From 18% to 20%
A VAT tax rate of 20% is applied to goods (work, services), property rights shipped (performed, rendered), transferred starting from January 1, 2019 .
At the same time, there are no exceptions for contracts concluded this year and continuing in nature with the transition to 2021 and subsequent years.
Therefore, for shipments starting from January 1, 2019, a VAT rate of 20% is applied, regardless of the date and conditions of the conclusion of contracts.
In this case, the seller, in addition to the price of goods (work, services) shipped starting from 01/01/2019, is obliged to present to the buyer for payment the amount of tax calculated at a rate of 20%.
In this regard, amendments to the agreement regarding changes in the VAT rate are not required. At the same time, the parties to the agreement have the right to clarify the calculation procedure and the cost of goods sold (works, services), transferred property rights in connection with changes in the VAT tax rate.
It is also necessary to take into account that changing the tax rate does not change for the taxpayer the procedure and time for determining the tax base for VAT.
Agree with the counterparty who pays the difference in the rate
The supplier and buyer need to agree in an additional agreement who will bear the losses from an increase in the VAT rate - these provisions are not spelled out in the Tax Code. When a difference in payment for a supply arises due to a change in the VAT rate, the seller will have only two options:
- Transfer a smaller quantity of goods to the buyer (advance minus increased tax).
- Ship the goods in the original/full quantity. In your reporting, reflect receivables and pay additional VAT at your own expense. If the counterparty does not agree to pay the difference, then this debt will remain for three years (clause 1 of Article 196 of the Civil Code). Then it can simply be written off.
Conclusion: a change in the VAT rate will increase the amounts for goods (work, services) offered by sellers, regardless of what cost formula is described in the contract. Any increase in price, even if a third force in the form of the state intervenes in its growth, will not cause delight in business.
Most of the price contradictions that have arisen will be resolved by the end of 2018. Mainly through the closure of contractual obligations with VAT at 18 percent. This is the solution that is preferred by most of the managers with whom we spoke while preparing this material. In any case, there will be those who will not have time or will not be able to reach an agreement, so already in the first half of 2021 we will have the first judicial practice on situations with VAT in the transition period.
Advance received in 2021, and shipment in 2021
If an advance payment is received before 01/01/2019 for upcoming deliveries, from 01/01/2019, VAT on the advance payment is calculated at a rate of 18/118%.
When shipping the above goods (works, services) from 01/01/2019 on account of a previously received prepayment, VAT is taxed at a rate of 20%.
Deductions of VAT amounts calculated at a tax rate of 18/118% from prepayment received before 01/01/2019 are made by the seller in 2021 from the date of shipment in the amount of tax previously calculated at a tax rate of 18/118%.
In this case, the amounts of tax accepted for deduction by the buyer when transferring an advance to the seller before 01/01/2019 are subject to restoration by the buyer in the amount of tax calculated based on the rate of 18/118%.
If, before the date of shipment, the buyer additionally pays the seller a VAT amount of 2 percentage points due to a change in the VAT rate, the Federal Tax Service of Russia recommends being guided by the following:
If an additional payment of tax in the amount of 2 percentage points is made by the buyer from 01/01/2019, then such an additional payment should not be considered as an additional payment of the cost on which VAT must be calculated at a rate of 20/120, but should be considered as an additional payment of the amount tax In this regard, the seller, upon receipt of a tax surcharge, should issue an adjustment invoice for the difference between the tax amount indicated on the invoice previously drawn up using a tax rate of 18/118 percent, and the tax amount calculated taking into account the amount of the tax surcharge (example 1).
If an additional payment of VAT in the amount of 2 percentage points is carried out from 01.01.2019 by persons who are not VAT payers, to whom invoices are not issued, then the amounts of additional tax payment are reflected in the sales book on the basis of a separate adjustment document containing the total ( summary) data on all cases of additional tax payments received by the seller from the specified persons during the calendar month (quarter), regardless of the readings of the cash register.
If an additional payment of tax in the amount of 2 percentage points is made by the buyer until December 31, 2018 inclusive, then, due to the lack of grounds in 2021, consider the specified additional payment as an additional payment of the VAT amount in the amount of 2 percentage points (since the current VAT rate in 2021 - 18%), such an additional payment should be considered as an additional payment for the cost , on which VAT must be calculated at the rate of 18/118. In this regard, the seller, upon receipt of an additional tax payment, can issue an adjustment invoice for the difference between the indicators of the invoice drawn up upon receipt of an advance payment at a rate of 18/118%, and the indicators after changing the cost of goods (work, services), property rights using tax rate of 18/118% (example 2).
