Loans for employees: few taxes, many transactions
The material was prepared by specialists from ZAO Consulting Group Zerkalo under the leadership of General Director Pereletova I.V.
Published: “Economics and Life Question-Answer” magazine, 9
The organization has invested in the construction of a residential building and plans to provide loans to its employees to purchase apartments. How will this affect the calculation of personal income tax and other taxes? Should we reflect the issuance of a loan in some documents (for example, in a certificate of income of an individual)? Please explain with an example how to calculate the amount of interest and what transactions need to be made. (L. Onishchenko, Moscow region)
* An individual who has received a loan from an organization may receive “conditional income” in the form of material benefits. Material benefits arise from savings on interest if the amount of interest for the use of borrowed funds is less than ¾ of the refinancing rate established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of receipt of the loan, or 9% per annum when issuing a loan in foreign currency (Article 212 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The determination of the tax base when receiving income in the form of material benefits, expressed as savings on interest when receiving borrowed funds, is carried out by the taxpayer (Article 212 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). That is, the organization does not have the obligation to transfer personal income tax to the budget for material benefit. This is explained by the fact that if an individual is not an employee of an organization, then the organization cannot find funds to transfer taxes to the budget. An organization can withhold money from its employees' wages (upon their written request). The taxpayer within the time limits determined by sub. 3 p. 1 art. 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (that is, on the date of payment of interest on borrowed funds), but at least once during the tax period established by Art. 216 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (year), is obliged to calculate and pay personal income tax on the material benefits received from savings on interest.
Moreover, since the organization is still a tax agent in accordance with Art. 230 of the Code, she is obliged to submit the relevant information to the tax authority.
Note that the Methodological Recommendations on the procedure for applying Chapter 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (which were approved by Order of the Ministry of Taxes of the Russian Federation of November 29, 2000 No. BG-3-08/415, canceled this year) allowed the taxpayer to authorize the organization that issued the borrowed funds to participate in relations regarding the payment of personal income tax for material benefit as its authorized representative. In principle, despite the cancellation of the Methodological Recommendations, any person can appoint his authorized representative in tax legal relations on the basis of Art. 26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. An authorized representative of a taxpayer - an individual exercises his powers on the basis of a notarized power of attorney (Article 29 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If, in accordance with the established procedure, the lender organization is appointed as an authorized representative of the taxpayer in relations with the payment of personal income tax, then from the amount of material benefit such an authorized representative determines the tax base, and also calculates, withholds and transfers to the budget the amount of calculated and withheld personal income tax. The assessed tax amount is withheld from the taxpayer by the authorized representative from any funds paid to the taxpayer.
Taxation of material benefits is carried out at a rate of 35% (clause 2 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). When determining the amount of material benefit, the refinancing rate established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of receipt of borrowed funds is taken into account. The tax base is the difference between the amount of interest calculated based on ¾ of the refinancing rate and the interest actually paid under the loan agreement.
The benefit is reflected in the personal income tax forms-1 and personal income tax-2 according to income code 2610 and on the taxpayer’s personal card.
In this situation, an organization can withhold tax on material benefits when paying wages to an employee, while the withheld amount of personal income tax cannot exceed 50% of the payment amount (clause 4 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The amount of personal income tax withheld from wages is recorded in the debit of account 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages” and the credit of account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”.
* The material benefit received by an individual from saving on interest is not subject to Unified Social Tax (Clause 1, Article 236 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Regarding the issue of paying VAT on interest received from employees for using a loan, it can be said that, in accordance with subparagraph. 15 clause 3 art. 149, as well as sub. 1 item 2 art. 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the specified interest is not subject to VAT. Moreover, paragraph 28 of the Methodological Recommendations for the Application of Chapter 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (approved by Order of the Ministry of Taxes of the Russian Federation of December 20, 2000 No. BG-3-03/447) determines that fees for the provision of a loan of funds are not subject to VAT taxation, but the provision of services for the provision of loans in other forms are subject to VAT.
For profit tax purposes, interest received by an organization under a loan agreement is in accordance with clause 6 of Art. 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation with non-operating income. The procedure for recognizing such income using the accrual method is established by Art. 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, according to clause 6 of which, for loan agreements that are valid for more than one reporting period, for the purpose of calculating profit, income is recognized as received and is included in the corresponding income at the end of the corresponding reporting period.
Suppose an organization calculates monthly advance payments for income tax based on the actual profit received. Reporting periods for such organizations are one month, two months, three months, and so on until the end of the calendar year (clause 2 of article 285 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Consequently, non-operating income in the form of interest under a loan agreement is recognized for profit tax purposes on a monthly basis and there are no differences in the recognition of income in the form of interest under a loan agreement in accounting and tax accounting in this case.
