Types of incentives
To increase sales and attract new customers, suppliers often use various reward systems.
For example, they provide customers with discounts, bonuses, bonuses, and gifts. The concepts of “discount”, “premium”, “bonus” are not defined in the legislation. However, taking into account current practice and economic meaning, they can be understood as follows.
A discount is usually a reduction in the contract price of a product, work or service for fulfilling certain conditions. One of the forms of discounts can be a reduction in the amount of debt the buyer owes for goods supplied, work performed or services rendered.
Premium is money paid to the buyer for fulfilling certain terms of the contract. For example, a bonus may be given for the volume of purchased goods, works, or services. At the same time, a premium associated with the delivery of goods can also be a form of discounts when this occurs to reduce the cost of delivery (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 7, 2012 No. 03-07-11/364).
Bonus is an incentive in the form of supplying the buyer with an additional batch of goods, performing a scope of work and providing services beyond what was initially agreed upon without payment. In fact, the bonus consists of two interrelated business transactions:
- providing a discount to reduce the price specified in the contract;
- sale of goods, works or services at the expense of the resulting accounts payable to the buyer. In this case, the amount of debt should be considered as an advance received (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 31, 2012 No. 03-07-15/118).
As a rule, bonuses are provided as part of promotions. For example, when buyers of a specific product are given a gift. This way you can promote new products or sell those that are not in demand. Document the action being carried out by order of the manager.
A gift is another type of incentive for fulfilling the terms of the contract. Like the bonus, it combines several concepts. In this case, one should take into account its economic essence and the mechanism of action of such incentives. For example, a seller may provide a gift if:
- acquisition by the buyer of a set of goods, works, services. For example, when you purchase two units of a product, the third is provided free of charge. This can be regarded as a bonus in kind;
- the buyer achieves the established volume of purchases. This can be seen as a bonus. That is, the buyer is first given a discount on the cost of the gift and it is provided against the resulting accounts payable;
- carrying out an advertising campaign. For example, all clients receive a gift on a holiday. And this is already a gratuitous transfer (clause 2 of article 423, article 572 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). This is explained by the fact that the relationship associated with the provision of this kind of gifts is stimulating and not encouraging in nature within the framework of the concluded agreement;
- other promotions and events.
The condition for providing incentives can be provided both directly in the contract with the counterparty, and in a separate agreement that is an integral part of it (clause 2 of Article 424 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The seller determines the type and amount of the incentive independently and coordinates it with the counterparty, for example, by sending the buyer a notice - a credit note (clause 2 of article 1 and clause 4 of article 421 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Situation: is it possible to provide a buyer-organization with gifts worth more than 3,000 rubles? The provision of a gift is subject to the buyer's fulfillment of certain terms of the contract.
Yes, you can.
After all, the limit is 3000 rubles. valid only for gift agreements between organizations, when one party transfers or undertakes to transfer ownership of an item free of charge to the other party. This follows from paragraph 1 of Article 572 and paragraph 1 of Article 575 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
But in the situation under consideration, we are not talking about gratuitous transfer. The seller rewards the buyer for fulfilling certain conditions and counter-obligations. This means that the cost of the gift given does not matter.
The courts adhere to a similar point of view (clause 3 of the information letter of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated December 21, 2005 No. 104).
The process of setting up discounts in the system
To set up any type of price reduction, you will need the following steps.
Firstly, in the “CRM and Marketing” subsection of the “Settings of Sections” section of the “Master Data and Administration” menu, check whether the ability to set manual and automatic discounts is enabled.
Manual discounts can then be entered when registering sales documents manually, the main thing is not to exceed the amount of the allowed manual discount. Otherwise, the program will not allow you to post the document.
The next step is to set up automatic discounts.
Secondly, the conditions for discounts are set in the “Conditions for providing discounts (markups)” directory. It is located in the “Settings and References” section of the “CRM and Marketing” menu.
When you follow the link and click on the “Create” button, you are asked to select one of eleven types of bonus conditions. Here you can arrange a reduction in cost for the form of payment, assortment, sales volume, etc. All options are presented in the diagram:
In the window that opens after selecting, you can specify the name of the condition, in what cases it is applied (across the entire product range or selectively), etc.
