Home — Articles
It happens that a VAT evader receives money from a buyer, but this tax is highlighted in the payment slip by mistake . At the same time, the buyer did not change the amount due from him, but simply determined the VAT by calculation and indicated its amount in the “Purpose of payment” field, or simply wrote: “ Including VAT 18% .” Is this situation familiar to you? Then our article is for you. You are not obliged to pay such VAT, since an invoice with the allocated amount of VAT was not issued to the buyer (Clause 5 of Article 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated March 31, 2009 N 20-14/2/ [email protected] ) . However, you should not calm down and expect that you will easily explain everything to the tax authorities when they come to you with an on-site audit. The thing is that the inspectorate will most likely see the VAT payment much earlier. And it’s good if the inspector starts by asking you for clarification. But, as practice shows, he can act differently, causing you a lot of trouble. So, what could a buyer’s mistake result in and what needs to be done to prevent negative consequences?
Causes and common types of errors
Payment orders are usually drawn up by an employee of the accounting or financial department. When filling out a document manually, errors are inevitable. Most often, employees make mistakes in the contract number or its date, incorrectly indicate the name of the paid goods or services, and when transferring tax, they make mistakes in the BCC and payment period. In 2021, due to the change in the VAT rate from 18% to 20%, cases of errors in indicating the tax rate and amount have become more frequent. We will tell you how and in what cases to write a sample letter about an error in the purpose of payment.
Some details must be corrected, but in some cases this is not necessary. A clarifying letter must be drawn up if the translation cannot be clearly identified, that is, it cannot be determined for what and on what basis the payment was made. If the error is not critical, a clarification notice need not be drawn up.
What could happen next?
Having discovered a payment with VAT , the inspectors will decide that you issued an invoice to the buyer with an allocated tax, which means you had to pay its amount to the budget (Clause 5 of Article 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, tax authorities believe that if a VAT evader has issued a VAT invoice, then he is obliged to file a declaration for this tax (Clause 3 of the Procedure for filling out a tax return for value added tax, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 15, 2009 N 104n; Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 23, 2007 N 03-07-11/512). True, the courts refuse to fine for failure to submit a declaration even those special regime officers who actually issued tax invoices (Resolutions of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated October 30, 2007 N 4544/07; FAS ZSO dated April 26, 2007 N F04-2469/2007 (33681-A70 -6)). To find out why VAT is indicated on the payment slip, the inspector must request written explanations from you (Clause 3 of Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) or call you to give explanations (Subclause 4 of Clause 1 of Article 31 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) as part of that desk audit, when which I requested a bank statement from. But often tax authorities do it much simpler: - block your current account for failure to submit a VAT return (Clause 3 of Article 76 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation); — write off the VAT indicated on the payment invoice for collection. A softer, but still unpleasant option is also possible, in which the tax authorities: - demand to pay the amount of VAT, penalties (Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and a fine (Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and in case of non-payment they threaten with undisputed write-off and blocking of the account; - they are required to submit a VAT return and are fined for late submission. All this is illegal. It is impossible to charge additional taxes, and also to conclude that a particular person has an obligation to submit a declaration and pay tax, based only on a bank statement, without studying the primary documents and establishing the substance of business transactions as part of an audit carried out by law (FAS Resolutions ZSO dated 03/28/2011 in case No. A45-12006/2010; FAS North Kazakhstan region dated 07/12/2006 N F08-3078/2006-1320A). Indeed, in this case, the conclusion that you have issued an invoice will have only a speculative nature, not supported by evidence collected in accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Clause 4 of Article 101 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Northern Territory of October 17, 2008 in case No. A21-13/2008 ). Actually, such evidence could only be the invoice itself (Resolutions of the FAS VSO dated January 31, 2006 N A19-17585/05-40-F02-3/06-S1; FAS UO dated August 24, 2006 N F09-7242/06- C2), but you did not exhibit it, and the inspection cannot have it. So the inspector’s actions can be challenged. However, it is better not to give her any reason for such actions, having ruled out in advance the possibility of suspecting you of charging VAT to the buyer. Let's see how to do this.
Who and in what cases draws up a notification to clarify the details of the payment order?
A letter of clarification is drawn up and sent by the person who transferred the funds. After all, only the payer has the right to dispose of his funds.
