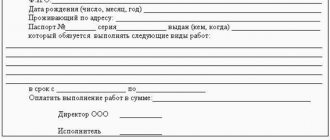
Every year, entrepreneurs make the same mistakes related to hiring employees for a short-term period. The most pressing issues remain the classification of work as seasonal, the provision of leave and the payment of compensation for it.
When formalizing labor relations with seasonal workers, companies and entrepreneurs should remember that the legislation provides for a number of features for regulating the labor of such employees. In this article we will look at what jobs are recognized as seasonal, what are the features of hiring, granting vacations, and dismissing such workers. This primarily concerns areas such as harvesting, landscaping, construction, tourism, catering and trade.
Seasonal work is work that, due to climatic and other natural conditions, is performed during a certain period (season), usually not exceeding six months. This definition is contained in Art. 293 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The main criterion for classifying work as seasonal - its urgent nature - is determined by natural conditions, and nothing else. This distinguishes them from temporary work - work for up to two months (Article 59 of the Labor Code). Temporary work can be separated from seasonal work, if it lasts less than two months, based on the criterion of natural conditions that determine the time-limited nature of the work.
Termination of a fixed-term employment contract
Termination of a fixed-term employment contract occurs in the following cases:
- after the main employee returns to work from maternity leave, and a new specialist is hired to replace him;
- after completing the work specified in the contract;
- after the end of the contract;
- after the end of the season, if the work was seasonal.
In order to terminate the contract, the employer is required to notify the employee three days before its end . If this has not been done and the subordinate continues to perform the work, then the contract automatically becomes indefinite.
Also, dismissal without warning can be appealed in court and the employee will be reinstated at work, also with an open-ended contract.
See here for information on how to file a lawsuit.
The only case when an employer may not send a warning about the end of the contract is when the main employee returns to work, since in this case the employee is dismissed automatically and without warning.
Subject of the agreement
1.1. Under this employment contract, the Employee undertakes to fulfill the duties of his profession/position [indicate work by position in accordance with the staffing table, profession, specialty indicating qualifications; specific type of work entrusted to the employee] at [place of work, and in the case where the employee is hired to work in a branch, representative office or other separate structural unit of the organization located in another locality, the place of work indicating the separate structural unit and its location], and The Employer undertakes to provide the Employee with the necessary working conditions provided for by labor legislation, as well as timely and full payment of wages.
1.2. Work under this agreement is the main place of work for the Employee.
1.3. Working conditions at the workplace in terms of the degree of harmfulness and (or) danger are [optimal (class 1)/ acceptable (class 2)/harmful (specify the class and subclass of harmfulness)/hazardous (class 4)].
1.4. The employment contract was concluded for seasonal work.
1.5. The employee must begin work on [day, month, year].
1.6. The employment contract terminates at the end of the season [date, month, year].
back to contents
Dismissal under a fixed-term employment contract
Dismissal under a fixed-term employment contract can occur in the following cases:
- after the end of the contract;
- at the initiative of the employer;
- at the initiative of the employee.
The first item on this list was covered in detail just above. In what cases can an employer fire employees hired to the organization for a certain period?
It’s worth clarifying right away that under no circumstances should pregnant women be fired, only if the entire organization is liquidated or an individual entrepreneur ceases his activities.
The standard rule applies to all regular employees: if an employee fails to fulfill his job duties without a good reason, the employer may impose a disciplinary sanction (reprimand or reprimand).
After a repeated violation, the employee may be fired. But in this case, it is necessary to carefully prepare all documents (memos, explanatory notes, acts, etc.).
If the dismissal occurs at the initiative of the employee, then in this case he must notify his superiors in writing three days before ceasing to fulfill his labor obligations. After this period, the contract is considered terminated.
Extension of the term of a fixed-term employment contract
Currently, the legislation of the Russian Federation provides for the extension of a fixed-term employment contract only in relation to:
- athletes;
- pregnant women;
- employees of higher educational institutions, if they are competing for a position previously held under a fixed-term employment contract.
Each contract extension must be accompanied by special annexes, which will indicate additional work or the next period for their implementation.
Taking into account the extension, a fixed-term employment contract should not last longer than five years.
In other cases, the law does not provide for the extension of such contracts.
An employer can hire an employee for a new period of work only by concluding another contract.
True, in this case it is necessary to take into account that repeated hiring of the same employee to perform the same work may attract the attention of various government services.
In addition, if you go to court, such an agreement may ultimately be recognized as unlimited.
Advantages and disadvantages of a fixed-term employment contract
Employees hired by the company under a fixed-term employment contract are entitled to the same social guarantees as those whose term of work in the organization is unlimited.
This is an absolute plus, since all the employee’s rights are respected, he is paid for sick leave and vacations.
Also, the employee will be able to receive payment in the event of dismissal due to the closure of the organization , if the term of his contract does not end during this period.