It is recommended to combine all created conditions into groups to facilitate search and use.
Thirdly, you need to go to the “Discounts (markups)” subsection of the “Prices and Discounts” section of the “CRM and Marketing” menu. Here, by clicking the “Create” button, you can select an automatic discount option from the 12 offered.
Discounts already introduced in the program are also presented here. For each of them, you can get information in the window on the right, or by clicking on it, a window with information will open.
Next, we will look at specific examples of setting up and applying discounts in the program.
Accounting: discounts
Discounts are provided by:
- at the time of sale or thereafter in respect of future sales;
- after the sale - in relation to goods sold, work performed or services provided. These are so-called retro discounts.
If a discount is provided at the time of sale or after it for future deliveries, then for accounting purposes this can be considered a sale at the price agreed upon by the parties. In this case, the established price may be less than what the seller declares under normal conditions. There is no need to reflect such a discount in accounting. You just need to reflect the implementation using standard postings.
Record the fact of implementation with the following entry:
Debit 62 (50) Credit 90-1
– sales revenue is reflected taking into account the discount.
If you pay VAT and it is levied on goods (works, services), then simultaneously with the sale, reflect its accrual as follows:
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
– VAT is charged on the actual sales amount;
Well, when you receive payment into your bank account, make the following entry:
Debit 51 Credit 62
– payment has been received from the buyer taking into account the discount.
This procedure follows from the Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 50, 51, 62, 68 and 90), paragraph 6 of PBU 9/99 and is explained in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 6, 2015 No. 07-04-06/5027.
If a discount is provided on a product, work or service that has already been sold, then reflect it in accounting depending on when the buyer was rewarded:
- before the end of the year in which the implementation took place;
- after the end of the year in which the implementation took place.
The discount was provided in the same year in which the sale took place. Adjust sales revenue for the period by the amount of the incentive at the time it was granted. In accounting, reflect such transactions as follows.
At the time of sale, before the discount is granted, complete the usual transactions:
Debit 62 Credit 90-1
– revenue from sales is reflected;
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
– VAT has been charged (only post if you pay tax and sales are subject to it).
At the time of discount:
Debit 62 Credit 90-1
– revenue from previously shipped goods, works, and services is reversed in the amount of the discount provided.
After issuing an adjustment invoice to the buyer:
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
– VAT is reversed from the amount of the discount provided.
This procedure is established by paragraphs 6, 6.5 of PBU 9/99.
The discount is provided in periods following the year in which the sale took place. Reflect it as part of other expenses in the current period as of the date of provision (clause 11 of PBU 10/99).
When identifying expenses from previous years in accounting, make the following entry:
Debit 91-2 Credit 62
– losses from previous years associated with the provision of a discount to the buyer (excluding VAT) were identified.
After issuing an adjustment invoice to the buyer:
Debit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” Credit 62
– VAT is accepted for deduction from the amount of the discount provided.
This procedure is established by paragraph 39 of the Regulations on accounting and reporting, the Instructions for the chart of accounts (account 91), paragraphs 6 and 6.4 of PBU 9/99 and is explained in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 6, 2015 No. 07-04-06/5027 .
Providing a discount (including in cash), which does not change the price of the goods under the terms of the contract, should be considered as a sale of property.
In accounting, reflect the provision of such a discount in the form of an additional batch of goods with the following entries:
Debit 62 Credit 90-1
– revenue from the sale of a consignment of goods within the discount is reflected (in the amount of the discount);
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
– VAT has been charged (only post if you pay tax and sales are subject to it);
Debit 90-2 Credit 62
– the amount of the discount provided to the buyer is included in the cost price (excluding VAT).
This order follows from the Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 41, 62, 68, 90).
If you provide a discount in cash, then make the following entries in your accounting:
Debit 90-2 (44) Credit 62
– a cash bonus has been awarded to the buyer;
Debit 62 Credit 51
– premium paid to the buyer.
This order follows from the Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 51, 62, 68, 90).
