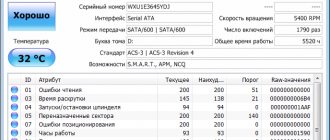
Storage of cargo in a warehouse must be systematic and well-organized. Warehousing implies their correct location inside the storage facility, compliance with regulations for their care and rules for proximity to other cargo, as well as ensuring their safety without loss of quality. Storing goods in warehouses always meets certain requirements, which include search marking of goods, the method of their placement depending on the dimensions of the packaging and the frequency of delivery of containers, the necessary climatic conditions and the possibility of combining goods with each other. For warehousing goods delivered by road transport companies, approximately the same rules apply for storing goods that you need to know about.
Existing placement methods
When a choice is made in favor of one or another product packaging system, you should first of all take into account the dimensions and packaging of the product. Although some additional parameters may also be taken into account. If we talk about the most common warehouses belonging to retail stores, the following placement methods are most often used here. They are:
- bulk;
- stackable;
- shelving;
- specific;
- suspended.
Non-standard methods are usually associated with the fact that products with non-standard dimensions have to be laid. In some cases, it is necessary to use ropes, rolled metal, car tires, etc. But in most cases, goods are placed in warehouses using the racking and stacking method. When choosing a suitable cargo placement option, the following factors are taken into account:
- Name of product. Products that belong to different product groups are stored separately from each other.
- Characteristics by weight and dimensions.
- The level of demand for certain products. It is illogical to store popular goods in hard-to-reach areas and at great distances.
- The need to organize batch placement of certain goods.
- Fire danger level.
For each case, the installation method and record keeping are selected taking into account individual characteristics and characteristics. We can safely say that it is absolutely impossible to place products in a warehouse without any system and order. It is required to use an efficient and clear unified warehousing and storage system. Most often, several basic methods of grouping stored products are used. They depend on a specific sign or characteristic.
- View. All products are sorted by type or type. The logic here is elementary and extremely simple. Cheese products are stored together with cheese products, sausage products are placed next to each other exclusively with sausages, etc.
- The consignment. Lots arriving at the warehouse are stored separately from each other. At the same time, the presence of identical or different products in one batch is not excluded.
- Parties and types. It also provides for the placement of each batch separately. But in addition, within a specific batch there is a division into types, varieties and types of products.
- Name. For sorting, product names and articles are taken into account. This method is most relevant in situations where the bulk of the cargo is of the same type or similar to each other.
Which method to choose depends on the specific individual situation.
Dividing the warehouse into zones
To properly organize the work of a warehouse, it is necessary to divide it into appropriate zones. Areas for long-term and short-term storage of goods are of primary importance. Most often, the area where short-term storage is provided is located near the goods loading area. The products that are in the highest demand are located there. Since high demand is associated with high turnover, it is in this area that you will most often need to look in order to take the next batch of products for sale. Experts recommend placing the heaviest goods in close proximity to the entrance. This will be especially relevant in situations where the warehouse is used for retail or small wholesale. Here, products are usually sorted depending on their dimensional characteristics.
If there are items and goods that are similar in functionality in the warehouse, they should also be located closer to each other. The same should be done with products that belong to the same category or type. Areas for temporary and permanent storage must be separated. Permanent storage areas are used for a group of goods, the list of which is determined in advance. Everything can be placed in the temporary storage area. Pay attention to storing valuables. They should be located near the guard or under the view of a surveillance camera. Zoning allows you to determine how different cargo should be located in warehouses and storage areas. If they are placed in accordance with a certain logic and scheme, accounting and turnover becomes much easier. Therefore, zoning is the first place to start working on organizing a warehouse.
Stacking
This is one of the options for how various cargo should and can be located in warehouses and storage facilities. When stacked storage, goods are placed in several rows. In this case, no special equipment is used for this. This method is relevant for storing homogeneous products, which are packaged in cardboard boxes, placed on pallets, bags, barrels, boxes and other types of containers. Stacking has several major disadvantages. Namely:
- minimal financial costs;
- ease of accounting;
- simplified inventory;
- a way to make the most of warehouse height.
But along with the advantages, there are also some objective disadvantages. Experts consider the main disadvantages:
- the range of goods placed in this way is limited;
- it is problematic to use equipment for loading and unloading operations;
- It is sometimes impossible to get products from the depths;
- if the warehouse is high, the space is used inefficiently;
- There are difficulties with depreciation of the warehouse.
When organizing the work of a warehouse, it should be taken into account that there are 4 main ways to implement stacking.
