Postings for maternity payments
Maternity benefits are reimbursed by the Russian Social Insurance Fund . Therefore, reflect such payments on account 69 “Calculations for social insurance and security” (Instructions for the chart of accounts).
In accounting, the accrual and payment of maternity benefits is documented with the following entries:
Debit 69 subaccount “Settlements with the Social Insurance Fund for social insurance contributions” Credit 70 – maternity benefits accrued;
Debit 70 Credit 50 (51) – maternity benefits were issued to the employee.
Example:
Reflection of maternity benefits in accounting.
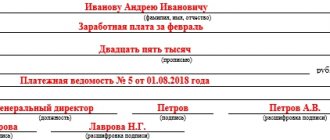
Secretary of Alfa CJSC E.V. Ivanova went on maternity leave from April 14 to August 31, 2011 inclusive.
The organization paid Ivanova maternity benefits in the amount of 107,956 rubles.
The accountant made the following entries in the accounting:
Debit 69 subaccount “Settlements with the Social Insurance Fund for social insurance contributions” Credit 70 - 107,956 rubles. – maternity benefits accrued;
Debit 70 Credit 50 – 107,956 rub. - benefits were issued from the cash register.
A collective or employment agreement may provide for payment of maternity leave based on the actual average earnings of the employee (Article 9 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
That is, the amount of benefits reimbursed from the Russian Social Insurance Fund is not in this case the upper limit of the amount of the payment. Such additional payments are not benefits; they are paid at the expense of the organization (Article 8 of the Law of May 19, 1995 No. 81-FZ, Art.
14 of the Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ). Therefore, they are reflected as follows:
Debit 20 (23, 25, 26, 44...) Credit 70 – an additional payment has been added to maternity benefits up to the actual average earnings;
Debit 70 Credit 50 (51) – an additional payment was issued to maternity benefits up to the actual average earnings.
Example:
Reflection in accounting of additional payments to maternity benefits up to actual average earnings.
Secretary of Alfa CJSC E.V.
Who pays maternity benefits, accounting entries of payments
Ivanova went on maternity leave from April 14 to August 31, 2011 inclusive.
The Alpha collective agreement provides for an additional payment to maternity benefits up to the actual average earnings.
The organization accrued to Ivanova during maternity leave:
- benefits at the expense of the Federal Social Insurance Fund of Russia in the amount of 159,179 rubles;
- additional payment at your own expense in the amount of 7002 rubles.
The accountant made the following entries in the accounting:
Debit 69 subaccount “Settlements with the Social Insurance Fund for social insurance contributions” Credit 70 – 159,179 rubles. – maternity benefits accrued;
Debit 26 Credit 70 – 7002 rub. – an additional payment to the benefit is calculated up to the actual average earnings.
How to calculate maternity benefits in accounting - monthly or in full on the day the employee brought in sick leave?
The full amount of the benefit must be accrued and reflected in accounting within 10 days after the employee brings the documents necessary to calculate the benefit. Such documents are an issued sick leave certificate and, if necessary, certificates of earnings from previous places of work for the last two years (Part 1 of Article 15, Part 5 of Article 13 of the Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ).
The benefit must be paid after it has been assigned as soon as possible established for the payment of wages (Part 1, Article 15 of the Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ).
However, if the influence of the FSS turned out to be insufficient, the subject has the right to file a corresponding application with the prosecutor’s office.
- In addition to filing a complaint with social security, it is also legal to go straight to court. If the judge rules in favor of the pregnant citizen, her maternity benefits will be forcibly recovered from the employer.
- Thus, entries for the payment of maternity benefits will depend on the source of funding for the specified payment. So, if funds are provided by social insurance, the accrual is recorded in the debit of account 69. However, if the source is the employer, the accrual will be made in the cost account that is used when recording wages in accounting. (13 votes, 4.90 out of 5) Loading...
Postings for maternity benefits in 2018
Reasons for refusal of reimbursement may include:
- the employee’s education does not correspond to the position she occupies, the subject lacks the required qualifications to perform specific duties;
- the employee’s salary is excessively high, based on her position and the duties she performs;
- entering the employee’s position into the staffing table shortly before she goes on maternity leave;
- a significant increase in a subordinate’s salary shortly before she goes on maternity leave;
- maternity benefits were provided to the woman at the moment when she actually performed her work duties.