Setting up the ability to provide discounts in 1C: Trade Management
In order to configure or make changes and additions to existing settings, you need to go to the “CRM and Marketing” section of the “Master data and sections setup” category of the “Master data and administration” menu.
Expand the “Marketing” category and check the checkboxes next to the lines: “Manual discounts in sales (in purchases)”, “Automatic discounts in sales”, as well as within these options opposite the lines related to restrictions on manual discounts in sales under agreements or by users, and lines with settings for loyalty cards and bonus programs.
There should also be a “daw” in the “Price groups” line - this is necessary so that later you can combine different products into groups for which the same price calculations and discounts will be established.
Thus, price groups can be created by type of product, for example, air conditioners, refrigerators, televisions, etc. Or types of goods, for example, shoes, outerwear, underwear. The system allows you to create price groups according to any characteristics convenient for you.
Settings for price groups, types of loyalty cards, bonus programs and discount conditions can be made in the “Settings and reference books for CRM and marketing” section.
After the necessary “checkboxes” have been checked, you can proceed to the settings for the types of discounts.
Accounting: bonus
Having provided a bonus, two business transactions must be reflected in accounting:
- discount on previously shipped goods, work performed or services provided;
- sale of goods, works or services against the resulting accounts payable to the buyer.
Reflect the first business transaction in the manner prescribed for reflecting the discount.
On the debt incurred, charge VAT on the advance payment. After all, money that was received earlier cannot be considered payment for goods that have already been shipped. In essence, this is an advance payment (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 31, 2012 No. 03-07-15/118).
In accounting, reflect the recognition of recovered accounts payable in advance and the sale of goods against this advance with the following entries:
Debit 62 subaccount “Settlements for shipped products” Credit 62 subaccount “Settlements for advances received”
– the amount of the restored debt is recognized as an advance received against a future bonus delivery;
Debit 76 subaccount “Calculations for VAT on advances received” Credit 68 subaccount “Calculations for VAT”
– VAT is charged on the prepayment amount, that is, the recovered debt.
After shipping a bonus shipment of goods, performing an additional amount of work or services, make the following entries:
Debit 68 subaccount “Calculations for VAT” Credit 76 subaccount “Calculations for VAT on advances received”
– VAT accrued on prepayment is accepted for deduction;
Debit 62 subaccount “Settlements for shipped goods” Credit 90-1
– revenue from the sale of bonus goods (works, services) is reflected;
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
– VAT is charged on proceeds from the sale of bonus goods (works, services);
Debit 90-2 Credit 41 (20)
– the cost of sold bonus goods (work, services) is written off;
Debit 62 subaccount “Settlements for advances received” Credit 62 subaccount “Settlements for shipped goods”
- prepayment has been credited.
Setting up an automatic discount (AC) for the first purchase
Let's look at what common price reductions are used in enterprises and how to configure some of them in the 1C program.
One of the most common promotions is that when you buy several units of products, get one more as a gift.
To generate such a bonus, as usual, in the “CRM and Marketing” menu, in the “Discounts (markups)” section, click on the “Create” button and select “Quantity discount”.
In the window that opens, in the “Discount Amount” line, select the number of units of goods that will be issued free of charge and the number of units of goods for which the promotion is valid. The name of the discount will be automatically filled in, and the joint application group can be selected from the drop-down list. Marks are placed opposite the method of application (discount) and the AC is assigned. Here you can also select clarifications on the product range participating in the promotion, as well as the ability to take into account characteristics.
By clicking on the highlighted line “Change” in the recipient field (the information must be recorded first), the validity period of the promotion is selected. The “Set status” button in the window that opens enables the discount effect. Here you can configure additional conditions for the discount:
- for certain types of loyalty cards;
- in specific individual or standard agreements;
- at marked warehouses.
By clicking on the highlighted line “Change general status”, you select the start and duration of the discount.
Let's check how everything works after setup. Let's open the document for the sale of goods and services, and on the goods tab, select any item. By clicking on the “Prices and Discounts” button, select “Assign automatic discounts”.
As we remember from the settings, every 4th unit should be provided free of charge. Using the “Print” button we will see the reflection of the operation.