- Direct placement. Each product package is placed in a new row in the same direction as the previous one. The direct method is often used in situations where boxes are stored
- Cross. Boxes located in the top row are laid perpendicular to their placement in the bottom row. This is relevant when the product is the same, but the packaging dimensions are different.
- The opposite. This placement provides that the direction of each new row of load will be opposite to the previous one. Suitable for stacking bags to increase stability.
- Pyramidal. This is a variation of all the previously mentioned methods. As the rows increase, each new one has a smaller area. This significantly increases the stability of the stack.
The stacking method is mainly suitable for warehouses with a small area intended for the operation of retail stores and outlets. And also for large warehouse areas that are not fully occupied.
Stacking rules
It is important to understand that when using the stacking method of cargo placement, nothing will hold or support it. That is, the stability and appropriate level of reliability of each stacked row should be ensured. To achieve the desired stability and safety, you need to adhere to the basic rules. This will ensure safety and will not harm the quality of the products stored in the warehouse.
- Stacking of goods should not create obstacles for the movement of people and the passage of special equipment performing loading and unloading operations. Therefore, there is a standardized passage size of 1.5 meters.
- When calculating the maximum row height, the strength of the packaging used for the product is taken into account. Or the emphasis is on the strength of the product, which will be at the very bottom under the influence of maximum load.
- Under no circumstances should goods be stacked if the packaging is damaged. This will lead to its damage and may also reduce the stability of the entire stack structure.
- When stacking, the use of slippery packaging is not allowed.
- To increase the strength of the structure, it is recommended to use wood spacers between tiers.
- Ventilation efficiency will be reduced between tiers. Because of this, the stack height must be taken into account based on the characteristics of the product. The same bags of sugar can be stacked in several tiers, but the total height of the stack should not exceed 2 meters.
- If barrels are stacked, in a horizontal arrangement you cannot make more than 3 rows. If the rows are vertical, then no more than 2.
- Tanks with flammable materials are stacked strictly in one row. In this case, the plug must be on top.
- A distance of at least 50 centimeters should be left between the wall and the stack. If there are heating devices near the wall, then the minimum distance increases to 150 cm.
By adhering to these rules, the goods will be stored reliably, nothing will spoil prematurely, and employees will not have to worry about accidental collapses of stacks.
26.05.21
Today we will step back from the fundamental analytical mood. Summer, after all, is just around the corner. We invite you to talk about our fun audit life, namely about fake-ups, epic fails, and simply anti-results that can result from an audit assignment. Naturally, we not only groan and shock the public, but also offer real steps to reduce the consequences when negative results are achieved. Let’s call it this: TOP-7 audit failures and how to get out of them with the least losses.
Shelving
There are special placement rules regarding racking of goods in a warehouse. This method requires the presence of special structures in the form of shelves. Their acquisition and installation is precisely the main disadvantage of the racking method. Plus, you will need special equipment and devices that allow you to carry out loading and unloading operations and other operations on the highest racks. Placing products on low shelves is most convenient for small-sized goods that are processed manually. If you need to place cargo on pallets, then use racks with many levels and high heights. Some modern warehouses are equipped with mechanized structures, which make it possible to automatically move cargo along the shelves with minimal time and effort for workers. Special mechanisms built into the racks are responsible for this. But this is the prerogative of large enterprises. Compared with stacking, the rack has a number of objective advantages:
- high level of safety during warehouse procedures;
- the ability to automate accounting and organize an address storage method;
- sustainable formation of units of goods in the warehouse;
- large height of racks, which is limited only by the height of the ceiling in the warehouse, the strength of the structures and the capabilities of loading and unloading equipment;
- maximum efficient use of space;
- easy access to any product.
Shelving is objectively considered the most effective and useful form of goods storage. But not everyone can fully switch to rack storage due to the need for large financial costs.
Rules for laying on racks
Although racks are characterized by increased stability, and are noticeably superior in this indicator to the stacking method, there are still some rules and nuances when stacking goods. Basically, the rules are aimed at making access to cargo as safe and convenient as possible.
- If the goods are homogeneous, it is advantageous to stack them on both sides of one aisle between the racks in the warehouse.
- The upper tiers are best used for goods with a long shelf life. Also suitable for goods placed in large containers.
- The most preferable filling is considered to be vertical, sequential as you move along the aisles between the racks.
- The lower tiers of warehouse racks are used for stacking goods with manual picking.
- All products must be stacked so that their markings are directed towards the aisle.
- The weight of the cargo placed on the rack must be monitored. Each design has a limited load capacity, specified in the product data sheet.
With regard to the rack storage method in warehouses, some additional rules and recommendations may apply.
Who can store the goods?
