On the territory of the Russian Federation, the document serving as the basis for the transfer of funds by banks is a payment order. The form of this form is approved at the legislative level, is unified and is used everywhere for non-cash payments. Each column of the specified order is intended for entering strictly defined information, which also serves specific purposes. An example of such information is the budget classification code. A payer who does not know the answer to the question of what a BCC is in a payment order is unlikely to be able to fill out this document without errors.
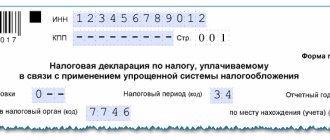
Payment order
Russian civil legislation calls payment cards one of the methods of non-cash payments. This instrument is used both for payments between commercial organizations and for fulfilling the financial obligations of an enterprise to the budget and funds. In the latter case, it is necessary to indicate the BCC in the payment order.
The specified details are subject to reflection in column 104 of the payment form put into circulation by the Regulations on the rules for the transfer of funds, approved by the Central Bank on June 19, 2012 N 383-P. This directly follows from the content of paragraph 5 of Appendix No. 2 to Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 12, 2013 No. 107n.
It should be emphasized that the above-mentioned act of lawmaking distinguishes between the concepts of UIN and KBC. The first of these details is reflected in the payment order as a zero in column 22 when paying funds calculated by the relevant person independently. However, this rule does not apply provided that the UIN is assigned by the recipient of the funds, i.e., the transfer is completed according to the relevant requirement. In this case, the unique accrual identifier is reflected in the “Code” column of the payment.
This conclusion is also confirmed by the Explanations of the Federal Tax Service of Russia “On the procedure for indicating the UIN when filling out orders for the transfer of funds to pay taxes (duties) to the budget system of the Russian Federation.”
How to find out the BCC for a specific payment?
Unfortunately, the Russian Ministry of Finance annually makes changes to the BCC coding due to a revision of the budget structure, the introduction of new tax regimes, compensation and benefits. New BCCs must be approved by the Ministry of Justice (Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation), then the information is published on the official website of the Federal Tax Service, so the current data reaches accountants with a delay. Sending a budget payment with an incorrect BCC leads to incorrect distribution of funds, so the payer is charged penalties. To avoid errors in the BCC number, an accountant or individual should clarify the details in one of the following ways.
Request details at a branch or on the bank’s website (relevant for standard payments). If the client regularly pays property tax, personal income tax or other common payment, the current details can be checked with the operator or customer service hotline employee. Banks that work primarily with legal entities often encounter BCC and have up-to-date information. Individuals paying taxes by receipt must use only the details from the payment order.
Checking the BCC on the Federal Tax Service website (www.nalog.ru/rn77/taxation/kbk/). An accountant or taxpayer can request a KBK code for a specific payment using the Federal Tax Service client portal. Having indicated the payer status (legal entities, citizens or individual entrepreneurs), the client should select the type of payment (for example, professional income tax). The Federal Tax Service system will automatically download a list of current BCCs. This method is used by accountants who make several tax payments for standard business transactions (for example, paying VAT).
Checking the CSC with the responsible inspector. A taxpayer can contact an inspector of the Federal Tax Service in person or by telephone during reception hours for citizens (organizations). Contact information for the tax inspectorate can be found on the Federal Tax Service website; in order to avoid arrears and erroneous payments, you should regularly check with the inspector about the status of the company’s personal account. Tax inspectors will be the first to learn new details and codes for payments to the budget.
Monitoring changes in legislation. Using the sites consultant.ru, nalog.ru, as well as news sites, the taxpayer can find out about the release of the next order of the Ministry of Finance, make changes to payment details, avoiding errors. For example, online magazines for accountants regularly publish a list of updated BCC and other details for taxpayers.
KBK field in a payment order
As stated earlier, the budget classification code is reflected in column 104 of the payment order and is indicated for the following payments:
- payment of taxes;
- contributions to funds;
- payment of arrears, penalties, fines and other fees;
- fixed contributions for individual entrepreneurs;
- National tax;
- other transfers in favor of government agencies.