Thus, in these cases, if the seller received an additional VAT payment in the amount of 2 percentage points, and, accordingly, adjustment invoices were issued, then upon shipment of goods (work, services), property rights, starting from 01/01/2019, VAT is calculated at a rate of 20%, and the amount of VAT calculated on the basis of the above-mentioned adjustment invoices is subject to deduction from the date of shipment of the specified goods (works, services).
The taxpayer also has the right to draw up a single adjustment invoice to two or more invoices drawn up earlier by this taxpayer.
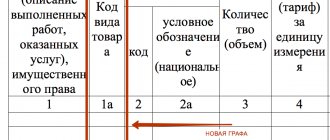
The difference between the tax amounts indicated in the adjustment invoices is reflected on line 070 in column 5 of the VAT tax return and is subject to accounting when calculating the total tax amount calculated at the end of the tax period. In this case, on line 070 in column 3 of the VAT tax return, the number “0” is indicated.
If before 01/01/2019 the taxpayer received an advance payment including tax at a rate of 20%, then VAT on the advance payment is calculated at a rate of 18/118%. In this case, no adjustment invoices are generated. When shipping the specified goods (works, services), property rights starting from 01/01/2019, VAT is calculated at a rate of 20%.
Tax accounting according to new rules from 2021
In 2021, Russia adopted several federal laws, according to which changes were made to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Innovations in the field of fiscal policy of the state came into force on January 1, 2021. In this article we will consider those changes that must be taken into account in the work.
VAT
The basic VAT rate is 20%
For shipments that will occur in January 2021 or later, the following new rates apply (Article 1 of Federal Law No. 303-FZ dated August 3, 2018):
— 20% – basic rate (instead of 18%);
— 20/120 – settlement rate (instead of 18/118);
— 16.67 – settlement rate (instead of 15.25).
There are no changes to other tax rates.
If the contract provided for prepayment in 2021 and shipment in 2019, then VAT on prepayment should be calculated at the calculated rate of 18/118, and on shipment - 20%.
Which party to the contract will pay for the rate increase depends on how the price is set:
- “price, plus VAT” – additional costs for the buyer. If he is entitled to a deduction, he will be able to compensate for the additional payment;
- “price, including VAT” or simply “price” - the increase in rate will be paid by the seller if he could not agree with the buyer on an increase in price.
In government contracts, the seller will pay for the rate increase, because according to Law No. 44-FZ, the price cannot be changed. But Law No. 223-FZ, according to the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, does not prohibit changing the contract price. It is possible to revise the cost of goods, works, and services due to an increase in VAT, unless this is prohibited by the procurement regulations (Information letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 28, 2018 No. 24-03-07/61247 “On the issue of changing the price of contracts after increasing the value added tax rate price").
If the tax difference of 2% is paid by the seller , then this amount cannot be included in income tax expenses.
If the seller was able to agree with the buyer on an additional payment above the established price and the tax additional payment of 2% will be received by him in 2019 separately from the advance payment, then the Federal Tax Service advises the seller to issue an adjustment invoice. In the VAT return, the seller will reflect the difference between the tax amounts in column 5 of line 070 of section 3 of the declaration and must be taken into account when calculating the total tax amount. Column 3 will indicate “0” (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 23, 2018 No. SD-4-3/ [email protected] “On the procedure for applying the tax rate for VAT during the transition period”).
When purchasing goods (works, services) using funds allocated from the budget, VAT does not need to be restored
From 2021, input VAT on goods, works and services purchased through subsidies and budget investments, as well as property rights, can be deducted if the money is allocated without VAT. This must be indicated in the documents on the provision of subsidies or budget investments (clause 2.1 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If goods, works, services, as well as property rights were acquired partially through subsidies or budget investments, then for deduction it is necessary to calculate the corresponding share (clause 4 of article 2 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 424-FZ).
Tax amounts that are not subject to deduction in accordance with this paragraph are not included in the cost of the specified goods (work, services), including fixed assets, intangible assets, property rights, but are taken into account as a lump sum as part of other expenses in accordance with Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation .
The innovations concern subsidies and budget investments received starting from 2021 (clause 7 of article 9 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 424-FZ).
More companies can apply the application procedure for VAT refund
According to the new rules (clause 10 of Article 2 of the Federal Law dated August 3, 2018 No. 302-FZ), in order to receive an accelerated VAT refund, the amount of VAT, excise taxes, income tax and mineral extraction tax transferred for the previous three years should not be 7 billion (as before), and not less than 2 billion rubles. Officials also softened the requirements for guarantors: the minimum amount of taxes paid was reduced from 7 billion to 2 billion rubles, obligations under guarantees can be not 20%, but 50% of the value of net assets.
