This is not just a tax, it is a whole taxation system. It is described in the Tax Code, in Chapter 26.3.
This system was initially mandatory for use when conducting certain types of activities. Now they are switching to UTII voluntarily. That is, if you conduct (again) the types of activities specified in the Tax Code, then it will be possible either to apply UTII or to apply another taxation system (basic, simplified) at the choice of the taxpayer.
Naturally, if you want to apply UTII, then you need to notify the inspectorate about it, that is, register as a taxpayer of this tax within five days from the start of one or more types of professional activities for which UTII can be applied.
Features of taxation of UTII of household services provided to the population
The legislation of the Russian Federation provides for the use of special tax regimes by taxpayers.
One of these modes is UTII, which can be used when carrying out certain types of activities. In sub. 1 item 2 art. 346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that one of these types of activities is the provision of household services. However, the possibility of using UTII when providing household services on the territory of a particular municipality must be established by an appropriate decision of the local government body. As a rule, the said decision specifies the types of services for the provision of which UTII may be used.
Situations often arise when household services are provided in a neighboring city or region. In this case, it is important to make sure that the possibility of using UTII is established by the legal act of the local authority in whose territory the activity will be carried out. This procedure is due to the fact that UTII for household services is paid at the place where these services are provided. In addition, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes the obligation to register with the local tax authority as a UTII payer.
Read about the procedure for registering as a UTII payer in this article .
What is UTII?
Let us immediately determine why this system received such a name - a single tax on imputed income. Because no matter what income and expenses occur, the tax will be calculated from the legally established (imputed) income, which will be calculated based on the basic profitability with adjustments for various coefficients and physical indicators (numbers, area, carrying capacity, etc.). d.).
In the Tax Code, Article 346.26, paragraph 2, provides a list of all types of work, professional services for which the imputed tax system can be applied. But which ones will fall under imputation are decided by local legislators, since this tax applies to local ones.
In simple words, UTII is an opportunity for small businesses to replace the payment of several taxes with the payment of one UTII based on a predetermined conditional income. The tax authorities are not interested in the actual income that will be received from a business transferred to UTII.
Below are all types of activities (according to the Tax Code) for which imputation can be applied:
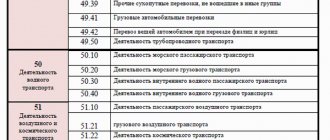
- household services, which ones, can be viewed using the codes given in the OKUN classifier (all-Russian classifier of services to the population);
- retail trade, which is carried out through stores with a sales area of less than one hundred and fifty square meters, and (or) carried out through retail outlets where there is no sales area;
- car repair, car washing, maintenance (warranty service and warranty repairs do not apply to UTII);
- veterinary services;
- services for providing parking spaces;
- services for the transportation of goods and transportation of passengers, with no more than twenty vehicles;
- catering, just like in retail trade, there is a division according to the area of the place allocated for serving visitors, it should be less than one hundred and fifty square meters and (or) catering points that do not have a service hall;
- placement of advertising on transport and on advertising structures; hotel services, the area of accommodation of residents should not exceed five hundred square meters;
- leasing space in premises for trade and catering (where there are no service halls, for example indoor markets, shopping complexes, fairs, etc.) and leasing plots of land for trade and catering.
There are restrictions on the use of UTII :
- the number of employees should be no more than one hundred people;
- participation in the formation of the authorized capital share of legal entities (no more than 25%);
- Individual entrepreneurs and organizations applying the Unified Agricultural Tax (unified agricultural tax);
- when renting out land and premises for use for gas station activities;
- schools, hospitals and similar catering establishments, since they are obliged to feed people according to their activities.
If, in addition to these types of activities, other activities are carried out, then a different taxation system should be applied to them.
How is UTII taxed for the provision of household services in 2018–2019?
In addition to the presence of the above regulatory legal act in force in the territory where household services are provided, it is necessary that these services belong to certain codes according to OKVED 2 OK 029-2014 (NACE rev. 2) and according to the classifier OK 034-2014 (KPES 2008), approved by order of Rosstandart dated January 31, 2014 No. 14-st, and were included in a special government list. Currently, such lists are contained in Government Order No. 2496-r dated November 24, 2016.
