An order for placing fixed assets on the balance sheet is one of the company’s basic documents, which ensures the commissioning of its property. When carrying out business activities, an enterprise needs transport, personal computers, equipment, etc. It is not enough to purchase all these things; they must be correctly reflected in the company’s accounting records.
- Form and sample
- Free download
- Online viewing
- Expert tested
FILES
Certificate of commissioning of fixed assets. Sample and Form 2021
To conduct its activities, almost every organization has at its disposal machinery, devices, buildings, equipment and other property on its balance sheet. Often companies receive new fixed assets at their disposal. To begin their operation, it is necessary to draw up an appropriate act.
Form
Until 2013, the act of primary documentation had to be drawn up in a special form. To date, the law does not require the use of a special unified form when drawing up a certificate of commissioning of fixed assets. As a rule, many organizations develop it individually, or compose it in any form.
However, you need to remember that the structure of the act must still meet certain requirements. For example, the document must be drawn up without blots or errors; it is necessary to adhere to the style of maintaining business documentation. The document can be divided into several parts:
- "a cap";
- document text;
- conclusions of the commission;
- signatures of responsible persons.
It is worth noting that quite often the commissioning act is confused with the OS-1 form, which is mandatory for the execution of another document. Thus, the unified form OS-1 does not confirm the commissioning, but rather the transfer of fixed assets from one organization to the disposal of another.
Results
The procedure for capitalizing OS takes place in several stages:
- receipt of OS by the company;
- work of the commission to determine the state of the OS and the need for improvement;
- collection of costs for bringing the OS to a state suitable for use on account 08;
- putting the OS into operation and transferring the cost of the OS to account 01;
- determining the useful life and depreciation method.
At the same time, at each stage, primary documents should be drawn up using independently developed or unified forms (depending on the accounting policy).
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.
Fixed assets are the assets of an enterprise that are used as means of labor in the process of the organization’s main activities. Before a fixed asset is put into operation and can bring profit to the enterprise, it is registered by the enterprise as a non-current asset. The types of non-current assets are quite diverse, and for each of them there are specific features when registering business transactions. The receipt of fixed assets in 1C 8.3, taking into account the current regulatory documents for accounting, is registered using accounting accounts.
Fixed asset accounts:
- 01 – Fixed assets; 01.01 – OS in the organization;
- 08.04.1 – Purchase of components of fixed assets;
Taking into account the names of fixed asset accounts, it is possible to construct a classification of non-current assets, which, after being accepted for accounting, will become fixed assets.
We have the following types of non-current assets/objects:
- OS – objects that are immediately ready for commissioning and have no additional costs after purchase;
- Equipment – not ready for commissioning and having additional costs after purchase;
- Equipment for installation – those requiring installation before commissioning;
- Construction projects are objects that are in the process of construction and are not ready for commissioning.
Each type of non-current assets has its own types of postings and documents in 1C 8.3.
As part of the 1C consultation, we will consider how to process the receipt of fixed assets, as well as equipment, in the 1C program for accounting for fixed assets - “1C: Accounting”, developed on the 1C: Enterprise platform.
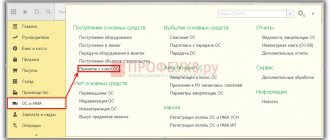
In the “OS and Intangible Materials” section of the main menu of the 1C:Enterprise accounting system, all receipt documents are combined into a separate block.
Fig.1 OS and intangible assets
What needs to be done to reflect the receipt of fixed assets for different types of non-current assets, and how to set up fixed asset accounts in 1C?
Free expert consultationNatalia Sivorina Consultant-analyst 1C Thank you for your request! A 1C specialist will contact you within 15 minutes.
Application of the OS-1 form
This document is drawn up in situations where one company transfers fixed assets to another. As a rule, the document is filled out not only by a representative of the company that receives fixed assets. Here the second party must also take part, which transfers these fixed assets.
Usually the act is drawn up and signed by the heads of the companies and their deputies. However, there may be situations where it is necessary to involve a third party. For example, when a fairly complex device, device or equipment is transferred. It is unlikely that it will be possible to do without qualified experts. Essentially, this form is intended to ensure that both parties fulfill their obligations under the previously drawn up agreement. It is worth noting that it makes no difference who takes part in the transaction. These can be private entrepreneurs or legal entities.
A document drawn up in the OS-1 form is the basis for the company that received fixed assets to register them and have the opportunity to put them into operation.
(Video: “1C 8.2 OS commissioning, use of fixed assets”)
How to draw up a certificate of commissioning of fixed assets in 2021
As a rule, the commissioning procedure is handled by a special commission created by the receiving party. For her appointment, the director issues an appropriate order. This group should include qualified specialists who are familiar with the new facility. The commission must consist of at least three employees. They are the ones who will evaluate the serviceability, performance, technical condition and other characteristics of the received property.