Also, social insurance employees may be alarmed by the fact that a woman is hired shortly before she goes on maternity leave.
Maternity leave - payments and accounting entries
- 1 Accounting: additional payment before actual earnings
- 2 Accrual procedure
Regardless of what taxation system the organization uses, maternity benefits are fully reimbursed by the Federal Social Insurance Fund of Russia (Part 1, Article 3 of Law No. 255-FZ of December 29, 2006). The procedure for paying for the first three days of incapacity at the expense of the organization does not apply to maternity benefits.
Attention
Pay the benefit from the funds of the Federal Social Insurance Fund of Russia for all the days that the employee was on maternity leave. This follows from Part 1 of Article 3 of the Law of December 29, 2006.
No. 255- FZ. A collective and (or) employment agreement may provide for additional payments to maternity benefits up to the actual average earnings of the employee (Article 9 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). This amount is not a benefit (Article 8 of the Law of May 19, 1995 No. 81-FZ, Article 14 of the Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ).
Accounting, postings: accrual of maternity benefits, payment of maternity benefits
Important
On compulsory social insurance for temporary disability and in connection with maternity”, the calculation and provision of maternity benefits, benefits for employment and labor, as well as benefits for caring for the employee’s baby are carried out by the employer. However, the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation must subsequently reimburse the funds spent on the payments in question to the employer.
The general scheme of this procedure goes through the following stages:
- The employee provides the head of the enterprise with a certificate of incapacity for work on the basis of pregnancy. Then the woman draws up an application in the prescribed form with a request to provide her with leave and appropriate payments in connection with the birth of the baby and caring for him. In this situation, the subject is recommended to find out in advance who pays for maternity leave: the employer or the state, as well as when the benefits will be accrued.
How are maternity benefits calculated for pregnancy, childbirth and child care?
First, you need to decide whether your region is participating in the Pilot Project; if so, then no wiring will be required, and if not, then:
- When a woman goes on maternity leave, you are provided with a sick leave certificate, on the basis of which you calculate a lump sum maternity benefit in accordance with her salary for the last two years
- then you need to apply for benefits if she is registered in the early stages of pregnancy
- when she gives birth, she provides the next sick leave for which you accrue benefits for child care up to one and a half years and a lump sum at birth
The postings will be similar for all operations,
- Dt 69 Kt 70
- KT 70 Dt 50(51)
If a woman in labor has a complicated birth, she will be entitled to an additional payment to the lump sum maternity benefit. Rate the quality of the article.
Payments from the Social Insurance Fund
The main subsidies paid from the Social Insurance Fund are the following payments:
- temporary disability benefits, postings will be presented below;
- for pregnancy and childbirth;
- in connection with registration in the early stages of pregnancy;
- at the birth of a child;
- caring for a child up to one and a half years old;
- when adopting a child;
- caring for a sick child or other family member;
- additional days off to care for disabled children;
- upon receipt of a work injury;
- at burial.
In another article, we provided a detailed breakdown of the list of such payments and methods for calculating them.
Accounting for a budgetary institution
Dt 0.401.20.211, 0.109.60.211, 0.109.70.211 Kt 0.302.11.730 - disability benefits accrued, posting, at the expense of a budgetary institution.
Dt 0.303.02.830 Kt 0.302.13.730 - benefits (posting) from the Social Insurance Fund have been accrued.
Dt 0.302.11.830 (0.302.13.830) Kt 0.201.34.610 - issuance through the cash register.
Dt 0.302.11.830 (0.302.13.830) Kt 0.304.03.730 - withholding money for transfer to the employee’s account.
Dt 0.304.03.830 Kt 0.201.11.610 - transfer from the account of a budgetary institution of sick leave (and other payments) to the employee's account (use of interim account 304 is not mandatory).
Kt 18 (KOSGU) - accounting for the disposal of funds from accounting accounts.
Dt 0.201.11.510 Kt 0.303.02.730 - crediting of compensation funds from the Social Insurance Fund, according to paragraph.
Postings for maternity benefits
72, 132 Instructions 174n.