The specific purpose of each payment to the budget of the Russian Federation or funds is contained in the BCC in the payment order. The importance of this requisite is difficult to overestimate.
A detailed decoding of the BCC is given in Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 1, 2013 N 65n. In accordance with the specified act of rulemaking, the budget classification code consists of 20 digits, combined into groups. Moreover, each group has its own meaning.
In order to answer the question of which BCC to indicate in a payment order, you need to understand the indicators of the budget classification code.
The first group, consisting of three digits, reflects the code of the chief administrator of budget revenues.
Values 4 to 13 contain information about the type of income and include:
- the fourth digit is the group of budget revenues;
- 5 and 6 values – subgroup of receipts;
- indicators 7 to 8 are intended to reflect information about the article;
- numbers 9, 10 and 11 indicate a sub-article;
- the final two values are used to indicate the revenue element data.
The remaining KBK indicators are intended to reflect information about the budget revenue subtype code, including:
- numbers 14 to 17 are used to indicate group;
- numbers 18, 19 and 20 contain analytics.
Instead of a conclusion, it should be noted that the budget classification code is of significant importance in settlements with the state represented by its bodies. It must be specified correctly. If the BCC is incorrectly indicated on the payment slip, then the corresponding amount may be attributed to unclear payments.
KBK structure: what information is contained in the details?
Typically, individuals and organizations use the KBK to register budget income; expense codes are relevant when receiving any returns from the state. The BCC consists of 20 characters encoding the values of the revenue administrator, type of income, budget program and economic classification of each payment. Specific values for each of the four sections of the details are established and updated by orders of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation. For example, in June 2021, an updated order of the Ministry of Finance No. 132-n was issued, establishing an up-to-date list of budget classification codes.
Budget revenue administrator (first three characters). This section of the BCC shows which government fund is receiving and tracking the payment. For example, for tax payments, penalties and fines for them, code 182 is used; when paying excise taxes in favor of the Federal Service for Regulation of the Alcohol Market, requisite 160 is used. In practice, the Federal Tax Service (tax payments, code 182), the Pension Fund of Russia (payments) usually acts as the administrator of budget revenues to the pension fund, code 392) and the Social Insurance Fund (payments to the social insurance fund, code 393).
Type of budget revenue (next ten digits). This section of the BCC clarifies what exactly funds are contributed to the state budget for. The combination encodes five indicators.
- Group (fourth character in KBK). This section of the type of income separates tax and non-tax budget revenues from gratuitous receipts, the requisite takes values from 1 to 13. Combinations 1 are most often used (profit and income taxes, insurance premiums, payment of state duties, compensation for damage caused).
- Income subgroup (fifth and sixth digits of the BCC). The combination specifies the name of the tax paid by a citizen or organization; it takes values from 01 to 18. For example, 01 is payment of income tax, 02 is contributions to compulsory social insurance, 08 is state duty.
- Article and sub-item of income (KBK signs from seventh to 11). The four-digit combination indicates the purpose of making the payment to the state budget. For example, 2010 is a combination for contributions to the pension insurance fund, 2090 is for payments to the Social Insurance Fund, 2101 is for payments for health insurance. A complete list of codes for articles and sub-items of budget revenues is approved by orders of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and is regularly updated.
- Income element (12th and 13th digits in BCC). This combination indicates the specific budget in favor of which this payment is made, values from 01 to 13 are used. For example, 01 indicates payments to the federal budget, 02 - payments in favor of the budget of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation (city, region), 05 - revenues to the municipal budget , 09 - budget of the federal health insurance fund.
The program by which the payment is executed (characters 14 to 17). This section of the BCC separates tax payments (code 1000), penalties and interest on them (code 2000), forced collections for arrears (code 3000) and other payments (code 4000). For example, when paying personal income tax you need to use combination 1000, when paying penalties for property tax - combination 2000.
Economic classification of budget income (characters 18 to 20). This combination indicates the type of economic activity for which contributions to the state budget are paid. The code takes values from 110 to 440. For example, 110 is budget tax revenue, 160 is contributions and deductions for social needs.
