The company often has employees who travel on official assignments. This category includes engineers performing repair functions in client offices, sales representatives traveling to negotiate the sale of goods, drivers, and couriers. According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the movements of workers are divided into business trips and traveling work.
How to establish the traveling nature of an employee’s work ?
Criteria for traveling work activity
The permanent activity of an employee related to his constant official movements is divided into labor (Article 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- on an expedition;
- in the field;
- on my way;
- traveling work.
How to take into account compensation for the traveling nature of work ?
Clear definitions of the nature of the work in question are not established by law, so the enterprise itself establishes them, taking into account a number of defining characteristics, when:
- The worker spends a significant proportion of his working time outside the company's premises, performing his actual duties at this time.
- The employee's primary responsibilities include travel.
- Other criteria are determined by the employer individually in relation to a specific position.
By internal regulatory document, the organization defines positions with the type of work that involves moving (Article 168, Part 2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and fixes the service territory for production movements.
The limit for a territory is indicated by an individual subject of the Federation or its region, a number of subjects or the entire territory of the Russian Federation.
How to draw up an employment contract with a condition regarding the traveling nature of the work ?
Nature of work in an employment contract: what it is, how to indicate
The display of TD conditions in the form of a description of the nature of work activity does not have a specific order outlined in the Labor Code. By this it should be understood that, determining the field, traveling, mobile or remote nature of the work, the procedure for concluding an employment contract is no different from drawing up an agreement in the case of providing working conditions that require the employee to stay in the company’s office. In this case, working relationships are considered in accordance with paragraph 49 of the Labor Code.
When registering a new employee for an enterprise, in accordance with Art. 56 of the current Labor Code (LC) of the Russian Federation, an agreement must be concluded between the employer and the employee. This document is called an “employment contract” (TD).
We recommend reading: Who has the right to privatize land plots
Differences between travel and business trips
The traveling nature of work is incompatible with the concept of a business trip, which is an employee’s trip for a limited period of time on a production assignment and by order of the employer from the place of permanent employment (Article 166 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Question: How to record compensation for expenses of an employee with a traveling nature of work? In accordance with the collective agreement and the regulations on the traveling nature of work, an employee whose work is traveling in nature is compensated for the actual costs incurred for travel, renting accommodation and daily allowances. The provision regarding the traveling nature of the work is included in the employment contract with the specified employee. In accordance with the procedure established by the collective agreement and the regulations on the traveling nature of work, funds (advance) for expenses associated with business trips are transferred to the employee’s bank account. The amount of compensation is determined on the basis of the advance report submitted by the employee. Advance payment for these expenses in the amount of 20,000 rubles. transferred to the employee's bank account. According to the advance report submitted by the employee and the supporting documents attached to it (drawn up on strict reporting forms with VAT amounts highlighted as a separate line), the employee’s actual travel costs amounted to 6,105 rubles. (including VAT 54 rubles), for renting residential premises - 10,620 rubles. (including VAT 1,770 rubles), daily allowance - 5,000 rubles. After approval of the advance report, the overexpenditure is reimbursed to the employee by transferring funds to his bank account. For profit tax purposes, income and expenses are accounted for using the accrual method. View answer
A specialist sent on a business trip retains his place (position) and average salary with compensation:
- travel expenses;
- costs of paying for accommodation;
- other expenses when not in the place of permanent residence (daily allowance);
- costs approved by the management of the enterprise (mobile communications).
To arrange a business trip, an order is issued at the enterprise, the employee is issued a work assignment and a certificate (travel permit). The business traveler receives money in advance for expenses (travel, accommodation, daily allowance). Upon returning from a business trip, the employee submits a report on the work done, the amounts spent and attaches documents on all types of expenses.