In accordance with the list, the following types of activities should be considered household services:
- sewing various clothes (codes 14.11.2; 14.12.2; 14.13.3, etc.);
- production of furniture according to individual orders of the population (codes 31.02.2; 31.09.2);
- a number of construction works (41.10; 41.20; 42.21; 43.21, etc.);
- repair of computers and peripherals (codes 95.11; 95.12; 95.21, etc.);
- etc.
Regional features of UTII
The above list can be considered as types of activities recommended by the state for the application of a single tax for entrepreneurs and firms operating in these areas. However, it is not at all a direct guide to action throughout the country. Thus, small businesses operating in the capital of our homeland are generally deprived of the opportunity to use this regime: until the beginning of 2012, a single tax was provided for only one type of activity - placing outdoor advertising. Then the Moscow authorities decided to grant the right to apply UTII for certain types of businesses in the territories newly annexed to the city, but only temporarily. From January 1, 2014, no types of activities are available for UTII in Moscow.
All other regions of the Russian Federation have the same freedom of action. The state gives each entity the right to independently determine which services it considers appropriate to impose a single tax on imputed income. Thus, local authorities have the opportunity to regulate the services market by providing some tax breaks to certain taxpayers. Moreover, previously the transfer to “imputation” was forced: if the activities of a small business entity fell under UTII, he had no other choice but to work according to this scheme. Since 2013, this regime has become voluntary: an entrepreneur is not obliged to become a UTII payer if it is not profitable for him.
Municipalities and district authorities can choose any number of types of activities - one, several or all - for the transition of entrepreneurs to “imputation”. Naturally, “amateur activity” at the local level is limited to the list permitted by tax legislation (Chapter 26.3 of the Tax Code), and no other services not included in it can be transferred to UTII.
It is also within the competence of local authorities to set a correction coefficient (K2) for each type of “imputed” work and services. The basic profitability itself is set at the legislative level, as well as the tax rate (15%). The Government of the Russian Federation annually determines the value of the deflator coefficient (K1), which is used by all “imputers” when calculating taxes.
UTII in the provision of household services: a physical indicator as the basis for calculating tax
To calculate the tax base, the physical indicator characterizing the type of business activity is of great importance. When providing household services, this indicator will be the number of workers involved in the process of providing services. Moreover, when calculating the physical indicator for an individual entrepreneur, he himself, as well as administrative, managerial and service personnel, should be taken into account.
If such personnel are not included in the calculation, claims from regulatory authorities are possible, which will lead to fines and penalties for incomplete payment of UTII.
The value of the basic profitability for this physical indicator is set equal to 1,500 rubles.
To learn how to correctly determine the physical indicator for calculating UTII, read the article “Basic UTII yield in 2018.”
How is the tax on EBIT calculated?
Imputed income is calculated using a special formula DB * FP * K1 * K2, the indicators in which mean:
- BD – basic monthly profitability per unit of physical indicator in rubles;
- FP is a physical indicator, which can be the area of a sales area or catering establishment; number of employees providing services; number of units of freight transport or seats in a passenger bus, etc.;
- K1 is a deflator coefficient, which is annually established by order of the Ministry of Economic Development (in 2021, K1 is equal to 2.005);
- K2 is a regional adjustment factor that reduces the estimated income.
This calculated imputed income is then multiplied by a tax rate of 15%, resulting in the amount of tax payable per month.
Despite the cumbersomeness of the UTII tax formula, it is quite easy to calculate. All indicators, except K2, are known in advance and are the same for all taxpayers in Russia. Regional K2 (ranges from 0.005 to 1) can significantly reduce the tax payable, so local authorities use it to develop certain types of activities.
Let’s make such a simple calculation using the example of cargo transportation for two units of transport, and take K2 as high as possible, i.e. equal to 1. The figures for DB and FP are indicated in Article 346.29 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
We calculate imputed income using the formula above: 6,000 * 2 * 2.005 * 1 = 24,060 rubles. That is, it is assumed that this is exactly the kind of revenue that cargo transportation with two units of transport will bring to the carrier. The tax on this amount will be 3,609 rubles per month or 10,827 rubles per quarter.
In reality, of course, these two units of transport, when fully loaded, can bring in an income of at least 500,000 rubles per month. If the carrier works on the simplified tax system Income, where the tax is calculated on real revenue, then with such income you will have to pay 30,000 rubles a month to the budget, which is almost 10 times more!
