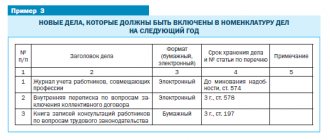
As a general rule, processed primary documents that relate to a specific accounting register (for example, cash, bank documents) are filed in separate folders in chronological order.
In practice, each accountant decides for himself how to store documents. This depends on the size of the enterprise, the types of activities, and the method of organizing accounting.
For example, many accountants file invoices issued to an enterprise for payment with payment documents, and applications for the issuance of money for business needs - with advance reports.
In a word, you can choose the method of storing primary materials that is most convenient for you. The main thing is that you can always quickly find the necessary document.
A special procedure is provided for invoices. You must store invoices received from suppliers and second copies of invoices issued to customers in special journals.
How long primary documents need to be stored is determined differently by different regulations. The Tax Code states that “accounting data and other documents necessary for the calculation and payment of taxes” must be stored for 4 years (Article 23). And documents confirming the amount of loss carried forward to the future in accordance with Article 283 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation must be kept for “the entire period while the organization reduces the tax base of the current tax period by the amounts of previously received losses.”
The Russian Ministry of Finance has a different point of view. In letter No. 04-01-10 dated February 9, 1999, officials of this department “clarified” that there is no contradiction here. We are simply talking about different documents: some are necessary for accounting purposes, others for tax purposes. But again, not a word about how to divide primary documents into accounting and tax documents.
Therefore, if in doubt, keep your primary accounting and tax documents for 5 years to avoid misunderstandings.
We should not forget that in addition to the Law “On Accounting” and the Tax Code, archival legislation regulates the storage periods for documents. Thus, the List of standard management archival documents generated in the activities of organizations, indicating storage periods (approved by order of the Federal Archive of December 20, 2021 No. 236) describes in detail which papers need to be stored for how long.
For primary accounting documents, this list also establishes a five-year retention period. But the list of documents on personnel records requires the following:
- vacation schedule for three years;
- documents on disciplinary sanctions within three years;
- documents on vacations and business trips - 5 years. And if employees are engaged in harmful and dangerous work, then 50/75 years. This means that if documents were created since 2003, then the minimum period for their storage in the organization is 50 years. If a document was created before 2003, then it is stored for at least 75 years.
How long to keep accounting documents
Primary documents and reports are stored for the periods specified in the archiving rules, but not less than five years after the reporting year. And keep the accounting policies for five years after the year in which they were last used for financial statements (Article 29 of the Accounting Law No. 402-FZ).
The procedure for storing accounting documents - why store documents?
The procedure for storing documents is regulated by the following main documents:
- Federal Law of October 22, 2004 No. 125-FZ “On Archival Affairs in the Russian Federation”;
- the basic rules for the work of the organization’s archives - approved by the decision of the Federal Archive of 02/06/2002 (hereinafter referred to as the Basic Rules);
- a list of standard management archival documents generated in the course of the activities of state bodies, local governments and organizations, indicating storage periods, approved by Order of the Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation of August 25, 2010 N 558;
- the current Regulations on documents and document flow in accounting, approved by order of the USSR Ministry of Finance dated July 29, 1983 No. 105.
The obligation to store documents generated in the activities of open and closed joint-stock companies is established by the Regulations on the procedure and periods for storing documents of joint-stock companies, approved by Resolution of the Federal Commission for the Securities Market dated July 16, 2003 N 03-33/ps. Limited liability companies are accordingly guided by the Federal Law “On Limited Liability Companies” dated 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ.
The procedure for storing accounting documents is defined in the Federal Law of November 21, 1996 N 129-FZ “On Accounting”, as well as in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Article 17 of the Federal Law of November 21, 1996 N 129-FZ “On Accounting” states that organizations are required to store accounting documentation (primary accounting documents on the basis of which the company maintains accounting records, accounting registers, financial statements) for terms established in accordance with the rules for organizing state archival affairs, but the minimum storage period cannot be less than five years.
A similar requirement is established in clause 98 of the Regulations on maintaining accounting and financial statements in the Russian Federation, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 N 34n.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation obliges taxpayers to ensure the safety of accounting and tax accounting data and other documents necessary for the calculation and payment of taxes for four years. This also applies to documents confirming the receipt of income, the incurrence of expenses, as well as the payment (withholding) of taxes. Individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system must comply with this rule, unless other deadlines are provided for by law.
Particular attention should be paid to the List of standard management archival documents
, formed in the course of the activities of state bodies, local governments and organizations, indicating storage periods, approved by Order of the Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation of August 25, 2010 N 558 (hereinafter referred to as the List).
This list includes standard management archival documents generated in the course of the activities of state bodies, local governments and organizations in the implementation of the same type (common to all or the majority) management functions, regardless of the form of ownership, indicating storage periods. The list contains documents grouped into sections, compiled when registering the facts of the economic life of organizations and Instructions for its use. Among the sections highlighted in the List, in particular, there is section 4 “Accounting and reporting”, containing subsections 4.1. “Accounting and reporting” and 4.2. "Statistical accounting and reporting."