An official document that reflects all the important nuances of providing a safekeeping service is considered to be a contract for the provision of such a service. According to this agreement, the executor-custodian is a non-profit or commercial organization (Article 886 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The bailor can be an individual individual or a legal entity (company) that deposits its own or someone else’s cargo for safekeeping (in the latter case, if there are documents confirming its authority to do so).
Address storage
There is also warehouse address storage, which has its own rules for placing various goods in the warehouse. Address styling is divided into 2 main categories or 2 methods.
- Dynamic method of address stacking. This provides for placement of products in an arbitrary cell. After stacking, the warehouseman simply enters this cell into the database for subsequent quick search for targeted cargo.
- Static method. Here, each addressable product has a pre-selected cell or rack with a constant number that does not change.
The static method is attractive because it allows you to concentrate the storage of a certain group of goods and products in a strictly designated place or zone. This will make it much easier to gain access and organize loading and unloading operations within the framework of order fulfillment. If we talk about the dynamic method, then the advantage here is the minimum time spent on placement. The dynamic stacking method makes it possible to make maximum use of the available warehouse space. When organizing a warehouse, all zones, racks and cells must receive special markings. It is important to use large symbols and clear labels. This will allow the storekeeper to find the right product with minimal time. Such a system for organizing product storage in a warehouse saves time and allows you to fully organize the entire process.
Structure
2.1. The structure and staffing level of the finished products warehouse is approved by [name of the position of the head of the enterprise], based on the specific conditions and characteristics of the enterprise’s activities, upon the proposal of the head of the sales department and in agreement with the [HR department, organization and remuneration department].
2.2. The finished products warehouse includes structural units formed on the principle of storing individual product groups.
2.3. The distribution of responsibilities between warehouse employees is carried out by the manager of the finished products warehouse.
2.4. [Enter as appropriate].
Alternative styling methods
The placement of goods is not limited only to the stacking and racking method of laying products. There are a number of alternative methods, which, although not so common, in some cases and in specialized warehouses turn out to be indispensable.
- If a warehouse is used to store meat or clothing, then it is rational to use special hangers. Many modern warehouses of this type are equipped with mechanized hanging systems. The electric drive ensures carousel movement of all goods.
- For large quantities of fruits and vegetables, the standard bulk storage method is often used. Thus, the load on the lower levels is minimal, and the products do not deteriorate due to compression under the influence of their own weight. Moreover, there are no special rules regarding the laying of bulks.
- Liquid cargo is stowed using metal and plastic tanks. They are usually located along the walls so as not to block passages or interfere with the passage of loading and unloading equipment.
The choice of a specific method of warehousing and stacking directly depends on the specifics of a particular product. The financial capacity of the warehouse owner and the need for its mechanization and automation are also taken into account. Despite all the variety of storage methods, the racking method is considered the most effective. It allows you to automate all processes, set up an electronic database and simplify the accounting of goods.
General provisions
1.1. The finished products warehouse is a structural unit of the sales department, is created within it and is liquidated by order of [name of the position of the head of the enterprise] in agreement with the head of the sales department.
1.2. The finished products warehouse is headed by a manager, appointed to the position by order of [name of the position of the head of the enterprise] upon the recommendation of the head of the sales department.
1.3. Employees of the finished products warehouse are appointed to positions and dismissed from positions by order of [name of the position of the head of the enterprise] upon the proposal of the head of the sales department and in agreement with the warehouse manager.
1.4. In its activities, the finished goods warehouse is guided by:
— regulations on the sales department;
- legislation of the Russian Federation.
1.5. [Enter as appropriate].
General storage rules
In addition to individual rules regarding a specific method of storing products, it is worth considering a few more general recommendations. They are relevant for any warehouse, regardless of the size, equipment used and method of storing goods. All these general rules boil down to the following. The owner or person responsible for the warehouse must:
- control the level of humidity and air temperature indoors and in each zone;
- provide effective and high-quality ventilation;
- carry out regular cleaning of the area;
- strictly follow current fire safety regulations;
- do not leave any goods in the area of passage and passage of loading and unloading equipment;
- use specially designated areas or premises for storing equipment;
- maintain, check and repair all mechanisms;
- do not allow overload on the racks;
- strictly control the number of levels when stacking.
All goods are subject to mandatory periodic refreshment. This procedure implies that clothes should be ventilated, bulk cargo should be mixed, as well as bulk products. When stacking, it is useful to periodically alternate levels. That is, the top goods should be laid down and the lower tiers raised up. With a competent approach to organizing the work of a warehouse, it will be possible to achieve maximum safety of products, minimize damage to goods and effectively use all available space.