All information can be entered either on a computer or by hand. To do this, you must use a ballpoint pen, and in no case a pencil. If the computer option for document preparation is chosen, there must still be “live” signatures of the responsible persons. As for stamps, their availability is determined by the regulations of the organization, since companies are allowed not to use stamp products when conducting their business.
How many copies should there be?
This document must be drawn up in at least two copies. However, if there is a need, their number can be increased. The act is stored in the organization along with other primary documents. When its validity period expires, the document is sent to the archive. As a rule, the period of such storage is established by the company’s internal rules.
Instructions for filling out the act
Although there are no strict requirements for the execution of this act, it is necessary to remember the standards for drawing up business documents. To correctly draw up the act, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- At the top there should be a “header” that states which agreement this act is an annex to. The date, number and place of drawing up this agreement are noted. Many companies note the name, details and position of the manager here.
- The title of the document is indicated in the center of the sheet. Below is detailed information about the facility that is planned to begin operation. You should also note the address and location where the new equipment will be installed.
- Information about organizations that take part in the preparation of the document is indicated. The act also includes the responsible persons who are members of the commission.
- The process of carrying out inspections and tests is described, and their results are noted.
- The commission makes a conclusion by noting whether the inspected object is suitable for work. Also, responsible persons determine the date from which the operation of this facility can begin.
- If any additional documents are attached to the act, they must also be mentioned in a separate paragraph.
- The document indicates which employee becomes responsible for storing new fixed assets.
- At the bottom of the document, members of the commission put their signatures with transcripts.
Sample order for write-off of fixed assets
The order is drawn up on an A4 sheet or letterhead. The preparation of the administrative act is entrusted to the clerk, secretary or lawyer. The document contains:
- full name of the organization with details;
- order number and date of preparation;
- the ascertaining part - the grounds for writing off property funds are prescribed;
- administrative part - a list of assets (names, inventory numbers) to be disposed of is indicated;
- manager's signature, company seal.
It is allowed to attach to the document a list of funds, the conclusion of the working group and the disposal certificate.
A sample order for write-off of fixed assets can be downloaded from the link.
Completed sample certificate of commissioning of fixed assets
Why is an order to put fixed assets into operation necessary?
When a company accepts an object or some other property on its balance sheet, it becomes necessary to prepare certain documents. One of them is an order to put new facilities into operation. This document is issued by the head of the receiving organization. It is on the basis of this order that the company receives or purchases fixed assets, capitalizes them, and registers them.
New objects can be added to the company’s balance sheet in various situations:
- donation;
- purchase;
- do-it-yourself production;
- production with the help of contractors;
- receipt as authorized capital;
- sponsorship.
After a special commission is created, a thorough inspection and verification of the object takes place. Experts determine its technical condition. If there are any defects, a defect report is additionally drawn up in form OS-16. When drawing up an order, special attention should be paid to the date of acceptance and commissioning of new fixed assets. It is from this date that tax records are kept. As for the timing, the law does not define a clear period within which new facilities must be put into operation. As a rule, this is decided by the director of the organization.
There is no need to use a standard form to draw up this order. As a rule, the document is drawn up in a free style. Often an organization creates an individual model for itself. Below is a sample order. However, this does not mean that the document must look exactly this way. You have the right to make any additions and changes to suit your needs.
It is allowed to use any order design style. The main condition here is the availability of the necessary information, which must be present in administrative documents. For example, there should be data about the object, the date the order was drawn up, signatures of the responsible persons.
Postings for accounting for fixed assets
The costs of forming the initial cost of fixed assets are collected on account 08 (chart of accounts, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance on October 31, 2000 No. 94n):
| Dt | CT | Operation description |
| 60 (76) | Purchased OS | |
| 60 (76) | VAT reflected | |
| VAT on fixed assets is accepted for deduction from the budget | ||
| Fees and duties are reflected in accounting | ||
| Received OS as a contribution to the management company | ||
| OS received free of charge from the founder | ||
| OS received free of charge | ||
| 10, 20, 23, 26, 70, 69, 76 | OS created in-house | |
| OS identified during inventory |
After the OS is ready for its intended use, the accountant will transfer the initial cost accumulated on account 08 to account 01:
- Dt 01 Kt 08 - OS put into operation.
The next step for the accountant is to determine the useful life of the asset. To do this, he must study the Classification of Fixed Assets (approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated January 1, 2002 No. 1). For tax purposes, the approved Classification of fixed assets should be used, but in accounting, a company can set the useful life not only in accordance with the classification, but also at its own discretion (clause 20 of PBU 6/01). The algorithm for calculating depreciation depends on the useful life and the chosen accrual method.