* The algorithm for calculating the amount of interest (simple, without capitalization) due for a loan issued can be used as follows (set out in the Regulation of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated August 4, 2003 No. 236-P “On the procedure for the Bank of Russia to provide loans secured by collateral to credit organizations (blocking) securities"):
C% (or SCB%) =In x N
, Where:
C% - the amount of interest for the period from the date of loan repayment (or the last payment of part of the loan) to the date of repayment (or payment of the next part) of the loan;
SCB% - the amount of interest based on 3/4 of the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for the period from the date of loan repayment (or the last payment of part of the loan) to the date of repayment (or payment of the next part) of the loan (for calculating material benefits):
In - the amount of interest for 1 day in the calculation period (from one payment to another);
In (Central Bank) - the amount of interest for 1 day, based on 3/4 of the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation (for calculating material benefits):
N is the number of calendar days in the time period from the day following the day the loan was granted until the day the loan (part of the loan) is repaid, inclusive
In this case, In( or In (CB) = Ok x ik : Nk, where:
Ok — the balance of the loan debt at the beginning of the k-th day of using the loan;
Nk is the number of calendar days in the calendar year on which the k-th day of the time period falls from the day following the day the loan was issued until the expected day of loan repayment, inclusive (365/366);
ik is the interest rate on the loan at the beginning of the k-th day of the time period from the day following the day the loan was granted until the expected day of repayment of the loan (part of the loan), inclusive (in percent per annum);
ik(CB) - Interest rate on the loan, based on 3/4 of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
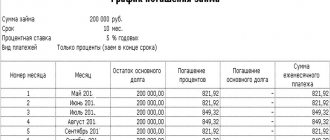
Example. The loan was issued to an employee of the organization on February 1, 2005 in the amount of 50,000 rubles. for 10 months (312 days) at 7% per annum. The principal is repaid in equal monthly installments along with interest.
We present the calculation of interest and material benefits when repaying a loan in installments (Table 1).
Table 1
| February | March | April | May | June | July | August | September | October | november | |
| Ok | 50 000,00 | 45 000,00 | 40 000,00 | 35 000,00 | 30 000,00 | 25 000,00 | 20 000,00 | 15 000,00 | 10 000,00 | 5 000,00 |
| N | 28 | 31 | 30 | 31 | 30 | 31 | 31 | 30 | 31 | 30 |
| In | 9,5628 | 8,6066 | 7,6503 | 6,6940 | 5,7377 | 4,7814 | 3,8251 | 2,8689 | 1,9126 | 0,9563 |
| Central Bank | 13,3197 | 11,9877 | 10,6557 | 9,3238 | 7,9918 | 6,6598 | 5,3279 | 3,9959 | 2,6639 | 1,3320 |
| WITH% | 267,76 | 266,80 | 229,51 | 207,51 | 172,13 | 148,22 | 118,58 | 86,07 | 59,29 | 28,69 |
| SCB% | 372,95 | 371,62 | 319,67 | 289,04 | 239,75 | 206,45 | 165,16 | 119,88 | 82,58 | 39,96 |
| MV | 105,19 | 104,82 | 90,16 | 81,52 | 67,62 | 58,23 | 46,58 | 33,81 | 23,29 | 11,27 |
| Personal income tax | 36,82 | 36,69 | 31,56 | 28,53 | 23,67 | 20,38 | 16,30 | 11,83 | 8,15 | 3,94 |
* To record settlements with employees of the organization for loans provided to them, the Chart of Accounts provides account 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations”, subaccount 73-1 “Settlements for loans provided”.
The amount of a loan provided to an employee of an organization in cash is reflected in the debit of account 73, subaccount 73-1, in correspondence with account 50 “Cash”.
Analytical accounting for account 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations” is maintained for each employee of the organization.
In accordance with clause 7 of PBU 9/99 “Income of the organization” (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 6, 1999 No. 32n), interest received for providing the organization’s funds for use is operating income. These incomes, in accordance with clause 16 of PBU 9/99, are recognized in accounting if the conditions specified in clause 12 of PBU 9/99 are met. In this case, for accounting purposes, interest is accrued for each expired reporting period in accordance with the terms of the agreement.
The amount of interest accrued under the loan agreement is reflected in accordance with the Chart of Accounts under the credit of account 91 “Other income and expenses”, subaccount 91-1 “Other income”, in correspondence with account 73, subaccount 73-1.