Dt 0.303.02.000 Kt 0.302.13.000 - funeral assistance has been accrued.
Dt 0.302.13.000 Kt 0.201.34.000 - funds were issued through the cash register.
Increase count. 18 on off-balance sheet (KOSGU 213) - withdrawal of funds from the cash desk of a budgetary institution.
Accounting for NPOs
The accrual of subsidies from the Social Insurance Fund to employees is reflected in the debit of the account. 69 “Calculations for social insurance” and credit account. 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages”. If the employee’s relatives receive assistance, then in the accounting this entry will look like this: Dt 69 Kt 76.
Temporary disability benefits have been accrued, posting: Dt 69 Kt 70.
Issue through the cash register - Dt 70 Kt 50.
Transfer via cash account - Dt 70 Kt 51.
Assistance paid to employees during pregnancy and childbirth is also reflected in Dt 69 and Kt 70.
Dt 51 Kt 69 - funds received - reimbursement of expenses from the Social Insurance Fund.
In the case when a lump sum funeral benefit is accrued and paid to an employee, the postings will be as follows:
- Dt 69 Kt 73 - accrual;
- Dt 69 Kt 76 - cases when a relative or other person receives help;
- Dt 69 Kt 76 - compensation for services of a specialized organization;
- Dt 73, 76 Kt 50, 51 - payment.
Source: //accountingsys.ru/provodki-po-dekretnym-vyplatam/
Postings for calculating a lump sum payment
The payment of all benefits is accounted for in account 70 - wages. The accountant will accrue benefits on the credit of account 70, and pay them on the debit. If wages are usually calculated from the organization’s sources, then benefits are paid from the Social Insurance Fund. All settlements with the Social Insurance Fund are carried out on account 69 “Settlements for social insurance”.
Thus, we will make the following entries:
- Debit account 69 – Credit account 70 - accrual of one-time benefit
Maternity payments are not subject to personal income tax. If the payment is from the cash register, then we will make the following entry:
- Debit account 70 – Credit account 50 “Cash”
If you transfer benefits to a bank card, we get:
- Debit account 70 – Credit account 51 “Current accounts”
Postings for maternity leave
Compare the calculated average earnings with the maximum possible value. If your result turns out to be greater, you must take exactly this amount to calculate benefits (clause 3.3 of Article 14 of Law No. 255-FZ).
Next, compare the amount with the established minimum. The minimum maternity benefit that a woman can count on is calculated based on the minimum wage. The minimum wage for 2021 is 7,500 rubles.
This means the minimum maternity benefit in 2021 is RUB 34,520.55.
Payroll accounting
As a rule, all employees have one deduction - personal income tax. Here, account 70 corresponds with account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”, posting: In postings for other deductions, the loan account changes, depending on where it goes.
For example, when withholding under a writ of execution in favor of a third party, account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” is used, posting: Insurance premiums are charged to the cost of production, i.e. To do this, take a maximum of 670,000 rubles. for 2015 and 718,000 rubles. for 2021.
In addition, in 2021, from July 1, the minimum wage has been increased to 7,800 rubles. This means that the minimum sick leave for pregnancy and childbirth from July 1 is greater.
1702 If you have employees who are going on maternity leave in 2021, then keep in mind that the calculation of maternity leave in 2021 is not the same as in the past.
Please note that the minimum and maximum amount of maternity payments in 2021 has changed.
Maternity leave: registration in 1C
To receive compensation, you need to submit to the Fund a statement of calculation from the enterprise containing information about the accrued amounts. The document “Application-calculation to the Social Insurance Fund” is entered on the basis of the document “Accrual on sick leave”.
4. Or you can choose to fill out automatically for all sick leave accruals by clicking the “Fill” button. After the “Application-settlement to the Social Insurance Fund” is completed, the Fund will become indebted to the enterprise.
Maternity benefits are provided to the employee at the expense of the Temporary Disability Fund, therefore it is not included in the total monthly taxable income in accordance with paragraph 4.3.1 of the Law (5). Also, it is not included in the wage fund, and therefore is not subject to contributions to social insurance funds according to instructions (6).