As you can see, the AS worked in quantity. The cost for 4 units of goods should have been 200 rubles, however, one product is provided free of charge (which is equal to a discount in the amount of its cost). The amount to be paid is 150 rubles, which corresponds to the cost for 3 units of goods.
In retail sales, the AC calculation occurs by pressing the “Calculate discounts” button.
The discount is displayed in percentage and total terms and corresponds to the price of one unit of goods. The promotion in the program worked.
Insurance premiums and personal income tax
If an organization has provided a discount, a bonus, paid a bonus, or reduced the debt of a citizen buyer, then the amount of such incentives does not need to be accrued:
- contributions for compulsory pension, social or health insurance (part 1 of article 1, part 1 of article 7 of the Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ);
- contributions for insurance against accidents and occupational diseases (clause 1 of article 20.1 of the Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ).
This is due to the fact that the income received by the buyer when providing incentives is not his remuneration within the framework of labor relations or civil contracts.
If an organization has reduced the debt of a citizen-buyer free of charge, that is, without fulfilling any condition, then such an operation is a regular debt forgiveness. Therefore, a person has an income in the amount of incentives. Personal income tax must be withheld from such income. True, under certain conditions this is impossible to do. Then report this to the tax office. All this follows from Article 41, paragraph 1 of Article 210, paragraphs 1 and 3 of Article 224, paragraph 1 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Article 415 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The same conclusion is expressed in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 11, 2012 No. ED-4-3/17276.
Setting up storage speakers and depending on purchase volumes
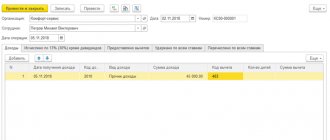
Such discounts are usually used for wholesale sales, as well as when using discount cards. Settings also occur in the “Discounts (markups)” form via the “Create” button. The type “Discount (markup) by percentage” is selected. In the window that opens, the discount amount is set as a percentage, indicating that the discount is provided, for example, to holders of certain discount cards. You can select a product segment for which a discount will be provided. In this case, it is necessary to indicate that for this position the number of identical goods must be equal to or greater than one.
On the “Conditions of provision” tab, you can select additional conditions using the “Add” button. For example, select a condition based on sales volume of at least 1000 USD for the entire period.
Next, you can assign the following sales volume thresholds at which the discount increases.
Another option for providing bonuses is a combination of a discount for the volume of purchase and for the first purchase.
The setting will also take place in the “Discounts (markups)” section.
The appropriate sales conditions are selected:
- for a 3% discount - “first purchase”;
- in 7% - purchase volume is at least 5,000 rubles.
Special conditions for customers, product range, etc. We won't exhibit it. Let's set the validity period of discounts from the current day and indefinitely. We also note the conditions for the joint application of discounts: “Addition”.
Let's select a sales document, and in the tabular section we will select goods worth 6,500 rubles. Click the “Prices and Discounts” button to mark the purpose of automatic discounts.
The line will display a 10% discount. Click the “Prices and Discounts” button and select “Open information about discounts for the current line.”
In the window that opens, you can see that both discounts worked: 3% for the first purchase, and 7% for the purchase volume over 5,000 rubles. Discounts were summed up according to specified conditions.
Promotion does not change the price
If the incentive does not change the price, then the income tax basis does not need to be adjusted. Incentives of this kind must be taken into account as part of non-operating expenses in relation to:
- goods - on the basis of subclause 19.1 of clause 1 of Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- works, services - on the basis of subparagraph 20 of paragraph 1 of Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
A similar point of view is reflected in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 23, 2013 No. 03-03-06/1/28984, dated December 19, 2012 No. 03-03-06/1/668, dated September 27, 2012 No. 03 -03-06/1/506, dated April 3, 2012 No. 03-03-06/1/175.
When using the accrual method, expenses in the form of incentives provided to the buyer are taken into account when calculating income tax in the reporting (tax) period to which they relate. This is established in Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
When using the cash method, expenses in the form of incentives provided to the buyer are taken into account when calculating income tax in the reporting (tax) period in which:
- paid the buyer a premium;
- transferred goods provided as a bonus or gift, but only if it was paid to your supplier;
- at the time of debt forgiveness, if a discount is provided that does not reduce the price. All other discounts reduce the price.
