Participants in the assignment of claims
From the name it becomes clear that the contract is concluded so that one party to the contract cedes its right of claim to another party.
By rights we mean receivables. So why do organizations resort to such measures? Let's take, for example, organizations conducting joint activities under a supply agreement, provision of services or provision of a loan. Sometimes, after some time of working together, the buyer, despite strict payment terms and penalties for delay specified in the contract, does not transfer money to the supplier.
The supplier decides to sell its receivables by concluding an assignment agreement with a third-party company. He can do this without notifying his debtor partner (Articles 382, 384, 385 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
When concluding an agreement for the assignment of the right of claim, the parties to the transaction are the following participants:
- seller (assignor);
- buyer (assignee).
The debtor, i.e., an organization that does not want to repay its creditor, is sent a letter indicating the details of the new creditor and the details of the assignment agreement on the basis of which the debt was transferred to it.
After signing the agreement, the assignor transfers all primary documents to the assignee. They will be confirmation of the purchased debt.
Such documents include:
- supply agreement (service or loan);
- delivery notes, acts, invoices, etc.;
- act of reconciliation between the assignor and the debtor.
After this, the parties to the transaction need to make the appropriate entries under the assignment agreement in accounting.
Civil aspects
The legal aspects of the assignment of a claim by the creditor (also called assignment) are regulated by the provisions of Art. Art. 382-390 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 382 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a right (claim) belonging to the creditor on the basis of an obligation may be transferred by him to another person, in particular, under a transaction (assignment of the claim). The assignment of a claim by a creditor (assignor) to another person (assignee) is permitted if it does not contradict the law (clause 1 of Article 388 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 382 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, in order to transfer the rights of a creditor to another person, the consent of the debtor is not required, unless otherwise provided by law or agreement. However, the debtor must be notified in writing of the transfer of the creditor's rights to another person. Moreover, notification to the debtor can be sent by both the original and the new creditor (clause 3 of Article 382, clause 1 of Article 385 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). According to paragraph 2 of Art.
The claim passes to the assignee at the moment of concluding the agreement on the basis of which the assignment is made, unless otherwise provided by law or agreement (clause 2 of Article 389.1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). By virtue of clause 3 of Art. 385 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the assignor is obliged to transfer to the assignee documents certifying the right (claim) and provide information relevant for the implementation of this right (claim).
The legislation does not establish mandatory requirements for the price under an assignment agreement; accordingly, the amount of payment for the assigned right of claim is determined by agreement of the parties (clause 1 of Article 424 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). See the Encyclopedia of Solutions for more details. The price of the assigned right (claim) under the assignment agreement.
In the situation under consideration, as a result of a transaction under an assignment agreement, the new creditor (organization “B”) must pay the original creditor (organization “A”) funds in an amount equal to the amount of the assigned debt. In this case, organization “A” is at the same time a debtor under the loan agreement in relation to organization “B”.
As a result of the transaction for the assignment of claims, organizations “A” and “B” have counter monetary claims. By virtue of the provisions of Art. 410 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the obligation is terminated in whole or in part by offsetting a counterclaim of the same type, the due date of which has come or the due date of which is not specified or determined by the moment of demand.
We suggest you read: How to include payment holidays in a rental agreement
For offset, a statement from one party is sufficient. At the same time, in order to recognize the offset as valid, it is necessary to have evidence of receipt of the application for offset of counterclaims by the second party (in the form of a mark on the application or in the form of a notification of delivery by mail) (clause 4 of the Information Letter of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated December 29, 2001 N 65, hereinafter referred to as Letter VAS No. 65).
As stated in paragraph 7 of Letter of the Supreme Arbitration Court No. 65, Art. 410 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation does not require that the requirement for offset arise from the same obligation or from obligations of the same type. Cases of offset of counter monetary claims based on different agreements are allowed.
Accounting for the assignment agreement with the assignor and payment
We will consider examples of transactions under an assignment agreement with the assignor below.
Example
LLC "Dream" sold hardware for 246,750 rubles, including VAT 20%, under a contract for the supply of goods to LLC "Lumiya". The purchase price of hardware is 153,550 rubles.
Mechta LLC signed an assignment agreement with Fialka LLC. The receivable amount is 228,690 rubles, including VAT 20% - 38,115 rubles. To ensure that the contract is drawn up correctly, Fialka LLC pays for a legal consultation of 1,500 rubles.