Table 2 shows the entries for recording the issuance and repayment of a loan by an employee (with the withholding of personal income tax on material benefits from wages) for the conditions of our example.
table 2
| No. pp. | Document date |
Features of obtaining loans at 0%
It is definitely not profitable for microfinance organizations to issue interest-free loans on an ongoing basis. Such promotions are carried out to expand the audience and attract new paying customers. This leads to a limitation - in one MFO, as a rule, you can only take out one loan at 0%. Of course, with some restrictions, which are quite noticeable when compared with conventional microloans.
To apply for a loan, you will need a standard set of documents for MFOs:
- passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation;
- mobile phone;
- Email.
The application procedure is no different from applying for a loan with an interest rate. The client fills out an interactive form, where he indicates:
- FULL NAME;
- passport registration information;
- date of birth;
- Family status;
- employment and income;
- place of residence;
- bank card details.
Loans without interest are displayed in your personal account along with regular ones, which makes navigation easier. Applications are processed in a standard mode, without priority. Considering that most microfinance services automate the process of processing the questionnaire, this does not affect the speed of rendering a verdict.
Amounts and terms
Loans at 0% are usually issued on terms less favorable to the client. The amount is limited to 10-15 thousand rubles, and the terms rarely exceed 21 days. The most common “size-term” pair is 10,000 rubles for 14 days.
The first loan without interest, as a rule, is aimed at mutual examination of the parties’ good faith.
Microfinance services check the solvency of a new client, and the borrowers themselves check the quality of the services provided.
Ways to receive money
Another limitation inherent to interest-free loans is the methods of obtaining credit funds. The loan is often transferred to a bank card , which is subject to a number of requirements :
- name card;
- Visa/MasterCard/World;
- supports automatic debiting of funds;
- supports automatic deposit of funds;
- belongs to the borrower.
In addition, payments can be made to Yandex.Money and Qiwi e-wallets. In some cases, payment in cash or by transfer in the Contact system is possible. Funds are credited instantly .
Taxation of material benefits
The MV amount is the tax base for personal income tax (Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The tax is calculated at a rate of 35% for residents and 30% for non-residents (clauses 2–3 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Thus, from the employee’s income, which the employer pays him monthly, the corresponding percentage of personal income tax from his MV from the BZ must be withheld. The amount of deduction cannot be more than 50% of income in cash, which is paid this month (clause 4 of article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the withholding amount exceeds the maximum, the balance is carried over to the next month. If it was not possible to withhold personal income tax during the tax period, the employer must inform both the tax office and the employee about this by sending them a 2-NDFL certificate. The employer pays the withheld personal income tax on the day of payment of income or the next (clause 6 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation); personal income tax cannot be paid in advance (clause 9 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Example 1 (continued)
The salary of resident V. A. Sokolov is 75 thousand rubles. per month. Salaries are paid twice a month: on the 15th and on the last day of the month. Thus, the transfer of personal income tax to the MV budget must occur no later than the specified dates in the following amounts:
04/03/2017 (since 04/01/2017 is a day off): 492 rubles. × 35% = 172 rub.
05/01/2017: 641 rub. × 35% = 224 rub.
06/01/2017: 182 rub. × 35% = 64 rub.
Conclusion
A loan for 30 days without interest is a convenient way to quickly receive money and hassle-free repayment in the same amount. There are no tricks or pitfalls in this service. However, the absence of overpayments comes with limitations: short loan term, small amounts, no debt payments in installments, and the ability to use the service only once.
However, comparing the advantages and disadvantages, there are more advantages in such promotions. Moreover, you can take out your first interest-free loan online in just 15-30 minutes. Loans repaid on time count toward your credit score, increasing it. Accordingly, in the future, the chances of receiving loans from the selected microfinance service on more favorable terms increase.
Interest-free loan for home purchase
Taxation of personal income tax for MV has exceptions specified in subsection. 1 clause 1 art. 212 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. One of them is that if the purpose of the BP is defined as the construction or acquisition of housing in our country, as well as land for its construction, then the MV for such BP is not recognized as income. In this case, the employee to whom such a work permit was issued must have the right to a property deduction. This deduction must be confirmed by a special notice issued by the tax authority, the form of which was approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated January 14, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected]
Thus, until the employee brings the specified notice, the accountant withholds personal income tax from him every month from the MV according to the BZ. After confirmation of the right to a property deduction, personal income tax is not accrued, however, the employer cannot return previously withheld personal income tax amounts, since they are not considered excessively withheld in accordance with clause 1 of Art. 231 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. You can return personal income tax amounts that were withheld before the notification was provided yourself at the tax office at your place of residence. Such clarifications are given in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 21, 2013 No. 03-04-06/8790.