In contrast to the periodic nature of business trips (as needed), traveling activities are an integral element of the employee’s work function and are permanent in nature. The conditions that determine the specified nature of work are necessarily reflected in the labor agreement of the parties (Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Attention! All trips within the framework of the performance of official duties are paid at the salary agreed upon when drawing up the employment contract. Payment based on average earnings applies only to business trips (Article 167 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If an employee registered for work with a mobile nature within one locality is sent on business to another city, the movement must be formalized in the form of a business trip.
Compensation of expenses for traveling and mobile work
author of the answer,
Question
Traveling and mobile nature of work: what is the difference between these concepts? What is the best way to compensate the expenses of such an employee: monthly bonuses to the salary, salary, or compensation by checks?
Answer
The Labor Code does not explain the concepts of “traveling nature of work”, “mobile nature of work” (more details in the rationale).
The condition on establishing the traveling (mobile) nature of the work for the employee must be reflected in the employment contract.
The employer independently determines the procedure for reimbursement of expenses.
If an employee’s work function involves constant work on the road, the employer has the right to establish for such an employee a traveling nature of work with reimbursement of expenses provided for in Art. 168.1 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Rationale
The legislation does not clarify the concept and does not define what should be understood by the traveling or mobile nature of work.
Relevant definitions are contained in some industry documents. Yes, the work has a traveling nature.
, if the performance of work duties involves regular travel within the service territory (areas) with the possibility of daily return to the place of residence[1].
Such an employee performs all duties stipulated by the employment contract outside a stationary workplace, at facilities located at a considerable distance from the location of the organization.
For example, the work of a courier, insurance agent, sales representative, or postman has a traveling nature.
It is obvious that traveling, as a rule, involves additional costs, primarily associated with paying for travel on public transport or using personal cars for business purposes.
Mobile nature of work
– this is a mode of operation with frequent relocation of the organization (movement of workers) or isolation from their permanent place of residence[2]. At the same time, the employee does not always have the opportunity to return to his place of residence every day.
Works with a mobile nature may include work that is performed on the road (conductor, flight attendant, etc.); involve frequent movement of employees (employees of mobile construction organizations).
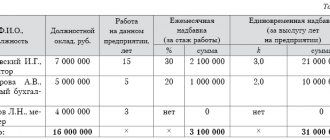
Employers are given the right to independently establish remuneration systems, including any allowances of a compensatory nature (Article 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Corresponding payments due to the special nature of the work can be reflected in the terms of collective agreements, local regulations, employment contracts (see letter of Rostrud dated December 12, 2013 N 4209-TZ).
Article 168.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes that for employees whose permanent work is carried out on the road or has a traveling nature, the employer reimburses the following expenses related to business trips: travel expenses; expenses for renting residential premises; additional expenses associated with living outside the place of permanent residence (daily allowance, field allowance); other expenses incurred by employees with the permission or knowledge of the employer.
The amount and procedure for reimbursement of expenses associated with business trips of employees specified in part one of Article 168.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as well as the list of jobs, professions, positions of these employees are established by a collective agreement, agreements, and local regulations. The amount and procedure for reimbursement of these expenses may also be established by an employment contract (Part 2 of Article 168.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
[1] clause 2 of the Instructions on the organization of business trips for military personnel of rescue military formations of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of Russia and employees of the state fire service in the system of the Ministry of the Russian Federation for Civil Defense, Emergencies and Disaster Relief, approved by Order of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of Russia dated January 10, 2008 N 3 .
[2] clause 1 of the Regulations on the payment of allowances related to the mobile and traveling nature of work in construction, approved by the Resolution of the USSR State Committee for Labor, the Secretariat of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions dated 06/01/1989 N 169/10-87
| She answered the question: E. A. Karapetyan , leading expert of the Consultant + Askon Information Center |
What documents will need to be completed?
The presence in the company of employees with a traveling option of work raises before the administration the issues of documenting this type of activity and compensation for expenses incurred by the employee in accordance with the law.
Options for assigning a category of work associated with constant movement (Article 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- contract of employment;
- agreement with the team;
- local (separate) normative act (LNA).