This follows from the provisions of paragraph 3 of Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Document the provision of incentives to the buyer in a deed.
Incentives for the purchase of food products
Situation: is it possible for a trade organization to take into account when calculating income tax the incentive to the buyer provided for in the contract for the supply of food products, which does not change their price?
Yes, it is possible if the incentive meets the requirements of the Law of December 28, 2009 No. 381-FZ.
This law sets out the rules for trading activities on the territory of Russia. They are effective from February 1, 2010.
According to these rules, an agreement for the supply of food products can only provide for one type of remuneration that is not related to a change in the price of the product. This is a reward to the buyer for purchasing a certain volume of goods. It does not matter how this remuneration is named in the supply agreement: discount, premium, bonus or gift (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 11, 2010 No. 03-03-06/1/643). The main thing is that the following conditions are met:
- the amount of the incentive cannot exceed 10 percent of the cost of the goods purchased by the buyer;
- incentives can be provided only for the supply of products that are not mentioned in the list of socially significant food products approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 15, 2010 No. 530.
This procedure is established by parts 4–6 of Article 9 of the Law of December 28, 2009 No. 381-FZ.
If all the specified conditions are met, then take into account the incentive for the purchase of a certain volume of goods when calculating income tax as part of non-operating expenses (subclause 19.1, clause 1, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Otherwise, do not take into account the incentive, since its provision does not meet the requirements of Part 4 of Article 9 of the Law of December 28, 2009 No. 381-FZ. Similar clarifications are contained in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 10, 2015 No. 03-07-11/20448.
Promotion changes price
Accounting for the calculation of income tax using the accrual method depends on when the incentive that changes the price was provided - in the same reporting (tax) period in which the sale took place, or in subsequent ones.
So, if the incentive was provided in the same period, then adjust the basis for calculating income tax in the current reporting (clause 7 of Article 274 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If a decrease in the price of goods affects the seller’s tax obligations for income tax in past reporting (tax) periods, then you can do one of the following:
- submit updated income tax returns for previous reporting (tax) periods;
- do not submit updated returns, but recalculate the tax base and the amount of tax for the period in which the incentive was provided, and reflect this in the tax return for the same period;
- do not take any measures to adjust the tax base (for example, if the amount of overpayment is insignificant).
Similar clarifications are contained in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 22, 2015 No. 03-03-06/1/29540.
For more information about this, see In what cases you need to file an updated tax return.
As for the cash method, sales income is recognized on it on the date of receipt of money from customers. Accordingly, there will be no need to adjust revenue after the incentive is provided. Even if it is a retro discount, that is, when the price of an already sold product changes. Indeed, in this case, the money received earlier must be reclassified as an advance, and under the cash method it is also taken into account in income. This means that the tax base will not change in any way. This follows from paragraph 2 of Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and is confirmed in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for the Moscow Region dated October 5, 2006 No. 22-22-I/0460.
The costs associated with providing a premium, bonus or gift to offset price changes should be taken into account in the same way as in a situation where prices do not change.
VAT
In an agreement for the supply of non-food products, the parties can establish a condition: the incentive - a discount, bonus, premium or gift - affects the price of the product or not.
If the incentive does not change the price of goods , then the VAT tax base does not need to be adjusted (clause 2.1 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When an incentive changes the price of an item , adjust the basis for calculating VAT. To do this, issue an adjustment invoice (subclause 4, clause 3, article 170, clause 13, article 171, clause 10, article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The amount of VAT on the difference resulting from a decrease in the value of the goods can be deducted (paragraph 3, paragraph 3, Article 168, paragraph 3, paragraph 1 and paragraph 2, Article 169, paragraph 13, Article 171, paragraph 10, Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Has the price changed for goods listed on multiple primary invoices? Then you can issue a single adjustment invoice to the same buyer (paragraph 2, subclause 13, clause 5.2, article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For more information, see:
- How to create and register an adjustment invoice;
- Procedure for issuing an adjustment invoice due to a price change;
- Under what conditions can input VAT be deducted?