Thus, when registering a state fee for consideration of a case in an arbitration court, an enterprise accountant uses in the BCC combination 182 (income administrator - Federal Tax Service), 1 (income group - tax), 08 (income subgroup - national duty), 01000 (item and subitem of income - general tax payments), 01 (income element - payment to the federal budget), 1000 (payment program - standard tax), 110 (economic classification - budget tax income). In practice, financial workers request the BCC for new payments on the Federal Tax Service website.
What is KBK in a payment order?
Concept and features
An example of such information is the budget qualification code (KBK), which to the uninitiated eye looks like a meaningless set of numbers, but, in fact, carries a lot of information. A payer who does not understand how this code is deciphered will not be able to fill out the form correctly, which can lead to serious problems.
KBK is an important detail of a payment order, indicated by the payer when filling it out and representing a sequence of numbers with which certain information is encrypted (encrypted). Thanks to KBK, you can find out where the payment was sent from, its intended purpose and a number of other information.
There are the following types of CBC:
- for businessmen conducting their activities on the basis of a patent taxation system;
- for payment of insurance premiums;
- to pay arrears;
- for payment of fixed fees (by notaries, individual entrepreneurs);
- to make payments.
The latest changes in the field of BCC and property tax are discussed in the video below:
For what purposes is it used?
The introduction of this code serves the following purposes:
- facilitating the process of compiling material documentation and analyzing budget indicators;
- correct and timely transfer of tax amounts for their intended purpose, divided into separate accounts;
- classification of budget revenue and expenditure items, as well as their sources.
How the issue is regulated
- Order No. 2-P of the Central Bank regarding non-cash payments, dated October 3, 2002;
- Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 107n approving the rules for entering information into payment documents, dated October 12, 2013;
- Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 65n approving budget taxonomy codes;
- Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 38n containing corrections to the code system;
- Federal Law No. 229, regulating payment procedures for writs of execution;
- Labor Code art. 137-138, regulating deductions from wages on the basis of an administrative document;
- Federal Law No. 212, which classifies errors in the KBK as significant;
- Tax Code, paragraph 12, listing the types of taxes;
- Tax Code, paragraph 14, which classifies vehicle tax as regional taxes;
- Tax Code, paragraph 45, according to which a payer who incorrectly indicated the code may appeal the prescribed payments in court;
- Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 38n, introducing new codes for collections for violations of the law.
How and where to indicate the code in the order
Detailed instructions on this issue are given in Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 65n dated July 1, 2013. In accordance with this document, the BCC has 20 numbers, combined into four groups:
- First group (administrative) : consists of 3 digits and is the code of the main revenue administrator;
- The second group (income) , contains 10 numbers reflecting the following information: from 4th to 13th - income option, where number No. 4 indicates the group of budget revenues, No. 5 and 6 - a subgroup of revenues, No. 7 and 8 - reflect information about the article, Nos. 9, 10 and 11 indicate the subarticle, Nos. 12 and 13 indicate the revenue element;
- Third group (program) , numbers 14 to 17: encodes the group of receipts;
- The fourth group (classifying) , numbers from 18 to 20: contains analytical data.
This is interesting: How to apply for unemployment benefits
Now a little more detail. The administrative group specifies to whom the payment is transferred:
- 182 – taxes;
- 393 – various non-budgetary funds;
- 392 – health insurance.
Income group. The first digit can take the following values:
- one – tax payment;
- two – foreign exchange source;
- three – income from business activities.
The second and third numbers indicate the purpose of the financial transaction:
The remaining two characters indicate:
- 01 - income tax;
- 02 — social security contributions;
- 03 - products sold domestically;
- 04 – goods for import;
- 05 - for income;
- 06 – property payments;
- 07 – payment for mineral extraction;
- 09 – state duty, as well as various penalties and penalties;
- 10 – income from export/import operations;
- 11 – profit from state property in use;
- 12 – payments for resource use;
- 13 – earnings from the use of government services;
- 14 – income from trade;
- 15 — fines and fees;
- 16 – payment of damage.