Subclause 1 of clause 2 of Article 176.1 (as amended by Federal Law No. 302-FZ of August 3, 2018) applies to operations for the sale of goods (work, services) completed starting from October 1, 2018, therefore, starting from the 4th quarter of 2021, a larger number organizations can rely on the declarative procedure for VAT refund.
The VAT benefit for the sale of waste paper has ended
In accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, waste paper refers to paper and cardboard waste from production and consumption, rejected and out-of-use paper, cardboard, printed products, business papers, including documents with an expired shelf life.
In 2021, the sale of waste paper was not subject to VAT (clause 31, clause 2, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, was introduced by Federal Law No. 174-FZ dated June 2, 2016). But the benefit has ended (Article 2 of the Federal Law dated June 2, 2016 No. 174-FZ “On amendments to Article 149 of Part Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation”). From 2021, the sale of waste paper will be subject to VAT at a rate of 20%.
However, now the tax will have to be calculated not by sellers, but by buyers of waste paper. They will become tax agents. They will be subject to the rules that apply when selling raw hides, scrap metal and secondary aluminum and its alloys (clause 8 of Article 161 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 424-FZ).
VAT benefits for warranty repair services
Until December 31, 2021 inclusive, there was no need to pay VAT on warranty repair services if certain conditions were simultaneously met (clause 13, clause 2, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clauses 1, 2, 6, 7, article 5, clauses 1–3 of Article 18 of the Law on Protection of Consumer Rights). From January 1, 2021, applying or not applying VAT benefits for warranty repair services will become the right, and not the obligation, of the taxpayer. Legislators moved this benefit to paragraph 3 of Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Clause 3 of Article 9 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 424-FZ).
Refusal of the benefit will allow the taxpayer to apply the VAT deduction in the general manner (clause 2 of Article 171, clause 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
To waive the benefit from the first quarter of 2021, you need to submit an application to the Federal Tax Service no later than January 9 (clause 5 of Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). An application for refusal of VAT exemption is drawn up in any form. There is no approved form, but the application should make it clear for which transactions the taxpayer is waiving the exemption and for how long. The validity period of the waiver of exemption cannot be less than one year (clause 5 of Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When returning goods, only a correction invoice
Tax officials, in their letter No. SD-4-3/ [email protected] , recommended that sellers, starting January 1, 2021, issue adjustment invoices when returning goods, regardless of whether:
- whether the buyer accepted the goods for registration;
- when was the shipment: before the new year or after;
- The entire shipment of goods or part of it is returned.
The adjustment invoice will include the same rate that was indicated on the original document. One copy of the adjustment invoice is given to the buyer if he is a VAT payer.
If the buyer has accepted for deduction the amounts of tax presented to him for the goods he accepted for registration, then the restoration of the VAT amounts in accordance with subparagraph 4 of paragraph 3 of Article 170 of the Code is carried out by the buyer on the basis of an adjustment invoice received from the seller.
Russian organizations and individual entrepreneurs do not need to remit VAT on the cost of foreign services received in electronic form
If a foreign organization sells electronic services in Russia, then from 2021 it will have to pay VAT itself (clause 3 of Article 174.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended by Federal Law No. 335-FZ of November 27, 2017). Russian organizations and individual entrepreneurs who purchase services will cease to be tax agents. To receive a deduction, they will need an agreement or settlement document indicating the amount of VAT, INN and KPP of the seller, as well as documents for transferring payment. At the same time, information about such foreign organizations must be posted on the website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
Organizations and individual entrepreneurs on the Unified Agricultural Tax became VAT payers
The use of the Unified Agricultural Tax no longer exempts these special regime employees from paying VAT (clause 12 of Article 9 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2017 No. 335-FZ). These taxpayers can receive deductions in 2021, but input VAT cannot be taken into account as expenses.
For 2021, these special regime employees can receive an exemption from VAT in the following cases (clause 1 of article 2 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2017 No. 335-FZ):
- the start of application of the Unified Agricultural Tax will be in 2021;
- The Unified Agricultural Tax has been used before; in 2021, revenue did not exceed 100 million rubles.
If a taxpayer wants to apply the VAT exemption from the beginning of 2021, he needs to submit a notification to the inspectorate at the place of registration no later than January 21 (taking into account the transfer) (Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended by the Federal Law of November 27, 2017 No. 335-FZ) .
If among your counterparties there are Unified Agricultural Tax payers, check whether they plan to work with VAT. If not, then ask them for documents regarding the right to exemption.