Accordingly, the amount of assistance is not included in the gross expenses of the enterprise. In form 1df, the amount of the benefit is reflected with income indicator 22 “Amount of state material and social assistance...”.
Maternity benefits: detailed procedure for calculating maternity benefits. Maternity payments are accrued for the period of maternity leave (standard period - 140 days).
The benefit is calculated on the basis of sick leave for pregnancy and childbirth. However, there are a number of important restrictions that apply to this benefit.
In particular, the amount of earnings that is taken into account when assigning benefits should not exceed the maximum amount subject to contributions for compulsory social insurance (in the part transferred to the Social Insurance Fund of Russia).
What documents are needed to apply for maternity benefits?
What are the features of maternity pay? How are maternity benefits calculated? What is the maximum and minimum period of maternity leave?
The result of the meeting is its written decision, which stipulates these points.
In accordance with this decision, all further entries are made to distribute net profit or cover losses (depending on the financial result of the company’s activities). First of all, it must be said that profits can be distributed only once and only based on the decision of the meeting.
Deposited salary, postings
Opposite the names of employees who have not received salaries, it is written “deposited”, and the amounts are recorded in the column “Intersettlement payments”.
The amount of unpaid wages deposited into the current account is considered unclaimed after the expiration of the statutory limitation period, which is three years.
After this period, the salary is transferred to the enterprise’s income under the heading “profit not related to core activities.” The deposited wages book is kept for 5 years, except in cases where the documents are used for legal cases.
Moreover, the beginning of storage is not considered the date the debt arose, but January 1 of the year following the year in which the accounts payable arose. From the accounting side of the organization, accounts payable arises; if necessary, deposit the employee’s salary.
Maternity benefits (maternity benefits)
The working bodies of the Fund provide financing to policyholders within 10 working days after receipt of the application-calculation (according to clause 8 of Procedure No. 26).
The amount of maternity benefits is credited from the Social Insurance Fund to a separate current account opened by the insured-employer in the bank exclusively for crediting insurance funds (in accordance with part two of Article 34 of the Social Insurance Law).
Benefits are paid to insured persons within the period immediately after the day of assignment of assistance, established for the payment of wages (see the page Salary payment deadlines). Maternity benefits are also provided to the unemployed.
Overpaid benefits to an employee: what to do?
The fact that the sheet is false must be indicated in the FSS decision to refuse compensation for benefits; inaccurate information about insurance coverage and salary from other employers.
You can find out about this only if you made a request to the branch of the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation at the location of the former employer, who issued a salary certificate for the previous 2 years and Appendix No. 1 to Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated January 24, 2011 No. 20n.
Account 70: settlements with personnel for wages
Mandatory withholding is income tax that must be remitted from the employee's income. The organization in this case is a tax agent.
On the day the salary is issued, 13% (30% for non-residents) is withheld from the amounts payable (except for certain types of benefits) and transferred to the budget.
Unreturned amounts of accountable funds (or if the employee did not submit an advance report) - D 70 K 71 Material damage caused by the employee - D 70 K 73.2 Amounts of previously issued loans - D 70 K 73.
1 The employee himself can ask in writing to withhold funds from his salary to pay off his obligations to the employer or to transfer funds to other organizations or individuals - D 70 K 76. Salaries of production employees were accrued in the amount of 789,000 rubles.
Calculation of maternity benefits for an employee who was on sick leave in the accounting year
Source: //urist-pomojet.com/provodki-na-dekretnye-75731/
Maternity payments - who pays, how to make accounting entries
— Business organization — Personnel — Who pays maternity benefits, accounting entries for payments
The question of who pays maternity benefits: the state or the employer is relevant not only for young mothers, but also for company accountants. Such transactions must be correctly reflected in the accounting accounts and also taken into account in a timely manner.
Grounds for calculating maternity benefits
The main task of the state is to provide its population with a decent standard of living and provide the necessary social and material support.
In addition, the birth of each specific child affects the improvement of the demographic situation of the country.
Due to the above reasons, the legislation of the Russian Federation regulates the provision of a woman during her pregnancy, as well as further care for a child up to 3 years.