To automatically determine the storage periods for accounting documents, we recommend using the free service “Archivist Online”
, which searches for documents according to three main lists, including the List of standard management archival documents approved by the Order of the Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation dated August 25, 2010.
It should also be noted that in accordance with Article 5 of the Federal Law of October 22, 2004 No. 125-FZ “On Archival Affairs in the Russian Federation,” archival documents include all documents, regardless of the type of their medium. This means document storage applies to both paper and electronic documents.
Please note that on January 1, 2013, the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting” comes into force, Article 29 of which states that Primary accounting documents, accounting registers, accounting (financial) statements are subject to storage an economic entity within the period established in accordance with the Rules for the organization of state archival affairs, but not less than five years after the reporting year. This brings into compliance the previously existing norms of tax and accounting legislation.
Documents of accounting policies, standards of an economic entity, other documents related to the organization and maintenance of accounting, including tools that ensure the reproduction of electronic documents, as well as verification of the authenticity of an electronic signature, are subject to storage by an economic entity for at least five years after the year in which they used to prepare accounting (financial) statements for the last time.
The procedure for destroying documents is regulated by:
- Federal Law of 02/08/1998 N 14-FZ “On Limited Liability Companies” (Article 50); Federal Law of November 21, 1996 N 129-FZ “On Accounting” (Article 17); Federal Law of October 22, 2004 N 125-FZ “On Archival Affairs in the Russian Federation”;
- List of standard management documents generated in the activities of organizations, indicating storage periods, approved by the Federal Archive on October 6, 2000 (hereinafter referred to as the List of standard documents);
- Basic rules for the work of archives of organizations (approved by the Decision of the Board of Rosarkhiv dated 02/06/2002).
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The procedure for destroying documents is as follows:
First of all, it is necessary to carry out an examination of documents and identify documents of permanent, temporary storage and documents that are not subject to storage (i.e. those that must be destroyed). Based on the results of the examination of the value of documents in the organization, inventories of permanent, temporary (over 10 years) storage and personnel records are drawn up, as well as acts on the allocation for destruction of files that are not subject to storage (clause 2.4.1 of the Basic Rules for the Operation of Archives of Organizations). Folders with documents (cases) that are subject to destruction are transferred for processing (disposal). The transfer of cases is formalized by an invoice, in which it is necessary to indicate the date of transfer of documents, the number of cases to be handed over and the weight of the waste paper. Loading and removal for disposal are carried out under the supervision of an employee responsible for ensuring the safety of documents in the organization. This procedure is provided for in clause 2.4.7 of the Basic Rules for the Operation of Organizational Archives. Ultimately, the expert commission must fix the correct procedure for destroying documents.
Responsibility for improper storage of accounting documents
First of all, the manager is responsible for organizing the storage of the organization’s documents, including primary accounting documents. The chief accountant of the institution is also responsible for the safety of primary accounting documents, accounting registers and financial statements.
Documentation may be lost as a result of natural disasters or illegal actions of third parties. If documents are lost as a result of someone’s unlawful actions (for example, theft), then this fact must be confirmed by law enforcement agencies. Loss of documents as a result of natural disasters is also documented by the relevant authorities. In the event of a fire, this may be a certificate from the fire inspection authorities.
In case of loss of primary accounting documents, the head of the organization, in accordance with clause 6.8 of the Regulations on Documents and Document Flow, appoints by order a commission to investigate the causes of the loss.
The absence of primary documents justifying the completion of any business transaction, in accordance with Art. 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation refers to gross violations of the rules for accounting for income and expenses, which means:
- lack of primary documents, or invoices, or accounting registers;
- systematic (twice or more times during a calendar year) untimely or incorrect reflection in the accounting accounts and in the reporting of business transactions of funds, tangible assets, intangible assets and financial investments of the taxpayer.
For violation of the procedure and terms of storage of accounting documents, administrative liability is provided - a fine for officials will range from 2,000 rubles. up to 3000 rub. (Article 15.11 of the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses). The absence of primary documents, invoices, and accounting registers is a tax offense. Responsibility for it is provided for in Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The minimum fine under this article is 5,000 rubles. The chief accountant is responsible for the safety of documents. It is he who has the right to make a decision on issuing such documents to employees of structural divisions of the enterprise.
As for liability for failure to comply with the rules for storing accounting documents, it can be both administrative and tax. As mentioned above, the absence of primary documents and accounting registers is a gross violation of the rules for accounting for income, expenses, and taxable items and entails a fine of 5,000 to 15,000 rubles. (Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
An administrative fine in this case can be imposed both for violation of archival requirements for storing documents (Article 13.20 of the Administrative Code - 300-500 rubles), and for a gross violation of accounting rules if, due to the lack of documents, the accounting statements are distorted (Article 15.11 of the Administrative Code - 2000-3000 rub.).