Explanations for the VAT return must be provided in a new format
The Federal Tax Service of Russia has updated the xsd scheme for responding to the requirement to provide explanations to the VAT tax return (Information of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 30, 2018 on the website https://www.nalog.ru/rn77/rn77/rn77/rn77/news/activities_fts/7933143 /). In particular, a list of new transaction type codes has been added - 33–44 in connection with the entry into force of federal laws dated November 27, 2017 No. 335-FZ, No. 341-FZ and No. 350-FZ on January 1, 2018.
In addition, the format of the requirements for providing an explanation has been changed (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated July 16, 2013 No. AS-4-2/12705). In the new requirement, the taxpayer may receive new error codes:
— code “5” – the declaration does not contain an invoice date or the date is indicated after the reporting period;
- code “6” - in section 8 or an appendix to it, a deduction is declared beyond three years;
- code “7” - in section 8 or its appendix a deduction is declared on an invoice that was drawn up before the date of state registration;
— code “8” – incorrect code for the type of operation;
— code “9” – an error when canceling entries in section 9 or its appendix.
The updated format and xsd schemes must be used starting January 25, 2021.
Income tax
Organizations can take into account the costs of holidays in Russia for employees and their families
From January 1, 2021, vacation costs can be taken into account in labor costs (clause 24.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, introduced by Federal Law No. 113-FZ of April 23, 2018):
- for travel;
- accommodation and meals, if included in the price;
- sanatorium and resort services;
- excursions.
According to clarifications from the Russian Ministry of Finance, to account for costs, an agreement is required between the employer and the tour operator or travel agent. If an organization enters into an agreement directly with a service provider, for example with a hotel, it will not be possible to take into account expenses (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2018 No. 03-03-20/45524).
The voucher can be purchased for employees, their spouses, parents, as well as children or wards under the age of 18 (if they are full-time students - up to 24 years).
Costs are standardized: no more than 50,000 rubles per year for each vacationer. At the same time, the total amount of expenses of the organization for vouchers, voluntary health insurance and payment of medical services to employees should not exceed the amount of labor costs.
It will not be possible to save by reducing the regional income tax rate
Previously, regions could reduce rates below 17% at will Since 2021, a restriction has been introduced: regions have the right to pass laws on a new rate reduction only if this is indicated in Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (for example, for SEZ residents, for participants in regional investment projects) (clause 15 of article 2, part 2 of article 4 Federal Law dated August 3, 2018 No. 302-FZ; clause 21 Article 2, Part 3 Article 9 Federal Law dated November 27, 2018 No. 424-FZ).
Reduced rates that were introduced before September 3, 2021 will remain in effect until the end of 2022 at most. But the region has the right to change its mind and raise them earlier. If the benefit expires, for example, on December 31, 2021, then the region has the right, by its decision, to extend it for another three years. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor changes in regional laws.
If there are no benefits, then the amount of income tax calculated at a rate of 3% must be transferred to the federal budget, and to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation - at a rate of 17%. This distribution, temporarily introduced in 2021, was extended by legislators until 2024 inclusive (Clause 15, Article 1, Part 4, Article 2 of the Federal Law of August 3, 2018 No. 301-FZ).
Income received upon leaving the organization or upon its liquidation is equivalent to dividends
Previously, this issue was controversial. At first, the Federal Tax Service explained that the definition of dividends established by Article 43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not allow for tax purposes to consider the property received by the participants of a liquidated company (including money) as dividends. (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated April 13, 2009 No. 3-2-06/39).
Later, the Ministry of Finance of Russia, in its Letter No. 03-03-06/1/8913l dated February 16, 2017, concluded that the excess of the value of property received during liquidation over the contribution to the authorized capital is recognized as dividends.
Now legislators have put an end to this dispute. From 2021, the difference between the income received upon leaving the company (during its liquidation) and the actual paid price of shares, shares or units is equal to dividends (Clause 1, Part 2, Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as amended by the Federal Law dated November 27. 2018 No. 424-FZ).
Upon liquidation, the participant who received the income will have to calculate income tax independently at the rates for dividends.
Property received upon exit from the company or upon its liquidation must be taken into account at the market value at the time of receipt.
The loss received upon leaving the organization or upon its liquidation can be taken into account in expenses
From 2021, a participant’s loss incurred upon liquidation of an organization or upon withdrawal from it can be included in income tax expenses. The amount of loss is the difference between the market price of the property received and the actual paid cost of the share. The loss is determined as of the date of liquidation or exit from the organization (clause 2 of Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended by Federal Law No. 424-FZ of November 27, 2018).