The program group specifies the payment option:
- 110 – taxation of income;
- 160 – public payments;
- 151 - profit from budget recombination;
- 152—receipts from third parties;
- 153 — financing by foreign credit institutions;
- 170 – earnings from trading;
- 171 – income from property revaluation;
- 172 - income from property recycling;
- 180 – other income.
BCCs for insurance premiums are described in the video below:
Sample filling
- 8th field - name of the organization transferring the withheld amount;
- 22nd field - unique identifier (if available);
- 60th field - sender code, if there is no code - 0;
- 101st field - payer status 19;
- 102nd field - 0;
- 104th field - allocated to KBK, put 0, because it is not provided for these documents;
- OKTMO - given at the place of registration of the bailiff service.
Payment for kindergarten with KBK (sample)
If a document is sent with an error to KBK
In case of incorrect encoding, money may be transferred to another address. As a result, the payment may not be counted, which may result in penalties or fines. The process of returning an erroneous payment is quite complex, especially if it ended up in the budget of another level, for example, in the regional one, instead of the public one.
Please note that the BCC must also be indicated for newly opened organizations. When paying the state fee, they need to fill out field 104.
You should know that if the tax inspectorate imposes a penalty on taxes paid on time with an erroneous indication of the KBK, the court will declare such a decision illegal. The payer, in such cases, can seek help either from the authority that received the payment or from the department to which the payment was sent.
The BCC for the simplified tax system is discussed in the video below:
What is KBK in a payment order?
The budget classification code in the payment slip is a special digital code that should indicate budget income and expenses. An organization's accounting department encounters these codes when it makes a payment to the budget system, but most often does not understand what this sequence of numbers is and what it means in the payment order. What KBK and payment cards are available from January 1, 2021 can be viewed on this page - the classifier contains up-to-date information. But to understand the structure of the code, let's take a closer look at it. Let's look at what the KBK consists of, how important it is to indicate it correctly on the payment slip, and what to do with errors.
The decoding is given in Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 1, 2013 No. 65n. In accordance with it, the BCC indicated in payment orders consists of 20 digits combined into groups. Each group has its own meaning.
Results
The budget classification code (or BCC) consists of 20 digits that identify the recipient of the funds and the type of income. The KBK requisite is used when paying taxes, contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Social Insurance Fund and other social insurance funds; the current code values are established by orders of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation. In practice, the BCC values are revised annually, so taxpayers should check the data on the Federal Tax Service website, consult with bank employees and the responsible tax inspector.
If an error is discovered in the BCC of a contribution that has already been sent, you should submit an application requesting clarification of the payment. A sample document can be downloaded on the Federal Tax Service website or obtained a form from the reception office of the district inspectorate. The paper can be submitted in person, through a legal representative, sent by registered mail, or transmitted electronically via EDI. As a rule, tax inspectors agree to transfer money to the required details, and also cancel the accrual of late fees.
Read more
- Budget classification code (BCC) in the 3-NDFL declaration: what is it?
- KPP (registration reason code): details of the details
- Correspondent account: considering the nuances and role of details
- Where can I get KBK and OKTMO?
What does the budget classification code consist of?
Each digit of the code indicated on the payment slip is also called a digit. The digits are combined into blocks as follows:
The first group is administrative. It consists of three digits and reflects the code of the chief revenue administrator. For example, the Federal Tax Service code in the payment order is 182; FSS code in the payment slip is 393.
The second block is profitable. It includes several information messages at once. The first of them (bit 4) is expressed in one digit and indicates the type of payment received. For example, the number 1 means that it came in the form of a tax, 2 - that it came in the form of gratuitous income, 3 - from business, etc.
Next comes a subgroup. These are two signs that indicate for what purpose the cash receipts from the payment order are intended. So, 01 - profit tax and income tax; 02 - tax or fee for social needs, 08 - state duty.
The table will help when filling out a payment order. It contains a detailed decoding of the KBK, the categories are indicated in a separate column.