Accounting entries under the assignment agreement from the assignor.
| Postings | Sum | Operation |
| Dt 62 Kt 90.1 | 246 750 | Hardware sold |
| Dt 90.3 Kt 68.2 | 41 125 | VAT charged (246,750 × 20/120) |
| Dt 90.2 Kt 41 | 153 550 | Cost of hardware |
| Dt 90.9 Kt 99 | 52 075 | Profit received under the supply agreement (246,750 - 41,125 - 153,550) |
| Dt 76 Kt 91.1 | 228 690 | Selling debt |
| Dt 91.2 Kt 62 | 246 750 | Write off accounts receivable |
| Dt 99 Kt 91.9 | 18 060 | Received a loss on the assignment of receivables (246,750 - 228,690) |
Fialka LLC transfers 228,690 rubles to Mechta LLC under the agreement, including 20% VAT.
Payment under the assignment agreement - postings:
| Dt 51 Kt 76 | 228 690 | Payment received from Fialka LLC |
If the assignment of a debt occurs before the payment deadline stipulated by the contract, the loss received from the assignment for profit tax purposes is taken into account in a special manner (clause 1 of Article 279 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
What is not included in income
At the same time, income in the form of property received under credit or loan agreements, as well as property received to repay such borrowings, are included in the list of income not taken into account under the simplified tax system (clause 10, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) .
From everything that has been said, the Ministry of Finance draws a conclusion: the money received by the assignee on the “simplified tax” to pay off the debt under the agreement for the assignment of the right of claim is not taken into account in simplified taxation system income.
But the interest received for using the loan, fines and penalties for late payment of debt under the loan agreement, as well as legal costs for paying state duties increase the tax base for the “simplified” tax.
Let us note that in any case, when the borrower receives funds that exceed the price paid for the acquired right of claim, the difference between the amount received from the debtor and the amount paid to the assignor is included in the income of the assignee organization. This conclusion was made by financiers in their earlier letters dated July 9, 2012 No. 03-11-06/2/85 and dated November 2, 2011 No. 03-11-06/2/151.
Assignment agreement - postings to the assignee
Since the assignee did not purchase goods or services, but only bought the receivable, he will take it into account as a financial investment.
And in the process of its formation, he has the right to include in the costs both the amount of the purchased debt and related expenses. Such expenses include the services of intermediaries, as well as any costs incurred associated with the purchase of this asset (clauses 8, 9 of PBU 19/02, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 10, 2002 No. 126n). Continuation of the example
Assignment agreement - postings to the assignee:
What is included in income
Interest accrued in accordance with the terms of the loan agreement is included in the non-operating income of the “simplified person” on the date of receipt of funds from the borrower (clause 1 of Article 346.15, clause 6 of Article 250, clause 1 of Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the amount received from the debtor upon repayment of the loan exceeds the price paid by the assignee for the acquired right of claim, when determining the tax base, the difference between the amount received from the debtor and the amount paid to the assignor should also be included in the income (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 9, 2012 No. No. 03-11-06/2/85).
EXAMPLE.
HOW TO REFLECT IN ACCOUNTING THE PURCHASE OF THE RIGHT OF CLAIM UNDER AN ASSIGNMENT AGREEMENT Volna LLC, which uses the simplified tax system with the object “income minus expenses,” on March 31 acquired from Bereg LLC, under an assignment agreement, the right of claim under a loan agreement for 200,000 rubles.
The money was transferred on March 31. The loan amount under the agreement is 300,000 rubles. Interest is calculated and paid monthly on the last day of the month at a rate of 10% per annum. The loan repayment period is April 30. There is no debt to pay interest on the date of assignment of the right of claim. The right of claim under the loan agreement is reflected in accounting as a financial investment (clauses 2, 3 of PBU 19/02 “Accounting for financial investments”, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 10, 2002 No. 126n). A financial investment is accepted for accounting at its original cost (clauses 8, 9 of PBU 19/02). In this example, this is the amount paid for the acquired right of claim - 200,000 rubles. The amount of interest due to the organization - the new creditor under the loan agreement is recognized as other income of the organization (clause 7, 10.1, paragraph 2, clause 16 of PBU 9/99 “Income of the organization”, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 6, 1999 No. 32n, clause 34 PBU 19/02). In this example, the amount of interest on April 30 will be: 2465.76 rubles. (RUB 300,000 × 10%: 365 days × 30 days). On the date the debtor fulfills the obligation to repay the principal amount of the loan, the accountant will record the disposal of the financial investment (clause 25 of PBU 19/02). Receipts related to the sale financial investments are other income (clause 7, 16 PBU 9/99, clause 34 PBU 19/02). The accountant included the initial cost of the disposed financial investment as part of other expenses (clause 27 PBU 19/02, clause 11, 16, 19 PBU 10/99 “Expenses of the organization”, PBU 10/99, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 6, 1999 No. 33n).The accountant made the following entries: March 31 DEBIT 58 CREDIT 76
- 200,000 rubles.