Process equipment that uses the best available technology can depreciate faster
According to Article 1 of the Law on Environmental Protection (Federal Law No. 7-FZ dated January 10, 2002 “On Environmental Protection”), the best available technology is the technology for the production of products (goods), performance of work, provision of services, determined on the basis of modern achievements of science and technology and the best combination of criteria for achieving environmental protection goals, subject to the technical possibility of its application.
From 2021, an increased coefficient of 2 can be applied to the depreciation rate for these types of main technological equipment (clause 1 of Article 259.3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended by Federal Law No. 219-FZ dated July 21, 2014). The list of such equipment is determined by the Government of the Russian Federation in Order No. 1299-r dated June 20, 2017.
Owners of heavy trucks have the right to include in expenses the entire amount of payment in the Platon system
Starting from 2021, the deduction for transport tax in the amount of payment for damage caused to federal roads by heavy trucks - vehicles with a permissible maximum weight of over 12 tons - has been abolished.
In this regard, the restriction on accounting for income tax expenses was also lifted. Previously, only the excess amount was included in income tax expenses. Now the entire amount of the fee in the Platon system can be taken into account as part of other expenses (clause 4 of Article 2 of the Federal Law dated July 3, 2016 No. 249-FZ).
The criteria for controlled transactions have changed
According to the new rules, domestic Russian transactions are considered controlled only when the transaction income threshold of 1 billion rubles is exceeded. Otherwise, the transaction is not controlled, even if it meets the criteria of paragraph 2 of Article 105.14 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The signs themselves have also changed:
- removed an independent criterion in the form of an income threshold of 1 billion rubles. A transaction that does not meet the criteria that remain in paragraph 2 of Article 105.14 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is not controlled, even if the income from it exceeds 1 billion rubles;
- added a criterion: the parties apply different tax rates to profits from the activities within which the transaction was concluded. This does not apply to some rates, for example for dividends;
- removed the criterion for a party’s participation in a regional investment project, etc.
In connection with the amendments, transactions from paragraph 1 of Article 105.14 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (for example, through intermediaries) are controlled if the income from them for the year exceeds 60 million rubles. This rule also applies to transactions with interdependent foreign entities. Under previous rules, such transactions were controlled regardless of the amount of income.
The new rules apply to transactions for which taxpayers recognize income and expenses starting in 2021. The date of conclusion of the contract is not important (Article 105.14 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended by Federal Law No. 302-FZ dated August 3, 2018 and No. 199-FZ dated July 19, 2018).
For 2021, taxpayers need to report according to the old rules.
Transport tax
Owners of heavy trucks will not only accrue tax, but also pay
From 2021, it is no longer possible to apply a transport tax deduction in the amount of payment for damage caused to federal roads by heavy trucks - vehicles with a permissible maximum weight of over 12 tons (payment through the Platon system).
Therefore, in the new year, taxpayers must not only count, but also pay advance payments for transport tax (clause 2 of Article 363 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended by Federal Law No. 249-FZ dated July 3, 2016).
The deadline for payment of transport tax is established by the law of the subject of the Russian Federation in which the car is registered (Article 356 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The tax period is the calendar year, the reporting periods are the 1st, 2nd and 3rd quarters (Article 360 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Advance payments for the first, second and third quarters must be paid if this is provided for by the law of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation (clause 2 of article 363 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
We remind you! In Moscow, taxpayers-organizations pay tax no later than February 5 of the year following the expired tax period. During the tax period, payment of advance tax payments by taxpayer organizations is not made (Clause 1 of Article 3 of Moscow Law No. 33 of July 9, 2008 (as amended on November 29, 2017) “On Transport Tax”).
In the Moscow region, tax payment is made no later than March 28 of the year following the expired tax period, and advance payments are made no later than the last day of the month following the expired quarter (Article 2 of the Law of the Moscow Region dated November 16, 2002 No. 129/2002-OZ “ On transport tax in the Moscow region").
Organizational property tax
There is no longer any need to pay tax on movable property
From 2021, property tax must be paid only on real estate. Movable property has ceased to be subject to taxation, regardless of whether it was subject to the benefit earlier (clause 1 of Article 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended by Federal Law No. 302-FZ of August 3, 2018).
New rules for calculating property tax when the cadastral value of real estate changes during the year
As a general rule, the changed cadastral value is used when calculating property tax for future years, but in some cases recalculation for the current or previous years is possible. From January 1, 2019, these exceptions were adjusted (clause 15 of Article 378.2 of the Federal Law of August 3, 2018 No. 334-FZ).