Financial assistance can be assigned to a woman on the following grounds:
- the doctor records the presence of pregnancy in the early stages;
- upon the course of pregnancy and further childbirth;
- upon the birth of a child, the mother is provided with a benefit for the newborn;
- when taking parental leave for a child up to 1.5 years;
- compensation in the amount of 50 rubles. every month when taking leave to care for a child up to 3 years old.
Thus, a woman must be registered with a gynecologist leading her pregnancy, who issues a certificate of incapacity for work at the 30th week of pregnancy.
A sick leave certificate is issued for 140 days during a standard pregnancy (70 days before and 70 days after childbirth). Also, in case of complications, additional days may be added.
In case of multiple pregnancy, sick leave is issued already at 28 weeks, and its duration is 194 days.
The benefit can be assigned to the following categories of women:
- having official employment;
- private lawyers and notaries, as well as private ones in case of voluntary registration of an insurance agreement with the Social Insurance Fund;
- unemployed citizens, if they are registered with the employment center;
- full-time students;
- military women.
Who makes maternity payments?
In most cases, young parents do not ask themselves who pays maternity benefits. However, all entities receiving such payments are advised to be informed about the authority that makes the payments.
So, based on Federal Law No. 255 of December 29, 2006. “On compulsory social insurance for temporary disability and in connection with maternity”, the calculation and provision of maternity benefits, employment and labor benefits, as well as child care benefits for the employee are carried out by the employer. However, the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation must subsequently reimburse the funds spent on the payments in question to the employer.
The general scheme of this procedure goes through the following stages:
- The employee provides the head of the enterprise with a certificate of incapacity for work on the basis of pregnancy. Then the woman draws up an application in the prescribed form with a request to provide her with leave and appropriate payments in connection with the birth of the baby and caring for him. In this situation, the subject is recommended to find out in advance who pays for maternity leave: the employer or the state, as well as when the benefits will be accrued. This will avoid conflicts if the payment deadline is violated, and you will have to find out the culprit of the violation.
- Based on the documents provided, the manager calculates the required amounts of the estimated benefits required for accrual.
- The employee then receives the benefit by transferring funds to her bank account or by issuing funds from the cash register. In these conditions, it is also important to be informed about who pays maternity benefits: the state or the employer. This will allow you to quickly resolve the conflict if a smaller amount is discovered than the pregnant woman is legally entitled to.
- When submitting the corresponding report to the Social Insurance Fund, the manager indicates information about the pregnant employee, and also provides supporting documents (a statement from the subordinate, a sheet of her temporary disability) and a request for reimbursement of the amounts spent on maternity payments.
- The FSS analyzes the submitted papers and also verifies the authenticity of the papers. If there are no questions or complaints to the employer, financial compensation is provided.
Grounds for which the Social Insurance Fund will refuse to reimburse an employer for maternity benefits
Regarding who pays for maternity leave, the Social Insurance Fund can make reimbursements only after a thorough check of the documents provided. In particular, the authenticity of documents is checked, as well as the correctness of their execution. The literacy of the calculation of maternity sums is also of great importance.
Due to the discovery of errors in calculations, social insurance may not only recalculate the amount of reimbursed funds, but also refuse compensation altogether. Reasons for refusal of reimbursement may include:
- the employee’s education does not correspond to the position she occupies, the subject lacks the required qualifications to perform specific duties;
- the employee’s salary is excessively high, based on her position and the duties she performs;
- entering the employee’s position into the staffing table shortly before she goes on maternity leave;
- a significant increase in a subordinate’s salary shortly before she goes on maternity leave;
- maternity benefits were provided to the woman at the moment when she actually performed her work duties.
Also, social insurance employees may be alarmed by the fact that a woman is hired shortly before she goes on maternity leave. These circumstances look especially implausible if the woman has not worked before or there was a significant break in her work activity.
The procedure for reflecting maternity benefits (BiR) in accounting
The average duration of an employee’s temporary disability due to pregnancy and childbirth is 140 days. However, there are often cases when a woman continues to perform her work duties after the start of sick leave.
In such circumstances, benefits will be accrued only for those days when the woman was actually on leave under the BiR and was minding her personal affairs.
For working days, despite the sick leave, only wages will be accrued.