– the right to claim under the assignment agreement has been acquired; DEBIT 76 CREDIT 51
- 200,000 rub.
– the right of claim has been paid to the seller. April 30 DEBIT 76 CREDIT 91-1
- 2465.76 rubles.
– interest accrued under the loan agreement; DEBIT 76 CREDIT 91-1
- 300,000 rubles.
– other income from the redemption of a financial investment is recognized; DEBIT 91-2 CREDIT 58
- 200,000 rub.
– the initial cost of the financial investment is written off; DEBIT 51 CREDIT 76
- 302,465.76 rubles. – funds were received from the debtor in order to repay the loan amount and interest for April. In tax accounting, Volna LLC recognizes non-operating income in the amount of the difference between the amount of the debt and the amount paid for the acquired right to claim the debt. The amount of income is 100,000 rubles. (300,000 – 200,000). Interest accrued in accordance with the terms of the loan agreement is also included in the non-operating income of the organization on the date of receipt of funds from the borrower.
Payment under the assignment agreement - postings to the debtor
After considering how accounting is carried out under an assignment agreement between the assignor and the assignee, let’s look at the debtor’s accounting.
How will the concluded agreement for the assignment of the right of claim affect its accounting? To begin with, remember that the debtor is only notified of the sale of his debt. He does not sign any documents related to the transfer of debt. In his accounting, only the analysis of his existing debt changes, i.e., the name of the creditor (recipient of the money).
Continuation of the example
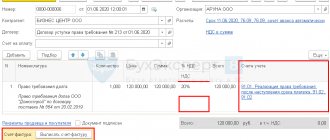
| Postings | Sum | Operation |
| Dt 41 Kt 60 | 246 750 | Supply of hardware from Mechta LLC |
| Dt 60 Kt 60 | 246 750 | According to the received written notification about the sale of debt, it is necessary to make adjustments to the analytics. Transfer debt from Mechta LLC to Fialka LLC |
| Dt 60 Kt 51 | 246 750 | The debt to Fialka LLC was repaid |
***
For some organizations, the sale of receivables is almost the only method of claiming their money for goods sold, services provided, or a loan issued. For example, if your buyer is behind on all payments, and you do not want to defend your rights in court and are at the same time prepared for some financial losses, then such agreements are what you need. For other organizations that are more confident in their own legal capabilities, concluding such agreements is one of the ways to increase their assets. But do not forget that the purchased debt may not be repaid, because no one can guarantee that the debtor will fulfill all of its obligations. And therefore this kind of investment is very risky.
Income received to repay the loan
It is interesting that the Ministry of Finance of Russia, in letters dated April 27, 2015 No. 03-11-11/24183, dated April 3, 2015 No. 03-11-11/18813, explains in detail why the money received to repay the debt under the agreement of assignment of the right of claim , the “simplified” assignee does not take into account in income.
Let us recall that an organization can sell the receivables of its buyer to another company, that is, assign the right to claim this debt. Such a concession is formalized by an assignment agreement (Article 382 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The original creditor who assigns the right to claim the debt to another company is called the assignor. And the company that buys the right of claim is the assignee.
In practice, a situation often occurs when the lender (creditor) cedes the right to claim money under a loan agreement to a new creditor. In this case, there is an assignment of the right to claim the debt under the loan agreement.
According to the rules of the Tax Code, “simplified” companies are required to determine the tax base in the same manner as for taxation of profits. That is, taking into account income from sales in accordance with Article 249 of the Tax Code and non-operating income in accordance with Article 250 of the Tax Code. Income listed in Article 251 of the Tax Code is not taken into account (Article 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Article 250 of the code, among other things, mentions income in the form of fines, penalties and other sanctions for violation of contractual obligations. It also talks about interest received under loan agreements, credit, bank deposits, securities and other debt obligations (clauses 3, 6 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Consequently, such income increases the tax base for the “simplified” tax.