Property tax can be recalculated for all periods when the previous value was applied if in 2021 the cadastral value is:
- will change due to the correction of a technical error in the cadastral value;
- will decrease due to the correction of errors made in determining the cadastral value;
- will change due to a decision of the commission or court to establish the market value;
- will decrease due to a decision of the commission or court confirming the unreliability of the information.
From 2021, if the characteristics of an object change, property tax is calculated at the new cadastral value from the date the information is entered into the Unified State Register of Real Estate . Thus, according to the old assessment, the tax will have to be paid for full months from the beginning of the year until the change in value, according to the new assessment - from the change until the end of the year. A month is considered complete if ownership arose no later than the 15th day or ceased after the 15th day
Changes in the rules for paying taxes and collecting penalties
If payment is late, penalties must be calculated differently
Penalties are calculated based on the amount of arrears, the number of days of delay and the size of the refinancing rate of the Bank of Russia (clause 3 of Article 58, clauses 4, 7 of Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clauses 5, 6 of Article 26.11 of Law No. 125 -FZ).
According to the amendments made to paragraph 3 of Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation by Federal Law No. 424-FZ of November 27, 2018, penalties cannot be greater than the arrears on which they are charged. Previously there was no such restriction. And penalties must also be accrued for the day when the arrears were repaid. Until December 27, 2021, it was not taken into account.
Thus, for arrears that arose before December 27, 2018 inclusive, penalties are accrued until the day the debt is paid. And for arrears arising after this date, penalties are accrued up to and including the day the arrears are paid. In this case, the amount of penalties cannot exceed the amount of arrears for which they are accrued.
If the refinancing rate changed during the period of delay, penalties for periods with different rates must be calculated separately.
If an error is detected, you can clarify the UFK account for payments to the budget
From 2021, if an error is detected, the taxpayer has the right to clarify the Federal Treasury account in the payment for taxes, insurance premiums, fees, penalties, and fines (Clause 7 of Article 45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended by the Federal Law dated July 29, 2018 No. 232-FZ). There are three conditions:
- no more than three years have passed from the date of payment;
- clarification will not lead to arrears;
- the money went to the budget, despite the error in the payment. This can be checked when reconciling calculations with the inspection.
When clarifying a payment, the tax authority is obliged to recalculate the penalties accrued on the amount of tax for the period from the date of its actual payment to the budget system of the Russian Federation until the day the tax authority makes a decision to clarify the payment.
The tax authority notifies the taxpayer of the decision to clarify the payment within five days from the date of adoption of this decision.
As you can see, the changes in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not global, but there are many of them. They must be taken into account when planning the organization’s financial activities for 2021.
The cost of goods shipped earlier will change in 2021
In accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code, when the cost of shipped goods (work, services) changes, including in the case of a change in price or clarification of quantity, the seller issues an adjustment invoice to the buyer.
If goods (work, services) were shipped before 01/01/2019, then if their value changes upward or downward from 01/01/2019, the tax rate in effect on the date of shipment (transfer) is applied, and therefore in the column 7 of the adjustment invoice indicates the VAT tax rate that was indicated in column 7 of the invoice for which the adjustment invoice was drawn up.
VAT rate for sales under government contracts
The Federal Tax Service of Russia, in a letter dated September 10, 2021 No. SD-4-3/17537, clarified that there are exceptions for goods (work, services), property rights sold under agreements (government contracts) concluded before the adoption of Federal Law No. 303-FZ and rolling over to 2021 is not provided.
Consequently, when selling goods (work, services), property rights shipped from January 1, 2021, a VAT rate of 20 percent is applied.
As for the procedure for presenting VAT to the customer under a government contract in connection with a change in the VAT rate from 18 to 20 percent, you should contact the Russian Ministry of Finance for clarification on this issue.
Correction of invoice for shipments until 2021
Corrections to invoices are made by the seller by drawing up new copies of invoices.
In the new copy of the invoice, it is not allowed to change the indicators (number and date) indicated in line 1 of the invoice compiled before corrections were made to it, and line 1a is filled in, where the serial number of the correction and the date of the correction are indicated.
In this regard, if corrections are made to the invoice issued for the shipment of goods (work, services) before 01/01/2019, column 7 of the corrected invoice indicates the rate that was in effect on the date of shipment of the specified goods (work, services) and reflected in column 7 of the invoice issued upon shipment.
Return of goods in 2021. Accounting with the seller
In accordance with paragraph 5 of Article 171 of the Tax Code, tax amounts presented by the seller to the buyer and paid by the seller to the budget when selling goods are subject to deductions in the event of the return of these goods (including during the warranty period) to the seller or refusal of them.