Due to the fact that the B&R benefit is reimbursed to the employer at the expense of social insurance funds, the posting for the accrual of funds looks like this: Dt 69 – Kt 70. Payment of benefits is reflected as follows: Dt 70 – Kt 50 (51).
However, answering the question of who pays for maternity benefits: the state or the employer, we can say that payment of benefits by the state directly to female employees can only be carried out under certain conditions.
In particular, for those structures that are participating companies in the “Direct Payments” social insurance project, the fact of the absence of a woman expecting a child will be obvious only from the working time sheet.
That is, such a payment under the accounting and accounting system is not reflected in accounting, since the benefit is transferred directly to the employee from the accounts of the Social Insurance Fund. However, the employer is responsible for the safety of all related documentation.
Additional payment to maternity benefits, expenses for this operation in conditions of difficult childbirth
Based on Instruction of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 01/97 dated April 23, 1997, women may be entitled to an additional period of leave in connection with labor and labor in the following situations:
- the birth was difficult or caused complications - an additional 16 days of rest;
- a woman gives birth to two or more children at one time - additional leave will be 54 days.
The maximum vacation period under the BiR will be 194 days. It is assumed that if the birth was difficult, and the woman carried two or more children, the additional days of rest do not add up.
To calculate payments for additional leave, the same principles are used as for the initial calculation of accruals.
However, it is necessary to issue additional days of rest as a continuation of the main sheet for temporary disability due to childbirth.
Otherwise, if the doctor has not indicated that the continuation of the vacation is in addition to the already assigned vacation, it is recommended to use the new calculation period to calculate the benefit. This will help avoid disputes with social insurance.
The considered additional payment for additional rest for a woman who has given birth will be reflected in the accounting accounts in the same way as the main operations on sick leave, in particular: Dt 69 - Kt 70 and Dt 70 - Kt 51.
The procedure for reflecting financial and economic benefits in accounting with the condition of additional payment before earnings at the expense of the employer
Often, the average salary of an employee used to calculate benefits is lower than her actual monthly earnings.
The manager has the right to provide for compensation of the difference between the benefit calculated according to the rules of social insurance, as well as the woman’s actual earnings, at the expense of the company. However, the right to such a procedure must be recorded in the text of the employment agreement with the subordinate.
In the absence of such a provision, the acceptance of such expenses for accounting in the context of profit taxation or for calculating the single tax on the simplified tax system is illegal.
The accounting entries for calculating maternity benefits at the expense of the company will depend on the adopted cost account of the enterprise. In particular:
- in a company engaged in the provision of services, the posting of the accounting allowance will be as follows: Dt 20 (23, 25, 26) – Kt 70;
- for trading companies, the calculation of benefits represents the following accounting procedure: Dt 44 – Kt 70;
- if the employee performed duties that were not directly related to the company’s field of activity, the posting could be as follows: Dt 91 – Kt 70.
Also, if the benefit is accrued from the employer, he must also calculate personal income tax from this amount and add insurance amounts to the amount of the surcharge.
Calculation of maternity benefits in 1C: Enterprise Accounting 8
Published 04/16/2019 00:24 Author: Administrator In this article I want to tell you how to reflect sick leave for pregnancy and childbirth (BiR) in the 1C: Enterprise Accounting program version 3.0. Using practical examples, we will look at how to calculate and analyze the movements of a given document according to accounting registers.
In this case, sick leave is fully paid at the expense of the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation. It must be remembered that such sick leave can only be paid if the period of 6 months from the end of maternity leave has not expired. The duration of maternity leave is 140 days (70 days before the expected birth and 70 days after). In case of complications, this period can be extended to 156 days, and in case of multiple pregnancy – up to 194 days.
Unlike sick leave for temporary disability, sick leave for BiR is always paid at 100%. Personal income tax and insurance contributions are not charged for this type of benefit.
The amount of the benefit depends on three components:
— duration of the maternity period;
— the size of a woman’s average earnings (average earnings include only payments for which contributions to the Social Insurance Fund were accrued);
— the number of days worked in the billing period.