If the recipient of the money believes that there is an error in the payment order, he needs to contact the payer and request a correction. The recipient of the money cannot independently take into account the funds at his own discretion without the permission of the payer.
| Error | Do I need to fix it? | Why |
| Wrong contract | Yes | The supplier may consider the payment as an advance under an erroneous contract and not pay the actual debt for goods and services. In this case:
|
| Incorrect name of product or service | Not necessary | If there are frequent errors or a large transfer amount, the discrepancy between the specified product or service and the recipient’s activity may raise questions from the bank, including blocking the account. It is better to indicate the correct name of the product or service, but in case of widespread errors, they still need to be clarified. |
| VAT rate | No | There are no legal or tax risks. Here, problems may arise for the payer when offsetting VAT from the supplier's advance payment by the Federal Tax Service if the inaccuracy flows into the advance invoice. |
When and how can the inspectorate detect VAT on a payment invoice?
The inspectorate may discover that VAT is included in the payment order much earlier than it comes to you for an on-site inspection. Tax authorities will see this during a desk audit of your declarations for the period in which the payment was made with the erroneously allocated VAT. The fact is that, when checking your declarations, the inspectorate may request from the bank statements from the taxpayer’s bank accounts (Clause 2 of Article 86 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The statement (Appendix 4 to the Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 30, 2007 N MM-3-06/ [email protected] ) for each payment indicates, among other things, its purpose, the wording of which the bank transfers from the corresponding field of the payment order. When analyzing statements, tax authorities specifically pay attention to payments including VAT. After all, apart from an on-site inspection, this is the only way to identify cases of VAT filing by those who are not payers of this tax.
Note Of course, the inspection can detect the VAT allocated in the payment during an on-site or desk inspection carried out at the buyer. However, in this case, the buyer will not have your invoice (since you did not issue it), and the inspector will have no reason to suspect you of filing VAT.
We draw up a correction letter about the purpose of payment in the payment order to the supplier
When it is necessary to change the purpose of payment in a payment order, the letter is drawn up in any form. There is no approved form at the legislative level.
The document must indicate:
- document number and date;
- sender and recipient data;
- details of the payment document in which the error was made;
- correct name of erroneous details;
- signature of the responsible persons (the same ones who signed the payment).
You can send a notification in any convenient way. It is not necessary to receive notification from the counterparty about the receipt of the letter. But it’s better to get it to make sure that the recipient of the money has made accounting corrections.
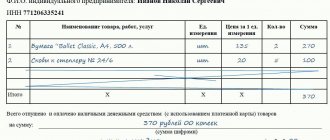
Sample letter about the correct purpose of payment
Accounting press and publications
"Accounting. Taxes. Law", N 19, 2004
THE INCORRECT VAT WAS INCLUDED IN THE PAYMENT
What to do if the amount of VAT in the documents for shipment of goods does not correspond to the amount of tax allocated in the payment order? Will this change the seller's tax obligations? And what amount of tax can the buyer offset: the one indicated in the payment order, or the one indicated in the shipping documents? Let's consider two situations.
Product at different rates
Situation 1. An organization ships goods that are subject to VAT at different rates (18 and 10 percent). In delivery notes and invoices, the amount of VAT for each item of goods is highlighted on a separate line. However, the buyer, when paying for the purchased goods, incorrectly allocated the amount of VAT in the payment orders - at one tax rate of 18 percent.
For the seller. He must transfer to the budget the amount indicated in the invoice, and not the amount that the buyer entered in the payment order.
The seller calculates the tax amount as a percentage of the tax base corresponding to the tax rate (clause 1 of Article 166 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Since in our situation the goods are sold at different tax rates, the tax base is determined separately for each type of goods taxed at different rates (Clause 1 of Article 153 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It is according to these principles that the tax in the invoice is calculated (clause 2 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Conclusion: the seller calculated the tax correctly and is not subject to recalculation due to the fact that the buyer decided to determine it in his own way.
This does not affect how the organization pays VAT: “on shipment” or “on payment”.
If, in accordance with the accounting policy, VAT is paid “on shipment,” then the calculated amount of tax must be transferred to the budget after shipment, of course, at the end of the tax period (clause 1, clause 1, article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Consequently, the fact that funds have been received under a payment order in which the VAT amount has been allocated incorrectly is irrelevant.