In a similar manner, take into account the receipt of incentives for work (services) when calculating VAT.
An example of how to reflect in accounting and taxation the payment of a bonus to the buyer for achieving the volume of purchases established by the contract. According to the terms of the contract, the premium does not change the cost of goods
LLC "Torgovaya" sells goods wholesale. The organization uses the accrual method. Income tax is paid monthly.
On October 5, Hermes entered into a purchase and sale agreement with Alpha LLC for the purchase of a consignment of goods. According to the agreement, if Alpha purchases goods from Hermes in the amount of 1,100,000 rubles. (including VAT - 100,000 rubles), Hermes pays Alpha a bonus in the amount of 30,000 rubles.
On October 15, Alpha purchased a batch of goods from Hermes in the amount of 1,100,000 rubles. (including VAT – 100,000 rubles).
The cost of goods sold by Hermes was 500,000 rubles. In pursuance of the terms of the purchase and sale agreement, on October 22, Hermes transferred a cash bonus in the amount of 30,000 rubles to Alpha.
The accountant made the following entries in the Hermes accounting.
October 15:
Debit 62 Credit 90-1 – 1,100,000 rub. – revenue from the sale of goods is reflected;
Debit 90-2 Credit 41 – 500,000 rub. – the cost of goods sold is written off;
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” – 100,000 rubles. – VAT is charged on sales proceeds.
22 of October:
Debit 90 (44) Credit 62 – 30,000 rub. – a cash premium has been awarded to the buyer.
Since the incentive in the form of a bonus did not lead to a decrease in the price of the product, the VAT tax base is not adjusted.
Debit 62 Credit 51 – 30,000 rub. – premium paid to the buyer.
Providing a bonus does not change the price of the goods, so the Hermes accountant applied the provisions of subclause 19.1 of clause 1 of Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and took into account the bonus in the amount of 30,000 rubles. as part of non-operating expenses.
In October, when calculating income tax, the accountant included:
- included in income – 1,000,000 rubles;
- included in expenses - 530,000 rubles. (RUB 30,000 + RUB 500,000).
An example of how to reflect in accounting and taxation the payment of a bonus to the buyer for achieving the volume of purchases established by the contract. Under the terms of the contract, the premium changes the value of the goods. The bonus is provided after the sale of goods
LLC "Torgovaya" sells goods wholesale. The organization uses the accrual method. Income tax is paid monthly.
On October 5, Hermes entered into a purchase and sale agreement with Alpha LLC for the purchase of a consignment of goods. According to the agreement, if Alpha purchases goods from Hermes in the amount of 1,100,000 rubles. (including VAT - 100,000 rubles), Hermes reduces their cost by 10 percent.
On October 15, Alpha purchased a batch of goods from Hermes in the amount of 1,100,000 rubles. (including VAT – 100,000 rubles).
The cost of goods sold by Hermes was 500,000 rubles. In pursuance of the terms of the purchase and sale agreement, on October 22, Hermes provided Alpha with a discount of 10 percent of the cost of the goods.
The accountant made the following entries in the Hermes accounting.
October 15:
Debit 62 Credit 90-1 – 1,100,000 rub. – revenue from the sale of goods is reflected;
Debit 90-2 Credit 41 – 500,000 rub. – the cost of goods sold is written off;
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” – 100,000 rubles. – VAT is charged on sales proceeds.
22 of October:
Debit 62 Credit 90-1 – 110,000 rub. – revenue from previously shipped goods is reversed (by the amount of the discount provided);
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” – 10,000 rubles. – VAT is reversed from the amount of the discount provided (based on the adjustment invoice).
Since the incentive in the form of a bonus led to a decrease in the price of the product, the tax base for income tax is adjusted in the current reporting period by the amount of the incentive.
In October, when calculating income tax, the accountant included:
- included in income – 900,000 rubles;
- included in expenses - 500,000 rubles.
When supplying food products, the contract may contain a provision for remuneration (bonus) for achieving a certain volume of purchases. The amount of such remuneration should not exceed 10 percent of the price of the purchased goods. This type of incentive does not change the price of goods, regardless of the terms of the contract. This procedure follows from the provisions of paragraph 4 of Article 9 of the Law of December 28, 2009 No. 381-FZ. Having provided remuneration for the volume of purchase, the VAT tax base does not need to be adjusted. A similar point of view is reflected in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 18, 2013 No. 03-07-09/38617.