To calculate average earnings, the employee’s income for the 2 years preceding the year in which the sick leave was issued is taken into account. If an employee worked for several employers, then she provides a certificate from her previous place of work. If the employee’s work experience is less than 6 months, then she receives benefits based on the minimum wage. Also, according to the minimum wage, the employee receives benefits
- if the average earnings for 2 years are less than the specified amount,
- if there was no income and there is no application to replace years in the billing period,
- if a woman worked in another organization and cannot confirm this fact with a certificate from the employer.
It is necessary to keep in mind that there are maximum values for the base for calculating insurance premiums, for example in 2021 - 755,000 rubles, in 2021 - 815,000 rubles.
Sick leave is calculated according to the BiR within 10 calendar days and issued on the day of payment of the next salary. The amount is not divided into parts, but is paid in one lump sum.
Maternity benefits are calculated and accrued in the 1C program: Accounting ed. 3.0 automatically if the information base does not contain organizations with more than 60 employees.
And so, let's give an example for clarity.
On April 4, 2021, the employee submitted sick leave for a period of 140 days to the accounting department. Work experience with this employer is 2 months, there is no certificate from the previous place of work.
1. Open the “Salaries and Personnel” menu - select the “All accruals” item
2. Add a new document using the “Create” button and select “Sick leave” from the drop-down list.
3. We fill out the document and see that our employee was automatically credited with the amount of 51,919 rubles. If you click on the link, you can find out the details of the calculation.
Since the employee did not provide a certificate of earnings from another employer for 2017-2018. and has been working at the current place of work for less than 6 months, the calculation is made according to the minimum wage. From January 1, 2019, the minimum wage was set at 11,280 rubles. We calculate the amount of sick leave for April 2021: 11280 * 24 months / 730 days = 370.85 370.85 * 27 days = 10012.95 rubles The benefit is calculated in the same way for the following months.
4. Calculation of average earnings is printed and attached to the sick leave certificate
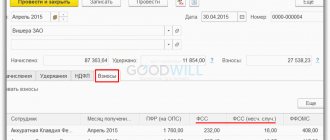
5. Using the Dt/Kt button, you can view the generated posting for the debit of account 69.01 and the credit of account 70.
Now let’s change the conditions of the example a little: let’s say an employee brought a certificate from her previous place of work. Her earnings for 2021 are 600,000 rubles. In 2021 – 0 rubles. We will display this information in the database.
Accordingly, the average daily earnings will now be 821.92 rubles, which is higher than the minimum wage (370.85 rubles). Let's make the calculation for April: 821.92 * 27 days = 22191.84 rubles. Subsequent months of maternity leave are calculated in the same way.
Thus, we looked at how to automatically calculate maternity benefits in the 1C: Accounting program ed. 3.0.
But if your organization employs more than 60 people, then automatic calculation is not provided. In this case, it is recommended to additionally use the 1C software product: Salary and HR Management. But, if for some reason salary calculation is carried out in 1C: Accounting, we will consider how to act in this situation. We will calculate the amount of the B&R benefit and calculate it using the document “Payroll for employees of organizations”.
We add an employee who needs to calculate the B&R allowance. Next, click on the “Accrue” button and select our accrual from the drop-down list.
A window appears in which we enter the already calculated benefit amount. After entering the amount, click OK.
Now you can see the amount of the accrued benefit, and use the amount link in the “Accrued” column to decipher and, if necessary, change the amount.
Now let's talk about reporting accruals for pregnancy and childbirth.
If the organization has less than 60 people and the benefit is calculated automatically, as in our first case with employee S.V. Larionova, then the data on it automatically falls into Section 3 of Appendix 1 to the Calculation of Insurance Premiums for the first half of 2021 (the benefit was accrued in April 2021 .)
Another situation, when there are more than 60 people in the database and the accounting allowance was manually accrued to employee Lifanova S.G., is not automatically reflected in this section; we need to fill out the document “Contribution Accounting Operation”.
Fill out this document -> Carry out
Now we again generate the report “Calculation of insurance premiums” for the half-year and see that the amounts for both maternity leave are included in Appendix 3 to Section 1 of this report.
Author of the article: Galina Kulinicheva
Did you like the article? Subscribe to the newsletter for new materials
Add a comment
Comments
0 Alina 05.15.2019 19:32 Thank you for the detailed article!!! Everything is sorted into shelves)))
Quote
Update list of comments
JComments