To properly keep track of expenses for mobile work, you must:
- introduce a condition on the type of employment in the employment contract (Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- approve the list of relevant positions and works in the contract with the team or LNA;
- provide for the conditions for documentary evidence of travel (in the contract, LNA);
- determine the amount and terms of payment of allowances (Article 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The establishment of allowances is the right, but not the obligation, of the enterprise administration, except in situations stipulated in legislation or industry agreements.
Registration procedure
The provision on the type of employment can be in the form of a separate document or be an addition to the company’s Rules of Procedure. In any form, the document must be approved by order of management. Employees of the organization for whom the type of employment in question is established must familiarize themselves with the document and sign with their own hands (Article 68 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If a traveling option of employment is established for a worker when he registers with a company, then this requirement is fixed in a clause of the employment contract. If such a need arose during the employee’s activities, then the condition is formalized in an additional agreement to the contract. In case of disagreement of the employee and with full legislative compliance with the procedure, the administration of the enterprise has the right to use the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 74) up to the termination of the labor relations of the parties.
The type of employment should also be reflected in the employment order (for the admission of a new employee) and the order in free form (for an existing employee).
An order establishing the type of activity is necessary to notify certain officials of the corresponding status. The text of the employment contract does not relate to public information, therefore, for example, an accountant learns about the need to accrue a bonus to an employee directly from the order.
Orders in connection with traveling activities
In an organization, the list of positions assigned to a traveling type of work may be subject to adjustments. In order not to change the entire Regulation, it is possible to determine such a list by a special order of management.
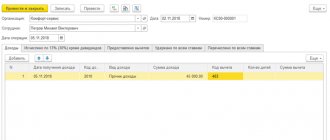
The procedure for recording trips and document flow is established by the enterprise independently (as opposed to a business trip). Forms of official assignment or traveler’s certificate (for developing a route sheet) can be used as a sample.
In any document executed, the signature of the management and the signature of the employee are required.
Attention! An order to send an employee with a traveling nature of work on a business trip is not issued.
If travel on duty is carried out using company vehicles, then it is mandatory to issue a waybill (in one copy) issued to the driver (against signature).
Mandatory points of travel documents (Order of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation No. 152):
- document number, its name;
- validity period of the document;
- information about the owner of the car;
- vehicle driver data;
- vehicle data.
It is mandatory to affix the day of issue, seal and stamp of the organization that owns the vehicle.
The waybill is registered in a special journal, the shelf life of which in the organization must be at least 5 years. It is also advisable to register service assignments with notes about the destination, purpose, and time of arrival at the sites.
A documented mobile type of employment affects the reduction of the company’s administrative costs, and in a number of situations, the reduction of expenses for travel and wages for employees.
Example of an order approving a list of positions
Limited Liability Company "AAA" (LLC "AAA")
December 25, 2015
Moscow
Order No. 1001-P on approval of positions for employees whose permanent work is traveling in nature
Guided by Art. 168.1 Labor Code of the Russian Federation,
I order:
Establish the traveling nature of work for employees hired and rehired for the following positions: - courier; - driver; - insurance agent; - legal assistant.
General Director _________/Ivanov A.A./
Procedure for preparing documents confirming expenses
By virtue of Part 1 of Art. 168.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation for employees whose permanent work is of a traveling nature, the employer shall reimburse the following for work-related trips:
- travel expenses;
- expenses for renting residential premises;
- additional expenses associated with living outside the place of permanent residence (daily allowance, field allowance);
- other expenses incurred by employees with the permission or knowledge of the employer.
According to Part 2 of Art. 168.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the amount and procedure for reimbursement of expenses related to business trips are established by a collective agreement, agreements, local regulations, and can also be established by an employment contract.
An employee, as an accountable person, can receive cash from the company's cash desk for travel-related expenses. Issuance is carried out on the basis of an order from the manager or an application from the employee.