Situation: should the seller adjust the VAT base if he paid remuneration to a citizen who purchased the goods at retail?
Yes, I should.
In this case, the remuneration paid changes the price of goods sold at retail, even if the contract contains a condition to the contrary.
The fact is that when an organization provides citizens with discounts, bonuses, bonuses, gifts, trading at retail, the provisions of paragraph 2.1 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation do not apply. This rule should be applied only to wholesale trade, when a contract for the supply of goods is concluded with buyers. Similar clarifications are in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 11, 2013 No. 03-07-11/26921.
Moreover, according to the logic of the Ministry of Finance of Russia, in the retail trade of food products, the norm of paragraph 4 of Article 9 of Law No. 381-FZ of December 28, 2009 also does not apply. After all, it regulates wholesale supplies.
Consequently, the incentive provided to a citizen changes the price of goods sold to him at retail, regardless of whether these goods are food or non-food. These conclusions are contained in the resolutions of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated February 7, 2012 No. 11637/11 and dated December 22, 2009 No. 11175/09.
That is, in any case, in a situation where an organization pays a remuneration to a citizen-buyer, the initial price of the product changes. Therefore, the VAT tax base will have to be adjusted for the amount of such incentive by drawing up an adjustment invoice. Draw up such a document in one copy, for yourself. After all, citizens who are not engaged in entrepreneurial activities do not pay VAT and therefore simply will not be able to take advantage of the right to deduction. The amount of VAT on the difference resulting from a decrease in the value of the goods can be deducted. All this follows from paragraph 1 of Article 143, paragraph 3 of paragraph 3 of Article 168, paragraph 3 of paragraph 1 and paragraph 2 of Article 169, subparagraph 4 of paragraph 3 of Article 170, paragraph 13 of Article 171, paragraph 10 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Setting a manual discount by the cashier
Let's consider the use of a manual discount by a cashier with established rights restrictions using an example.
KKM cashier Masyuk D.V. to open a cash shift goes to the “Cashier Workplace” section of the “Sales” menu. Using the “Operations with cash register” button, the fiscal registrar is selected and by clicking on the button of the same name, it opens a shift.
Using the “Search” button, the cashier finds the product in the window that opens, for example, “Desktop fan”, clicks on it and with the “Move to document” button reflects the selected item in the receipt.
By pressing the “Manual discounts” button, Masyuk opens a window in which the following are indicated:
- amount before reduction
- maximum RS in total and percentage terms,
- automatic discount in total terms (if installed).
The cashier just needs to indicate the RS size and press the “OK” button.
Let's assume that Masyuk decided to cheat and give the buyer a larger percentage of cost reduction than is established at the enterprise. According to the conditions of the example, the maximum volume is 4%, but the cashier enters 10%.
The program determines the total expression of the discount provided from the specified percentage and highlights both indicators in red, because The specified maximum size has been exceeded.
Let's assume that the cashier insists on providing the discount he has specified and clicks "OK". A warning appears again indicating that the maximum discount has been exceeded. The program clarifies whether the seller plans to continue? Let's say Masyuk clicks "OK".
A completed receipt form opens indicating the product, its price, the amount of the discount and the total cost after the reduction. Let's say a cashier presses the "Cash Payment" button to accept money from a customer. The program will offer to calculate the discount, after which it will display two error messages indicating that the specified maximum amount has been exceeded.
Thus, the cashier will not be able to calculate the buyer and process the sale, trying to give an increased discount. To change the discount, you can click on its size highlighted in the receipt; the same window will open as in the beginning. The seller will put the correct percentage in it. After which the program will make it possible to smoothly complete the sale.
simplified tax system
Organizations that pay a single tax on income do not take into account expenses, including incentives provided to customers, when calculating it (Clause 1, Article 346.18 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For organizations that have chosen such an object of taxation as income reduced by the amount of expenses, the list of expenses taken into account when calculating the tax base is limited by Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The costs of paying or providing customers with appropriate incentives - discounts, bonuses, bonuses or gifts - are not included in this list.