What to indicate in a payment order
For tax and non-tax income:
- 01 - taxes on profits, income;
- 02 — insurance contributions for compulsory social insurance;
- 03 - taxes on goods, works, services sold in Russia;
- 04 - taxes on goods imported into Russia;
- 05 — taxes on total income;
- 06 — property taxes;
- 07 - taxes, fees and regular payments for the use of natural resources;
- 08 - state duty;
- 09 - debt and recalculations for canceled taxes, fees and other obligatory payments;
- 10 - income from foreign economic activity;
- 11 - from the use of state or municipal property;
- 12 — payments for the use of natural resources;
- 13 - income from the provision of paid work, services and compensation for state expenses;
- 14 - from the sale of tangible and intangible assets;
- 15 — administrative fees and charges;
- 16 - fines, sanctions, damages;
- 17 - other non-tax income;
- 18—receipts for settling settlements between budgets of the budget system of the Russian Federation.
The third block also includes a group and a subgroup (two and three numbers in a row, respectively).
The next element in the payment order defines the budget code and consists of two digits, designated as follows:
- 01 - federal;
- 02 - subject of the Federation;
- 03 - local, etc.
What to indicate in a payment order
Codes by which administrators classify incoming payments. The codes are indicated in Appendix 1.1 to the Directives approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 1, 2013 No. 65n.
Codes for distribution of payments - budgets:
- 01 - federal;
- 02 - subject of the Russian Federation;
- 03 - budgets of intra-city municipalities of federal cities;
- 04 - urban district;
- 05 - municipal district;
- 06 - Pension Fund of the Russian Federation;
- 07 - FSS of Russia;
- 08 - FFOMS;
- 09 - TFOMS;
- 10 - rural settlement;
- 11 - urban district with intracity division;
- 12 - intracity district;
- 13 - urban settlement.
This is interesting: Paper wedding, how many years have you been married?
Next are 4 key numbers that determine the “reason” for the payment (category numbers in the BCC are 14, 15, 16, 17). It is important to understand here that there can be only three reasons:
- payment of the tax itself (fee, contribution);
- payment of penalties on it;
- payment of a fine thereunder.
So, for example, at the time of writing, when filling out payment orders, the following designations are generally accepted: payment - 1000, 2100 - penalties, 3000 - fine. For example:
- 182 1 0100 110 - when paying personal income tax to the budget;
- 182 1 0100 110 - upon payment of penalties for personal income tax;
- 182 1 0100 110 - payment of a fine.
And finally, the last three digits of any code are a classifier of the type of income (tax, non-tax, from property, etc.). For example, 010 is tax income; 130—receipts from the provision of paid services, work and compensation of costs; 150 - gratuitous receipts from budgets.
What to indicate in a payment order
Analytical group of budget income subtype
The values of the codes are approved by the Ministry of Finance of Russia, the financial body of the subject of the Russian Federation, municipal formation. If not approved, please indicate:
- 110 - tax revenues;
- 120 - from property;
- 130 - from the provision of paid services, work and compensation of costs;
- 140 - the amount of forced seizure;
- 150 - gratuitous receipts from budgets;
- 160 — insurance contributions for compulsory social insurance;
- 180 - other income.
Items of disposal of non-financial assets:
- 410 - decrease in the value of fixed assets;
- 420 - decrease in the value of intangible assets;
- 430 - decrease in the value of non-produced assets;
- 440 - decrease in the cost of inventories.
Explanations
- Administrator
- Type of income (group, subgroup, article, subitem, element)
- Subtype of budget revenues (group and analytical group)
The administrator consists of three characters and determines the revenue administrator code. Administrators, for example, are the Federal Tax Service (code 182), the Social Insurance Fund (code 393), the Pension Fund (code 392)
The type of income is the same for all budgets of the country and includes:
- group
- subgroup
- article
- sub-article
- element (defines the type of budget).
The income group has the following meanings:
- 100 - tax and non-tax revenues;
- 200 - gratuitous receipts.