According to paragraph 4 of Article 172 of the Tax Code, VAT is deducted in full after the corresponding adjustment operations in connection with the return of goods or refusal of goods are reflected in the accounting records, but no later than 1 year from the date of return or refusal.
Based on the provisions of paragraph 13 of Article 171 and paragraph 10 of Article 172 of the Tax Code, when the cost of shipped goods changes downwards, including in the case of a decrease in the number of goods shipped, the basis for deducting VAT from the seller is the adjustment invoice issued by the seller.
In connection with the above, when returning from 01/01/2019 the entire batch (or part) of goods, both accepted and not accepted by buyers, it is recommended that the seller issue adjustment invoices for the cost of goods returned by the buyer, regardless of the period of shipment of goods , then available until 01/01/2019 or from the specified date.
Moreover, if in column 7 of the invoice for which the adjustment invoice was drawn up, a tax rate of 18% is indicated, then in column 7 of the adjustment invoice the tax rate of 18% is also indicated.
When returning from 01/01/2019 goods paid for by persons who are not VAT payers, to whom invoices are not issued, and shipped to these persons before 01/01/2019, an adjustment document containing summary (consolidated) data on return transactions made during a calendar month (quarter), regardless of the CCT readings.
VAT rate 18% in the contract
If your agreement specifies a VAT rate of 18%, then there is no need to change it.
From 01/01/2019 you ship goods/provide services at a rate of 20%, in accordance with clause 4 of Art. 168 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. If you are still confused by this situation, then draw up an additional agreement to the contract, which will spell out all the “inconvenient” points.
This situation can cause confusion because nowhere in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does it say what should be spelled out in the contract and how to act if the situation has changed.
Judicial practice shows that the buyer can sue the supplier and win the case if the contract specifies one contract amount, and you suddenly unilaterally indicate a different price in the invoice and demand payment of exactly that amount.
The situation in this case is slippery, because the law obliged us to raise VAT. The Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated August 28, 2018 No. 24-03-07/61247 states that, according to Part 2 of Art. 34 of the Law on the Contract System, the contract price is not subject to change for the entire duration of its validity. But in the same letter, a few paragraphs below, Government Resolution No. 1186 of December 19, 2013 is quoted, which states that the essential terms of the contract can be revised if changes occur due to circumstances beyond the control of the parties.
So if you are in a situation where you could lose a large amount due to a rate change, please refer to this ruling.
Return of goods in 2021. Accounting with the buyer
According to subparagraph 4 of paragraph 3 of Article 170 of the Tax Code, tax amounts accepted for deduction by the taxpayer on goods (work, services) are subject to restoration in the event of a downward change in the cost of shipped goods (work, services), including in the event of a decrease in price or decrease in quantity shipped goods (works, services).
Taking into account the above, if the buyer has accepted for deduction the tax amounts presented to him for the goods he accepted for registration, then the VAT amounts are restored by him on the basis of an adjustment invoice received from the seller, regardless of the period of shipment of the goods, that is, until 01.01. 2019 or from the specified date.
How to negotiate a price increase with the buyer
In order not to lose profit after the VAT increase, sellers raised prices. For example, in 2021 the product cost 118 rubles, 100 rubles is the price excluding VAT. With the new tax rate, it will cost 120 rubles, and the buyer will have to pay 2 rubles more.
Explain to the buyer: but his VAT deduction amount will increase. This is understandable to counterparties under the general tax regime. But simplifiers or imputators do not claim deductions, so they will have to pay more. And if such buyers are against raising prices, you may have to bear the extra costs.
Tax agents when purchasing from foreign companies
According to the provisions of paragraphs 1 and 2 of Article 161 of the Tax Code, when taxpayers - foreign persons not registered with the tax authorities - sell goods (works, services), the place of sale of which is recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation, the tax base is determined as the amount of income from the sale of these goods (works) , services) including VAT, which is calculated and by the tax agent purchasing these goods (works, services) from a foreign person.
Tax payment is made by tax agents simultaneously with the payment (transfer) of funds to such taxpayers.
Thus, the tax amount is calculated by the tax agent specified in paragraph 2 of Article 161 of the Tax Code when paying for goods (work, services), i.e. either at the time of transfer of the prepayment, or at the time of payment for goods (work, services) accepted for registration.
When goods (work, services) are shipped as payment previously transferred by a tax agent, the moment of determining the tax base does not arise for such a tax agent.
Taking into account the above, if payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (work, services) shipped from 01/01/2019 is transferred to a foreign person who is not registered with the tax authorities before 01/01/2019, then VAT is calculated by the tax agent on the date of transfer of the specified payment using a tax rate of 18/118%. When the specified goods (works, services) are shipped against the previously listed payment, VAT is not calculated by the tax agent.