If the organization works “on payment”, then the obligation to pay the budget the amount of VAT on the cost of the goods arises only as payment is received from buyers (clause 2, clause 1, article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But even in this case, the incorrectly allocated amount of VAT will not affect the amount of tax that must be transferred to the budget. Let us recall that the amount of VAT is calculated as the percentage share of the tax base corresponding to the tax rate (clause 1 of Article 166 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, the tax is paid on the basis of a declaration for the corresponding tax period, which, in turn, is compiled on the basis of the sales book (clause 6 of the Instructions for filling out a VAT tax return, approved by Order of the Ministry of Taxes of Russia dated January 21, 2002 N BG-3- 03/25). The sales ledger records invoices issued to customers when goods are shipped. Our invoice highlights the VAT amount calculated taking into account different tax rates. Consequently, this exact amount will be included in the declaration and it is this amount that must be paid to the budget for the tax period.
For the buyer. It credits the tax shown on the invoice if the total invoice amount matches the payment amount.
Let us remind you that in order to receive a deduction for purchased goods, the buyer must fulfill several conditions (Articles 171, 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Firstly, the purchased goods must be used in an activity subject to VAT. Secondly, they must be registered. Thirdly, the buyer must have a correctly executed invoice. And fourthly, the deduction can be made on the basis of documents confirming the actual payment of tax amounts.
It is the last condition that interests us. On the one hand, it is completed - the goods and the tax amount are paid, on the other hand, the VAT amount is highlighted incorrectly in the payment document. Is it possible to offset VAT in this case?
In our opinion, it is possible, but only in the amount indicated in the invoice, and not in the payment document. After all, virtually all the conditions for receiving a deduction have been met.
But if the tax amount indicated in the payment order was less than in the invoice, then without problems it would be possible to offset only the VAT amount from the payment order. Clause 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation requires, in order to receive a deduction, the presence of documents confirming the actual payment of tax.
To avoid possible problems with the tax authorities, it is still better for the organization to obtain written confirmation from the buyer that VAT is allocated incorrectly in the payment order, indicating the correct tax amount.
VAT is not included in the price
Situation 2. An organization applying the benefit under Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation sold goods and issued the buyer documents for the shipment of goods and an invoice marked “Without VAT”. However, when paying for the goods, the buyer indicated in the payment order the amount of VAT at a rate of 18 percent.
For the seller. When using the right to exemption from taxpayer obligations under Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, organizations should not calculate and pay value added tax to the budget. At the same time, the VAT amount is not allocated in the invoices, but the note “Without VAT” is made (clause 5 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The Tax Code provides for only one case when organizations using the right to exemption under Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation must pay VAT to the budget - if the tax amount is allocated in the invoice (clause 1, clause 5, Article 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In our case, the VAT amount is not highlighted in the invoice, so the organization has no obligation to transfer it to the budget. Even if the tax amount is indicated in the payment order.
For the buyer. If VAT is not highlighted in the invoice received from the supplier, the buyer will not be able to offset it under any circumstances. The reason for this is clause 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, according to which the presence of an invoice with the presented VAT amount is a prerequisite for receiving a deduction.
A.S.Filimonov
Head of Tax and Legal Department
LLC "APN - Audit"
Signed for seal
17.05.2004
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— ———————————————————— ——
How to correct a tax payment
There are rules for clarifying tax payments:
- No more than three years have passed since the date of transfer.
- Clarification will not lead to arrears.
- The payment went to the budget.
It is impossible to clarify the payment if the payer made a mistake in the Federal Treasury account number or bank details. It is considered not to have been received by the budget, and can only be returned.
To correct an error in a payment order, you must compose a letter in any form and also attach a copy of the incorrect payment order to it.
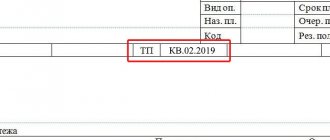
Sample letter about incorrect purpose of payment to the Federal Tax Service
When composing a notice, it must indicate:
- sender's details (name, address, TIN, OGRN);
- tax office details;
- data of the payment document in which there was an inaccuracy;
- details that need to be corrected with their correct values.