Note: additionally calculated tax on UTII and simplified tax system Income can be further reduced by contributions paid by individual entrepreneurs for themselves or for employees.
Prepare a UTII declaration for only 149 rubles
We recommend using our free calculator to calculate UTII.
From this example it is clear that the UTII system is unprofitable for the state, because it greatly reduces the tax burden on business. That is why they have tried to cancel this regime more than once, but the final date was constantly postponed.
Since 2021, imputation has not been applied in Russia, but regional authorities had the right to prohibit its operation on their territory earlier (for example, in Moscow this regime has not been in effect since 2014). After the abolition of UTII, individual entrepreneurs can work under the PSN regime, which is similar in tax burden. Unfortunately, patents are available only to individual entrepreneurs, although it has been proposed more than once to give this opportunity to legal entities.
But while the imposed regime is still in effect, businessmen should take advantage of the proposed tax breaks. Let's find out further what types of activities fall under UTII in 2021 for organizations and entrepreneurs.
Results
In order to transfer household services to UTII, you need to study local regulations to see if this special regime is established in your territory for this type of activity and familiarize yourself with the government list of household services to see if it contains the code for your type of activity.
If legal acts allow it, you can register as a UTII payer. The tax must be calculated based on a physical indicator, which for household services is the number of personnel involved in their provision. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
What is the essence of UTII
In everyday life, few people use the word “imputed”, but in order to understand the essence of UTII, you need to find out the meaning of this word. For tax purposes, “imputed income” means that income that the government imputes, assumes, or considers possible for the taxpayer to receive in each particular case.
At the same time, imputed income is measured not in the actual amount of revenue for goods and services in rubles, but depending on what and how many indicators are taken into account when calculating the tax. For example, a cargo carrier with one car will earn a certain amount, but if he has two or three cars, then the income will be more, respectively, exactly two or three times.
By the same logic, a store with an area of 40 square meters will be twice as profitable as a store with an area of 20 square meters. Further, if there are three hairdressers working in a beauty salon, then by hiring three more hairdressers, the employer will double the revenue exactly twice. Of course, in reality this is not the case; the real income will be much higher (but sometimes lower) than the calculated one.
Documentation
In order for the taxes paid by the LLC to correspond to UTII or in order to withdraw from the single tax, the following list of documents must be submitted:
- Application for the transition of an organization or entrepreneur to a single tax. In this case, the entrepreneur or organization is considered a single tax payer on imputed income for certain types of activities. The application is submitted using forms UTII-1 and UTII-2.
- Application for exemption of an individual entrepreneur or organization from the single tax. The application is submitted using UTII-3 and UTII-4 forms.
In order to ensure that the calculation of UTII for an LLC does not contain errors, it is necessary to monitor all changes occurring in the tax legislation of the Russian Federation.
The deadline for paying this tax is the 25th day of the month following the reporting quarter.
Calculation
As the name suggests, in this case taxes are calculated based on imputed income rather than real income. The calculation takes into account the base profitability indicator and two adjustment factors. The first coefficient is established by the Government of the Russian Federation for a calendar year. The second coefficient is determined by regional authorities. The size of the second coefficient may depend on the location of the activity, as well as its focus. If an LLC pays tax on imputed income, then its rate is 15%.
LLC reporting on UTII includes tax returns on transport and land taxes, personal income tax, a report on the average number of workers of the organization, reports to the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund, accounting reports, reports to statistical authorities.
In cases where not all types of activities fall under the imputation for an LLC, it is possible to combine different taxation systems. For example, for an enterprise operating in various directions, it is possible to combine UTII with the simplified tax system. An important point in this case is that the enterprise must keep separate records of all business transactions, property and liabilities using UTII and the simplified tax system.
How to replace UTII
And yet, if UTII is abolished from January 2021, then payers of this regime will need to choose a different taxation system now.
Most of all, imputation is similar to the patent system (PSN), but the problem is that it is only available to individual entrepreneurs. In addition, there is another tax regime (NTR), which only individuals can switch to.
But small companies, after the abolition of UTII, will find themselves in a worse position than individual entrepreneurs, because fewer preferential tax systems are available to them. Of the most obvious options for them, only the simplified tax system remains in the “Income” and “Income minus expenses” options.
Let's take a detailed look at the features of each mode that you can switch to if the UTII abolition in 2021 does happen.
Free tax consultation