces that remain in the columns, dashes are placed. This is not mandatory, but if reporting is strictly adhered to, they are necessary.
- Entries for one year are preceded by a title entry in which nothing is written except the words “Year XXXX” (the number is indicated) and dashes to the left and right of these words.
- The numbering of records in each year begins with one. The link to the record should look like this: “Record No. N XXXX year.”
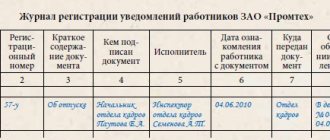
The columns, in order, must contain the following information:
- serial number;
- date DD.MM.YY (written in full);
- last name, first name and patronymic of the person being instructed;
- date of birth or year of birth of the person being instructed;
- his profession and position. If we are talking about an employee of another organization, then it is necessary to fill out the column on the basis of an official identification card or an order according to which the employee is allowed to work;
- type of training provided. It can be introductory, primary, repeated, targeted, planned or unscheduled. If the instruction is targeted, then the document or article of the document on the basis of which instructions are given is indicated;
- for repeated or extraordinary briefing - the reason or basis for the conduct (order, instruction);
- surname with initials and position of the person conducting the instruction. As a rule, the instructing and authorizing person is the same employee. But if this is not the case, you should indicate separately: “Instructed - I. I. Ivanov, allowed - P. P. Petrov,” and then indicate the grounds for admission;
- signatures of the employee who received the instructions and the employee who conducted the instructions. The signature must be indelible (that is, you must not sign in pencil);
- number of shifts and dates of internship (filled in if necessary);
- signature of the employee who completed the internship (also if necessary);
- signature of the employee who tested the trainee’s knowledge and allowed him to work, as well as the date. Together with the two previous columns, it forms the general supergraph of the internship. It may also include an assessment of the trainee’s knowledge, but this is usually impractical, since clearance is given only in cases where the trainee has confirmed that he has mastered the instructions, and if he has not confirmed this, there will be no clearance.
This is what the magazine looks like in general. Using a sample safety training log, you can maintain this document in most enterprises. However, the internal rules of a particular organization may imply changes in the structure of the journal. For example, we can talk about weather or technical conditions, the lifting height for construction work, the degree of danger when eliminating dangerous situations, and so on.
What does the TB magazine regulate?
Maintaining it is a norm of law, but many companies have elevated filling out the form in question to the category of formal. For them, this is a way to relieve themselves of responsibility. At the same time, maintaining it and conducting regular briefings makes much more sense and imposes certain obligations. This applies to both the employee and the employer.
Responsibilities of the employee:
- comply with the stated requirements regarding hazardous work. This applies to both work at a construction site and in cultural institutions and offices;
- undergo training according to the employer’s schedule, record this in the journal by signing;
- undergo on-the-job training, be it a workshop or an office;
- confirm knowledge in the field of occupational health and safety.
Employer Responsibilities:
- carry out the required activities for conducting TB training;
- take on-the-job training arrangements;
- provide the required information regarding the safety of all types of work performed in full;
- do not allow those who have not been instructed to work;
- regularly monitor employees’ knowledge in the area in question;
- inform employees about the likely risk of carrying out a particular operation in their workplace.
Legislation
The main document regulating employee health issues is the Labor Code. Article 212 clearly states the employer's obligation to notify its employees of possible health risks . The same article states that the employer is obliged not to allow employees to work who have not undergone safety training.
Article 225 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that every employee of an organization, including managers, must know safety rules.
If a person is just starting a job, the manager is obliged to educate him about these rules. The employee must listen to all safety briefings and then sign in the logbook.
Journals are the most convenient form of reporting , therefore they are used everywhere. They are filled in manually. Requirements for keeping logs can be found in GOST 12.0.004-2015.
Administrative responsibility
Recently, cases of violation of safety rules have become more frequent, leading to accidents. This explains the close attention to the management and fulfillment of their obligations by employers. For violation of the rules provided by law, a fine is due:
- for the head of the enterprise - 110-130 thousand rubles;
- safety engineer – 15-25 thousand rubles;
- repeated violation of 200 thousand rubles or suspension of activities for 3 months;
- for an official upon repeated detection, 35-40 thousand rubles, in parallel with a ban on carrying out similar work for 1-3 years;
- if detected violations lead to the death of a person - criminal liability.