Sample letter about the correct purpose of payment to the tax office
You can send a notification:
- in writing in person to the Federal Tax Service or by mail;
- in electronic form through an EDF operator.
Letter to clarify the purpose of payment
A letter to clarify the purpose of payment is drawn up when employees of organizations discover an error or inaccuracy in an already executed payment order. This letter is not just part of business correspondence, it refers to the primary documentation of the company.
For your attention! This document can be downloaded from ConsultantPlus .
When and what errors occur
Errors in payments between counterparties are made by the compilers of payment orders, i.e. employees of accounting departments. In this case, incorrect data can be in a variety of points in the document: for example, the number of the agreement under which funds are transferred is incorrectly indicated, the purpose of the payment is incorrectly written, or, sometimes, VAT is allocated where it is not necessary, etc.
This can be corrected unilaterally by sending a letter to the partner to clarify the purpose of the payment.
In this case, the other party is not obliged to send a notification of receipt of this message, but it will not be superfluous to make sure that the letter has been received.
Is it possible to challenge a new payment assignment?
Typically, changing the “Purpose of payment” parameter occurs by mutual agreement and without any special consequences. But in some cases complications are possible. For example, if the tax inspectorate during an audit discovers such a correction and considers it a way to evade taxes, sanctions from the regulatory authority can be considered inevitable. It happens that friction regarding the purpose of payment arises between counterparties, especially in terms of payments on debts and interest. In most cases, in order to challenge the correction, the party protesting it will have to go to court, and no one will give guarantees of winning the case, since such stories always have many nuances.
An important condition necessary in order to avoid possible problems is that information about changes in the purpose of the payment must be transmitted to the banks through which the payment was made. To do this, you just need to write similar letters in a simple notification form.
Who writes a letter to clarify the purpose of payment?
This letter is drawn up by the company that transferred the funds.
Usually the text itself is written by a specialist in the accounting department or another employee authorized to create this type of correspondence and who has access to the generated payments.
In this case, the document must be signed by the head of the company.
How to write a letter correctly
A letter to clarify the purpose of payment does not have a unified template that is mandatory for use; accordingly, it can be written in any form or according to a template approved in the company’s accounting policy. At the same time, there is a number of information that must be indicated in it. This:
- name of the sending company,
- his legal address,
- information about the addressee: company name and position, full name of the manager.
- a link to the payment order in which the error was made (its number and date of preparation),
- the essence of the admitted inaccuracy
- corrected version.
If there is several incorrectly entered information, then they must be entered in separate paragraphs.
All amounts must be entered on the form in both numbers and words.
How to format a letter
The law makes absolutely no requirements for both the informational part of the letter and its design, so you can write it on a simple blank sheet or on the organization’s letterhead, and both printed and handwritten versions are acceptable.
The only rule that must be strictly followed: the letter must be signed by the director of the company or a person authorized to endorse such documentation.
It is not necessary to stamp the message, since since 2021 legal entities are legally exempt from the need to do this (provided that this requirement is not specified in the company’s internal regulations).
The letter must be written in at least four copies :
- you should keep one for yourself,
- transfer the second to the counterparty,
- the third to the payer's bank,
- the fourth to the recipient's bank.
All copies must be identical and properly certified.
How to send a letter
There are several ways to send such a letter.
- personally from hand to hand,
- courier delivery,
- via Russian Post by registered mail with acknowledgment of delivery,
- through the Internet.
When sending via the Internet, it is important that the company has an officially registered electronic digital signature, although even this does not guarantee that the recipient will read the letter.
How and for how long to store a letter
After sending, all letters about clarification of the purpose of payment must be registered in the journal of outgoing documentation, and one copy must be placed in the folder of the current “primary” company. Here it must remain for the period established for such documents by law or internal regulations of the company, but not less than three years . After losing its relevance and expiration of the storage period, the letter can be transferred to the archive of the enterprise or disposed of in the manner prescribed by law.
Source: https://assistentus.ru/forma/pismo-ob-utochnenii-naznacheniya-platezha/
Is it possible to challenge a payment change?
Sometimes the recipient of the money does not agree with the changes made by the payer. Unfortunately, it is quite difficult to challenge a letter of clarification. This must be done in court. It is advisable to resolve the problem through negotiations.