In addition, another advantage is that in order to conclude a fixed-term contract, certain conditions are required, and not just the desire of the employer. If they are not met, the employee can appeal his dismissal in court and get a job with the company under an open-ended contract.
But fixed-term contracts also have their downside - after the expiration of such a contract, the employee quits.
Firstly , this is not always convenient, especially if a person worked during the absence of a permanent employee, since he can be fired even without warning.
Secondly , in the future, an employee who often enters into fixed-term contracts may have problems with calculating a pension, since it will be difficult to choose a period of continuous service.
Thus, fixed-term employment contracts are very common in our country. When entering into such an employment agreement, always be aware of the conditions that allow it.
The use of a fixed-term contract also involves taking certain actions to continue cooperation with the employee or to dismiss him.
When is a contract for a season legal?
Let's start with what kind of work is recognized as seasonal according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This definition is given in Art. 293. This type of work includes those that, due to climatic conditions (or other natural reasons), can only be performed for a certain period (season), usually 6 months. I’ll say right away that 6 months is not a strict limit, the season can last a little more or less, it all depends on the conditions and the specific type of work.
The seasonality of work is determined by law; the entrepreneur himself cannot decide that the work he offers is seasonal. Where can I see a list of such works? There are several documents that need to be taken into account, we will highlight three of them separately:
- Resolution of the People's Commissariat of the USSR No. 185 of October 11, 1932 - the date of the document should not confuse anyone, it is still valid to this day.
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 382 of 04/06/1999 is also a valid document approving the list of seasonal activities for which there is a deferment / installment plan for paying taxes.
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 498 of 07/04/2002 - approves the list of seasonal industrial sectors, the enterprises of which have features in calculating the insurance period.
These lists are basic. When working in a specific sector of the economy, you also need to pay attention to the presence of industry (as well as inter-industry) agreements. They may also contain lists of work that are considered seasonal - in this case, the timing of the season is also established, since it can last more than six months. There are such agreements for organizations in the timber industry, housing and communal services, and automobile/urban ground transport (passenger transportation).
It turns out that you can sign an employment agreement with an employee for a season only when the work offered to him is truly seasonal - that is, included in any of the lists given above. The lists of seasonal work that we have named overlap in many ways. That is why work in crop production is recognized as seasonal, but summer work in a travel agency is not.
Frequently asked questions on the topic of fixed-term employment contracts
How to terminate a fixed-term employment contract early?
Termination of an employment contract can occur for several reasons, including at the initiative of the employee, at the initiative of the employer, and due to circumstances beyond the control of the parties.
Regardless of the reasons for terminating an employment contract, the procedure for terminating an employment contract is accompanied by many legal features and requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The employment contract provides for several cases of dismissal :
- termination of the enterprise's activities;
- change of owner of the enterprise;
- staff reduction;
- gross violation of work duties;
- repeated violation of work instructions, work duties without a good reason.
An employment contract can be terminated prematurely for several reasons. An agreement on early termination of an employment contract requires several grounds:
- by mutual agreement of the parties (Article 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- at the initiative of the employer (Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- at the initiative of the employee (Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
What are the grounds for concluding a fixed-term employment contract?
The following are considered unconditional conditions for concluding a fixed-term employment contract (Part 1, Article 59 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- temporary absence of the main employee;
- temporary work;
- seasonal work;
- work abroad;
- work that goes beyond the normal activities of the employer;
- temporary increase in production volume;
- the employing organization was created for a certain period;
- for the period of study and internship;
- election to office;
- ensuring the activities of elected bodies;
- sending an employee to temporary work by employment authorities;
- alternative civil service.
Conditions for concluding an agreement by agreement of the parties (Part 2 of Article 59 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- employer - small business entity;
- the employee is a pensioner;
- medical indications;
- performance of work requires moving to the Far North;
- urgent work to prevent disasters, etc.;
- election to a position on a competitive basis;
- creative professions in the media, cinematography, etc.;
- with managers, deputy managers, chief accountants;
- the employee is undergoing full-time training;
- the employee is a part-time worker.
Working time and rest time
4.1. The employee is assigned [a five-day work week with two days off/a six-day work week with one day off/a work week with days off on a sliding schedule/a part-time work week].
4.2. The duration of daily work/part-time work is [value] hours.
4.3. The start and end times of work, the time of the break and its duration [in the case of providing days off on a sliding schedule - alternating working and non-working days] are established by the internal labor regulations.
4.4. The employee is entitled to an annual paid leave of [value] days at the rate of two working days for each month of work.
4.5. The employee is granted an additional annual paid leave of [value] calendar days [indicate the basis for providing additional leave].
4.6. For family reasons and other valid reasons, the Employee, upon his written application, may be granted leave without pay, the duration of which is determined by agreement between the Employee and the Employer.
back to contents