If payment for goods (work, services) shipped before 01/01/2019 is made by a tax agent from 01/01/2019, then taking into account that the VAT tax rate of 20% is applied to goods (work, services) shipped starting from 01/01/2019 January 2019, VAT is calculated by a tax agent using a tax rate of 18/118%.
A similar procedure for calculating VAT is carried out by the tax agent specified in paragraph 3 of Article 161 of the Tax Code.
Long-term contract
The contract for the supply of goods or performance of work was concluded before the entry into force of Federal Law No. 303-FZ, that is, until 2021, and is long-term in nature with the transition to 2021 and subsequent years.
In this regard, a logical question arises: what VAT rate should be applied for a long-term contract? The Federal Tax Service of Russia in paragraph 1 of the letter dated October 23, 2021 No. SD-4-3/ [email protected] “On the procedure for applying the VAT tax rate during the transition period” clarified that no exceptions are provided for taxpayers in this case. The date and terms of the agreement (2018) in this case do not matter.
Based on paragraph 1 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the seller, in addition to the price of goods (work, services) shipped starting from January 1, 2021, transferred property rights, is obliged to present for payment to the buyer of these goods (work, services), property rights the amount of tax calculated according to the tax rate of 20 percent.
There is no need to make changes to the contract, but at the request of the party to the contract, the party has the right to clarify the calculation procedure and the cost of goods (work, services) sold and property rights transferred in connection with a change in the VAT tax rate.
A similar opinion on this issue was expressed by the Russian Ministry of Finance in letters dated September 7, 2021 No. 03-07-11/64049, dated September 7, 2021 No. 03-07-11/64178, dated September 10, 2021 No. 03- 07-11/64576.
Electronic services of foreign companies
According to paragraph 3 of Article 174.2 of the Tax Code, foreign organizations providing services in electronic form specified in paragraph 1 of this article, the place of sale of which is recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation, calculate and pay tax if the obligation to pay tax in relation to transactions for the sale of these services is not assigned to tax agent, that is, a foreign intermediary organization carrying out business activities involving participation in settlements directly with buyers of services on the basis of agency agreements, commission agreements, agency agreements or other similar agreements with foreign organizations. The above rule comes into force on January 1, 2021.
Thus, when, starting from January 1, 2021, foreign organizations provide services in electronic form specified in paragraph 1 of Article 174.2 of the Tax Code, the place of sale of which is recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation, the obligation to calculate and pay VAT to the budget rests with the foreign organization , regardless of whether who is the buyer of these services, an individual or legal entity.
In accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 174.2 of the Tax Code, when foreign organizations provide a number of services in electronic form, the place of sale of which is recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation, the tax base is determined as the cost of services, taking into account the amount of tax, calculated on the basis of the actual prices of their sales. In this case, the moment of determining the tax base is the last day of the tax period in which payment (partial payment) for such services was received.
Based on paragraph 5 of Article 174.2 of the Tax Code, the amount of tax is calculated by foreign organizations subject to registration with the tax authorities in accordance with paragraph 4.6 of Article 83 of the Tax Code, and is determined as the percentage of the tax base corresponding to the estimated tax rate of 16.67%.
Taking into account the above, if, when foreign organizations provide services in electronic form, payment (partial payment) for these services was received starting from 01/01/2019, then the taxation of such services is carried out by foreign organizations taking into account the following features:
- if services were provided in electronic form before 01/01/2019, then VAT is calculated at the estimated tax rate in the amount 15,25 %.
- if services are provided in electronic form starting from 01/01/2019, then VAT is calculated at the estimated tax rate in the amount 16,67 %.
If payment is received by foreign organizations before 01/01/2019 for the provision of services in electronic form, starting from the specified date, VAT is not calculated by foreign organizations. In this case, the responsibility for calculating and paying VAT to the budget rests with the buyer - an organization (IP) that is a tax agent .
New rules for identifying clients when exchanging currency
Gulnara Ruchkina
Doctor of Law, Professor, Head of the PRED Department of the Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation
— On December 27, 2021, new rules for identifying clients by banks came into force. When buying or selling currency for an amount up to 15 thousand rubles (or their equivalent in another currency), client identification is still not required. If the transaction amount is larger, the client provides a passport, the data of which the credit institution independently enters into the application form.
That is, if you want to change more than 15 thousand rubles, you will not have to fill out forms, questionnaires, and so on yourself. And the credit institution will not have to require additional information to identify clients, in addition to that provided by the law “On combating the legalization (laundering) of proceeds from crime and the financing of terrorism.”