When making changes to the purpose of payment, you must remember that such transactions are carefully reviewed by regulatory authorities. If the Federal Tax Service sees signs of tax evasion in such letters, then claims may be made: additional taxes and penalties will be assessed. The most common issue that arises is prepayment under a supply agreement, which is later reclassified as a transfer under a loan agreement. This clearly shows a way to avoid paying VAT on the buyer's advance payment, and questions from the tax inspectorate are inevitable.
Letter to counterparty
Letter to clarify payment to counterparty: sample (VAT)
pismo_ob_utochnenii_platezha_kontragentu_obrazec_nds.jpg
There are often situations when a company, interacting with partners and contractors, makes errors or inaccuracies in payment documents. In particular, we are talking about the completeness of information regarding the purpose of the payment (field “24” in the payment order), which should list information about what services or goods are being paid for, the dates and numbers of the agreements on the basis of which it is made, information on VAT (Appendix 1 to the Regulations of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 383-P dated June 19, 2012). Tax authorities are very demanding about the correctness and specificity of filling out such information. An insignificant (for example, spelling) error will not lead to problems, but if the buyer has not allocated VAT on the delivery, then the impossibility of obtaining a tax deduction may become a reality, since it is the allocation of VAT in the payment that is the basis for the validity of its reimbursement (clause 4 of Article 168 of the Tax Code RF).
If an inaccuracy in the purpose of payment creates a threat of material losses or other troubles, it should be eliminated by writing a letter to the partner to clarify the payment. Let us remind you how to do this.
Letter to counterparty about VAT
The recipient of the payment does not have the right to adjust its purpose in the payment order; he can only clarify the wording with the partner. Only the owner of the transferred funds - the payer - can change or supplement this information. The change must be formalized by a letter certified by the persons who signed the payment order (Article 209 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 7 of Article 9 of the Law “On Accounting” No. 402-FZ of December 6, 2011).
The procedure for making amendments to the purpose of payment and the special requirements that must be observed in this case have not been established by the legislator, and a standard form for such a document is not provided. Therefore, when faced with the need to correct or supplement VAT information in a payment invoice, companies independently decide how to draw up the document, how to certify it and deliver it to the counterparty (by courier, by registered mail or electronically via TKS).
If such clarifications in the purpose of payments occur systematically, for example, due to logistics or technological features, it is worth developing a special document template and drawing up a letter to the counterparty about VAT clarifying the payment using this sample.
Following the requirements of business correspondence, when writing a letter, they usually adhere to the structure of an official document and use a business style, formatting the text on letterhead or regular office paper. The essence of the changes is presented briefly and clearly. The letter is certified by the manager, or a person authorized for such actions, and the chief accountant.
Letter to clarify payment to counterparty: sample (VAT)
Here is an example of a letter clarifying the purpose of payment:
Limited Liability Company "Lekar"
454200, Chelyabinsk, st. Rossiyskaya, 222
TIN 7404789456 / KPP 740401001
Potapov Alexey Petrovich
Dear Alexey Petrovich,
In payment order No. 451 dated 09/14/2020, when paying for inventory items under agreement No. 652/20 dated 09/01/2020, we made an inaccuracy in the “Purpose of payment” field - VAT was not indicated in the payment amount.
In this regard, we ask you to consider the following payment purpose as correct:
“Payment for building materials under supply agreement No. 652/20 dated 09/01/2020. The payment amount is 1,200,000-00 rubles, including VAT 20% - 200,000-00 rubles.”
We also ask you to give written consent to clarify the purpose of payment.
Director of Lekar LLC Rebrov I. N. Rebrov
Thus, the buyer agrees on the change in the payment document with the recipient and asks for his written consent to this action. It is more expedient to provide in advance in the contract for the occurrence of such a situation and to include in it a clause on the payer’s right to adjust the purpose of the payment by notifying the recipient in a corresponding letter, without the need to obtain his consent. With this option, you won’t have to wait for a response from your partner, and you won’t need to include in the letter a clause indicating his consent to clarification.
You can always view the full texts of regulatory documents in the current edition in ConsultantPlus.
Source: https://spmag.ru/articles/pismo-ob-utochnenii-platezha-kontragentu-obrazec-nds