Group 100 “Tax and non-tax income” (and we are only interested in this in this article) contains the following subgroups of income:
- 101 - taxes on profits, income;
- 102 — insurance contributions for compulsory social insurance;
- 103 - taxes on goods (work, services) sold on the territory of the Russian Federation;
- 104 - taxes on goods imported into the territory of the Russian Federation;
- 105 - taxes on total income;
- 106 — property taxes;
- 107 - taxes, fees and regular payments for the use of natural resources;
- 108 - state duty;
- 109 - debt and recalculations for canceled taxes, fees and other obligatory payments;
- 110 - income from foreign economic activity;
- 111 - income from the use of property in state and municipal ownership;
- 112 - payments for the use of natural resources;
- 113 - income from the provision of paid services (work) and compensation of state expenses;
- 114 - income from the sale of tangible and intangible assets;
- 115 - administrative fees and charges;
- 116 - fines, sanctions, compensation for damage;
- 117 - other non-tax income;
- 118 - receipts (transfers) for the settlement of settlements between budgets of the budget system of the Russian Federation.
The budget income type code has one of the following income element codes:
01 - federal budget; 02 — budget of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation; 03 - budgets of intra-city municipalities of federal cities; 04 — budget of the city district; 05 - budget of the municipal district; 06 - budget of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation; 07 - budget of the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation; 08 - budget of the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund; 09 - budget of the territorial compulsory health insurance fund; 11 - budget of the urban district with intra-city division; 12 - budget of the intracity district; 13 - budget of the urban settlement.
KBK field in a payment order
Each field in the payment order is assigned its own number.
The payment order has a separate field for KBK (this is the 104th field), and it must be filled out correctly (you can see the rules for filling out a payment order in the “Regulations on the rules for transferring funds” (approved by the Bank of Russia on June 19, 2012 No. 383-P If the BCC is indicated incorrectly on the payment slip, then the corresponding amount may be classified as unexplained payments. The Federal Treasury may classify it as “unclarified.” At the same time, an error in indicating the BCC on the payment slip can lead to arrears in taxes and insurance premiums.
Here is an example of a completed payment slip with entered data about the recipient:
- field 104 of the payment order indicates the KBK for transferring personal income tax;
- 105 - OKTMO;
- 106 - basis - current payment (abbreviated as TP);
- 107 - period (MS - abbreviated month);
- 108 - this field contains “0” (when paying on demand, the number of the document with the demand is entered in this field of the payment order);
- 109 - “0” (the payment field is intended to indicate the date of submission of the declaration or settlement. If the payment is made regardless of the submission of reports, “0” is always placed in this payment field);
- 110 - the field always remains empty in the payment order;
- 24 - brief purpose of payment: type of tax and payment period.
KBK in payment in 2021
What is income for the budget, for taxpayers is payment to the state treasury of taxes and equivalent payments and insurance premiums (except for “injuries”). Therefore, each of them first goes to the accounts of the territorial body of the Federal Treasury and is classified there on the basis of the BCC.
For any taxpayer or tax agent, regardless of its organizational and legal form, it is very important to correctly fill out a payment order, since errors, for example, incorrectly filling out this field in a payment order, can lead to money being credited to the “wrong address.” The Federal Treasury may classify it as “unclarified.” This means that the payer has an unpaid obligation to the state, i.e., outstanding arrears, penalties, fines and other sanctions from the state, in this case to the payment administrator. This can be avoided if you indicate the budget classification code correctly.
Order No. 245n dated November 30, 2018, which amended the current guidelines for the application of the BCC, contains new budget classification codes:
- excise taxes New budget classification codes have been introduced for dark marine fuel, petroleum raw materials for refining, state duties for issuing excise stamps, etc.;
- a new BCC for a single tax for individuals on professional income, a fee introduced for self-employed citizens;
- codes for paying taxes on additional income from the production of hydrocarbons, calculated according to the norms of Art. 333.45 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If the KBK is incorrectly indicated on the payment, what to do?
Step 1. An application must be sent to the tax office or the territorial branch of an extra-budgetary fund to clarify the details of the payment order. The application is written in any form. Please attach a copy of the payment slip with the bank's stamp to your application.
Step 2. Tax inspectors must make a decision on the issue of clarifying payment within 10 working days. This period begins to count from the date of application, when the inspectors received your application for clarification of payment, or from the date of signing (registration) of the act of joint reconciliation of calculations (if it was carried out).