Interest-free loan in kind: taxation
An employee’s knowledge book can be issued to the company’s goods, materials, fixed assets, etc. The things transferred must be defined by generic characteristics, that is, they cannot be unique with specific characteristics that only they have. A non-monetary loan can be repaid in money or the same things. The main qualities of the transferred items should be indicated in the contract (name, grade, quantity, size, etc.) so that the borrower returns the corresponding property.
When issuing this type of work permit, the employer must take into account some taxation nuances. As for income tax, the transfer of money or things as a loan is not considered an expense (clause 12 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and repayment of the loan is not considered income (clause 10 of Article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Cash loans are not subject to VAT (subclause 15, clause 3, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Under a non-monetary loan agreement, the employer's property becomes the property of the employee. In paragraph 1 of Art. 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the sale is equated to the transfer of ownership of things, and, according to subparagraph. 1 clause 1 art. 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the sale is called an object for VAT. Therefore, the transfer of things under the BZ agreement is subject to VAT. The price of the transferred property is determined as the current market price. When calculating such VAT, the employer has the right to deduct the corresponding input VAT that he paid when purchasing valuables transferred under the BZ.
Example 2
01/01/2016 V. A. Sokolov received ceramic tiles produced at the Voskhod LLC enterprise, where he works, as a BZ. The cost of the tiles was 135,000 rubles. without VAT. The loan term is 1 year. The employer must pay VAT to the budget in the amount of 135,000 rubles. × 18% = 24,300 rub.
Answer Profbukh8
Elena Kurakova Profbuh8.ru
Olga, you didn’t write what configuration you are working in
Olga Surikova
I have a main question regarding INTEREST-FREE LOANS RETURNED before 12/31/2015 for which I did not charge matt benefits and personal income tax and I want to correct everything now?
Yes, thank you, what document should I use to enter this into program 8.3 so that everything fits correctly?
Enterprise Accounting, edition 3.0 (3.0.43.213)
Interest-free loan in kind: accounting
The accounting value of the transferred assets may or may not correspond to their assessment in the business contract. If a difference exists, it will be reflected in other income or expenses. In accounting, transactions on business history are reflected as follows:
| Description | Dt | CT | Documentation |
| The book value of the property was written off when issuing a business license | 41 (01, 10…) | Transfer and acceptance certificate (invoice) | |
| Income is reflected if the contract value is higher than the book value | Transfer and acceptance certificate (invoice) | ||
| An expense is reflected if the contract price is lower than the book value | Transfer and acceptance certificate (invoice) | ||
| VAT is charged on the amount of the loan issued by the property | 68 subaccount “VAT” | Invoice | |
| Repayment of debt in kind with property or money | 41 (01, 10, 50, 51…) | Acceptance certificate (invoice), payment order, bank statement |
Example 2 (continued)
The book value of the tiles was 105,000 rubles. Let's assume that the refinancing rate did not change throughout the year and amounted to 9%. Then the personal income tax amount will be equal to: 35% × 2/3 × 9% × 159,300 = 3,345 rubles. The accountant recorded the following entries:
| Description | Dt | CT | Sum |
| The book value of the property was written off when issuing a business license | 105 000 | ||
| The excess of the contract value over the book value is reflected | 30 000 | ||
| VAT is charged on the amount of the loan issued by the property | 68 subaccount “VAT” | 24 300 | |
| BZ extinguished | 159 300 | ||
| Personal income tax withheld from MV according to BZ | 68 subaccount “NDFL” | 3 345 | |
| Personal income tax is transferred to the budget | 68 subaccount “NDFL” | 3 345 |
Advantages and disadvantages of loans
A promotional loan without interest on the card instantly - beneficial in cases where funds are needed urgently, but you don’t want to deal with overpayments. A significant drawback is that you can only get a loan at 0% once. Some microcredit services offer regular customers interest-free loans as an incentive, for example, for every third loan.
For clients
For newcomers to the lending industry, interest-free loans allow them to evaluate the performance of the service, the quality of the services provided and their own capabilities. Since this type of lending does not “punish” the client for the issued loan, this allows you to quickly receive money on the card , use it for its intended purpose and return it without overpayments.
Of course, the main advantage of a 0% loan is the speed at which funds arrive in your account. Considering that all you need is a passport, the ability to do everything online and receive an answer within half an hour is the most profitable method of lending.
For microfinance services
By issuing a loan at 0%, microcredit services attract new clients , who in the future will become permanent ones . As a rule, the next loan after the interest-free loan is issued with a pleasant bonus, for example, a reduced interest rate. Thus, the customer base expands and strengthens. After all, the client is more likely to return to the service that provided favorable conditions.