When selling goods at discounts, include in income the amounts actually received from customers, that is, minus the discounts provided. This follows from paragraph 1 of Article 346.15, paragraph 1 of Article 249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 11, 2013 No. 03-11-06/2/7121.
Setting up and applying a manual discount
There are situations in an enterprise when it is necessary to use manual discounts (MD). At the same time, any manager would like to avoid arithmetic errors, inattention or incorrect behavior on the part of the cashier when the buyer is given a larger discount than what is established in the store.
To do this, when creating a PC, its maximum threshold is set. Moreover, both for the entire assortment and for individual categories.
How to enable the ability to use a PC in the program was discussed above.
After this, you need to give the rights to the cashier (seller) to establish a PC. To do this, in the “Master data and administration” menu, in the “Administration” section, select the “User and rights settings” subsection. In the window that opens, clicking on the “Users” hyperlink opens the corresponding form.
In it you need to select a specific employee, select the line with his data and click the “Sales Rules” button.
In the window that appears in the “Cashier Workplace” tab, the rights of the employee are set:
- Opening and closing cash register shifts;
- Postponing or adjusting checks;
- Depositing or withdrawing funds;
- Return and reservation of goods.
There is also the right to manually change loyalty cards and edit buyer data. The administrator sets the necessary rights.
On the “Discounts (markups)” tab, a limit on the maximum RS size is set. To do this, check the box next to “Limit manual discounts” and enter the maximum discount percentage in the field of the same name.
It is necessary to take into account the fact that if the “tick” is checked, and the discount percentage is not assigned, then the cashier will not be able to set the PC.
In the same window there is a hyperlink “Check by price groups.” Clicking on it will open a field for selecting a price group and setting a different maximum discount for it.
For example, a maximum manual discount of 10% is provided for the entire product range, and only 7% for the “TV” price group.
After the data is entered, by clicking the “Save and close” button, user rights and maximum PC sizes begin to work.
OSNO and UTII
As a rule, it is always possible to determine what type of activity the incentives provided to customers relate to. Therefore, if an organization applies a general taxation system and pays UTII, incentives provided to customers within the framework of activities transferred to UTII and activities on the general taxation system must be taken into account separately for the purpose of calculating income tax and VAT (clause 9 of Article 274, clause 7 of article 346.26 and clauses 4, 4.1 of article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Incentives - discounts, bonuses, premiums or gifts that an organization provides to customers as part of its activities under the general taxation system - subject to the conditions for their recognition in the tax base, can increase expenses.
Do not take into account incentives that are provided to the buyer as part of activities transferred to UTII for tax purposes (clause 1 of Article 346.29 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Setting up discounts on the client’s birthday and depending on the payment method
Another popular promotion is an increase or provision of an additional discount on the entire assortment or group of products on the buyer’s birthday. Usually, it is used not only on the birthday itself, but also several days before and after it.
It is difficult to create a card in the system for each specific customer. Therefore, the birthday is indicated on the loyalty card as soon as it is issued by the buyer. In the system, a new discount is created in the same place in the “Discounts (markups)” form. In the “Conditions of provision” tab, click on the “Add” button and select “For the client’s birthday”. In the window that opens, you can set the number of days this discount is valid.
After recording the discount, it will be automatically included when making payments and using the client’s discount card on the specified days.
One of the problems that delays settlement times is the use of cash. While the buyer counts out the required amount, the cashier recalculates and gives out change, quite a lot of time passes. If an exchange is also required, then settlements are delayed indefinitely. Using plastic cards is much more convenient and faster. Accordingly, to stimulate non-cash payments, you can organize a promotion - pay by card and get an additional discount.
Setting up a discount occurs in a similar way, only the condition of provision is selected: for the form of payment. In the window that opens, select “Cashless”.
Now, when registering a sale by bank transfer, an additional discount will be issued, for example, 4%. In the size that will be specified in the system.
By analogy, you can set discounts for the time of sale, availability of a card, etc.