Step 3. After the deadline has expired, be sure to order a tax certificate of settlements with the budget or a reconciliation report to make sure that the inspectors credited the amount to the correct BCC.
An error was discovered in the KBK after payment: what should I do?
In a number of cases, individuals and accountants of organizations receive notifications about the accrual of a tax penalty, non-payment of any contributions, or the receipt of funds under an incorrect budget item. Such situations arise due to various errors in the KBK number. According to the law, an error in the KBK is not a basis for the accrual of penalties and recognition of the payment as not listed (the payment order contains additional information for the operator). To correct the error, the taxpayer must act consistently.
Reconciliation of current tax debt. Using the Federal Tax Service website, the portal of the State Services project or the contact telephone number of the tax office, two or three days after sending the funds, you should check the debt on mandatory payments and find out where the paid funds were transferred. For example, if there is an error in the Program field (KBK signs 14 to 17), the funds are transferred to the required current account and the Federal Tax Service inspector offsets the payment at the request of the payer.
Contact the Federal Tax Service with a statement about the detected error. The payer should submit a written application with a request to clarify the affiliation of the funds paid for the selected tax period. The payment clarification paper is drawn up in two copies and must contain the data of the head of the Federal Tax Service and contact information about the payer. The document must be accompanied by a receipt for the transfer of funds and indicate a request to transfer the money to the correct KBK. The paper can be handed over to the inspector in person, through a representative with a power of attorney, sent by registered mail or through the EDI (electronic document management) system. The application is reviewed within ten working days.
If the Federal Tax Service refuses to transfer funds to the correct details and continues to charge penalties, the payer has the right to apply to the district court with a request to transfer the money, as well as cancel the accrual of a fine for late payment. In practice, the best option is to negotiate with the tax inspector and deposit the missing amount before the start of the proceedings. Typically, inspectors make positive decisions, transferring funds to the correct KBC details.
Budget classification codes (BCC) of payment order
The instruction on the use of new budget classification codes (BCC) from January 1, 2005 was approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 72n dated August 27, 2004. And in accordance with the Directive of the Bank of Russia dated August 25, 2004 No. 1493-U “On the specifics of using settlement document formats when making electronic payments through the Bank of Russia settlement network,” the maximum length of field 104 of a settlement document has been increased to 20 characters.
KBK (field 104) are budget classification codes filled in field 104 of the payment order. For each type of tax, the payment order indicates its own budget classification code (BCC). The maximum length of field 104 (KBK) of the settlement document has increased to 20 bits (characters).
The maximum number of BCC characters entered in detail 104 (field 104) is determined to be 20, and this is specified in Appendix 11 to Bank of Russia Regulations dated June 19, 2012 N 383-P “On the rules for transferring funds.”
And the very meaning of the BCC can always be clarified using the Table of Codes for Classifying Budget Revenues of the Russian Federation, administered by the Federal Tax Service, which is given in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated December 16, 2005 No. MM-6-10 / [email protected]
The structure of the budget income classification code of the Russian Federation (KBK) consists of 20 categories, combined into 4 parts, and has the following form:
| Rank | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| Parts | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| Code name | Administrator | Group | Subgroup | Article | Sub-article | Element | Program | Economic classification | ||||||||||||
Let us consider the structure of the budget classification of income code (KBK) of the Russian Federation in more detail.
Part 1: 3-digit administrator code
Administrator - occupies 1-3 categories of the KBK, consisting of three characters (symbols) and corresponding to the number assigned to the main manager in accordance with the list of main managers of the corresponding budget.
Administrators of budget revenues are:
- tax authorities;
- other government bodies;
- governing bodies of state extra-budgetary funds;
- local government bodies;
- legal entities or individuals authorized by the specified government bodies, as well as state (municipal) institutions created by these bodies
As an example, here are the codes of individual administrators:
- code of the Federal Tax Service of Russia - 182-0-00-00-000...;
- code of the Federal Customs Service of Russia - 153-0-00-00-000...;
- code of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation – 392-0-00-00-000...;
- code of the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation – 393-0-00-00-000...;
- code of the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund - 394-0-00-00-000... etc.