Destruction of documents without observing their retention periods is illegal
and entails administrative liability. In accordance with Art. 13.20 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation establishes administrative sanctions for violation of the rules of storage, acquisition, accounting or use of documents in the form of a warning or the imposition of an administrative fine.
Where to store
The enterprise must store all accounting documentation in a specially designated place, an archive. A small room without windows is usually allocated for it, which is filled with shelving and closed cabinets. If the room has windows, they are covered with curtains or blinds so that street light does not penetrate into the room. If the archive is located on the ground floor, in order to protect important papers from theft, metal bars are installed on the windows.
Strict reporting forms are usually stored in safes or locked rooms. The archive must be managed by a separate employee who is responsible for the safety of all papers.
As a rule, the head of the company is personally responsible for the safety and security of accounting documentation. It is he who will be asked by representatives of regulatory government bodies in case of loss of documentation or its absence. In this case, the economic entity bears personal responsibility. In Art. 23 of the current Tax Code states that the responsibility for maintaining reports lies with the taxpayer himself, whether he is an individual or a commercial organization.
Destruction of documents based on their shelf life
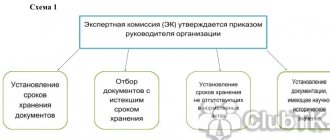
In accordance with clause 1.1 of the Model Regulations on the permanent expert commission of an institution, organization, enterprise, approved by Order of the Federal Archive of January 19, 1995 No. 2 for examining the value of documents created in the process of the organization’s activities, selecting and preparing them for transfer to state storage In the archives, the organization creates a permanent expert commission.
It includes the most qualified specialists from all existing structural divisions of the company who can assess the value of certain types of documents. The composition of the expert commission is approved by the head of the organization. It is the expert commission in the organization that deals with the selection of documents for permanent and temporary storage, and it also makes decisions on the destruction of documents whose storage periods have expired.
This expert commission conducts an examination of the value of documents at the stage of preparing them for archival storage and selects documents of the organization for further storage and destruction. Accordingly, the liquidation commission must create an expert commission and conduct an examination of all existing documents of the organization.
Based on the results of the examination of documents by the liquidation commission, a procedure for destroying documents whose storage period has expired should be organized. The principles of physical destruction of documents are established in clause 9.9. National standard of the Russian Federation “System of standards for information, library and publishing. Document management. General requirements. GOST R ISO 15489-1-2007”, approved by Order of Rostekhregulirovanie dated March 12, 2007 N 28-Art.
According to the Federal Law of October 22, 2004 N 125-FZ “On Archival Affairs in the Russian Federation”, during the liquidation of non-governmental organizations, archival documents, documents on personnel, as well as archival documents formed in the process of their activities and included in the Archive Fund of the Russian Federation, are included in the Archive Fund of the Russian Federation, terms whose temporary storage has not expired are transferred by the liquidation commission in an orderly state for storage to the appropriate state or municipal archive on the basis of an agreement between the liquidation commission and the state or municipal archive. At the same time, the liquidation commission organizes the organization of archival documents of the liquidated organization.
Consequently, if the storage period for documents has not expired, the liquidation commission must organize their ordering and transfer to the state or municipal archive under the appropriate agreement.
If the organization is not the source of acquisition of state and municipal archives, then the destruction of documents is carried out without coordination with the archival authorities.
In organizations that do not transfer documents to the state archive, documents subject to destruction are determined only after drawing up annual sections of inventories of permanent storage cases, and for personnel - only after approval by the head of the organization.
The destruction of documents with expired storage periods must be documented in an act prepared by an expert commission and approved by the head of the organization. There is no unified form for such an act, so the organization must develop its own form (the act must contain all the details considered mandatory by Law N 129-FZ) and consolidate its use in the company’s accounting policies. We remind you once again that the independently developed form of the act must contain all the details classified as mandatory by Law No. 129-FZ.
Documents are destroyed only if an inventory is carried out for the specified period. If the period covered by the documents is not reviewed, they cannot be destroyed. The beginning of the document storage period is considered to be January 1 of the year following the year in which they were compiled (or accepted for accounting). For example, the calculation of the storage period for files compiled in 2010 begins on January 1, 2011.
Read about the main types of accounting documents and the storage periods applicable to them in the article “Main types and storage periods of accounting documents”
.
It should also be noted that regardless of whether the organization is the source of acquisition of state archives or not, the allocation of cases for destruction
can be carried out by a specialized (archival) company. This approach allows:
- minimize the risk of erroneous (illegal) selection of documents for destruction or delegate it to a third party;
- reduce non-core workload on the accountant;
- significantly increase the efficiency of identifying cases for destruction;
- prepare an act on the allocation of cases for destruction in strict accordance with the legislation.