The simplest method is linear; you can read more about it in the material “Linear method of calculating depreciation of fixed assets (example, formula).”
Legal basis for issuing an order
In the “Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation”, approved by the Order of the Ministry of Finance, fixed assets are understood as assets that are used by the organization:
- as means of production;
- to manage the company.
The list of such funds is not precisely defined by the legislator and is open in nature. As an example of material assets, the Regulations indicate:
- perennial plantings;
- building;
- bosom;
- bodies of water;
- laboratory equipment;
- cars;
- draft animals;
- investments that were made in the OS.
An important condition for classifying property as basic assets for an enterprise is the service life of such assets, which must be more than 12 months.
When classifying material assets as fixed assets, it does not matter how they came to be owned by a legal entity.
Replenishment methods
Replenishment of the enterprise’s property is possible, including, by:
- purchasing objects;
- accepting valuables as a gift;
- obtaining real estate for long-term lease or use;
- creating value in-house;
- received as a contribution to the authorized capital, etc.
The requirement to keep records of all company property is formulated in the Federal Law “On Accounting”. The main document reflecting the financial condition of a legal entity and containing detailed information about its assets is the balance sheet.
All capital goods purchased or received by the organization must be recorded in the company's accounting records. Therefore, after completing transactions for the acquisition of tangible assets intended for the company’s business activities, it is necessary to organize their recording as fixed assets in accounting documents.
This is ensured by drawing up an Order to place property on the balance sheet.
Procedure for accepting fixed assets for accounting
OS can be supplied to a company in different ways:
- purchase;
- receiving as a gift;
- exchange;
- production in-house or under a contract;
- identification of surpluses during inventory;
- receipts under a leasing agreement;
- contribution as a contribution to the authorized capital.
The main regulatory legal act regulating the accounting of fixed assets is PBU 6/01 (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n). According to clause 4 of this PBU, in order to capitalize an asset as fixed assets, a number of conditions must be met:
- the asset will be used in the production of products or provision of services, for rental or leasing, as well as for the needs of management personnel;
- it will be used for more than 12 months;
- the company does not intend to resell the asset;
- it will bring income.
For accounting purposes, it is recommended to classify assets as fixed assets when their value is more than 40,000 rubles. (clause 5 of PBU 6/01). For tax purposes, the threshold for accepting depreciable property for accounting is 100,000 rubles. (Clause 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
To learn how to eliminate the difference between accounting and tax accounting, read the article “A way to take into account fixed assets worth from 40 to 100 thousand rubles in tax accounting, avoiding differences with accounting.”
The asset accounting unit is an inventory object. When accepting an asset, a commission is created that determines the compliance of the OS with technical documentation and the intended conditions of use, and also decides on the need to bring the OS to a state suitable for use (Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated January 21, 2003 No. 7).
Fixed assets are accepted for accounting at historical cost - the procedure for its formation depends on the method of receipt of the asset to the company:
- for the purchase of fixed assets - the cost of the asset itself;
- for a contribution to the management company - the monetary value agreed upon by the founders;
- when donated and identified during inventory - the market value on the date the asset was accepted for accounting;
- in the case of an exchange, the value of the objects transferred in exchange.
In all cases, in addition to the indicated expenses, the initial cost includes actual expenses for delivery, installation of OS, intermediary and consulting services (clause 8 of PBU 6/01).
VAT and other refundable taxes are not included in the cost of fixed assets - read more about this in the article “How to claim VAT on fixed assets or equipment for deduction?”
Features of drawing up an order
The following may prepare a draft document as directed by the manager:
- accounting service;
- enterprise lawyer;
- assistant manager
The sample order is not established by law. An analysis of the requirements of the Law “On Accounting”, as well as the basics of document flow, allows us to identify the following necessary elements of such an order:
- the name of the organization in which the order is issued, its details (if the document is drawn up on a standard form, then this part is replaced by the header of the form);
- the name of the document (for example, “order to register fixed assets” or “order to register fixed assets”, etc.) and its serial number;
- the date of preparation of the document and the place of its signing;
- the basis for issuing the order (indicates why the property appeared in the enterprise);
- a detailed description of the means of production that is accepted for balance (indicating all characteristics, serial numbers, maximum power, color, smell, texture, etc.);
- an indication that the property is accounted for as a fixed asset;
- determining the initial cost of the asset;
- establishing a maximum service life of a means of production;
- assigning an inventory number to property;
- assignment of material value to separate groups and categories;
- indication of the name and position of the employee appointed as the financially responsible person for the safety of property;
- determination of the room or workshop in which the equipment will be used;
- attachments: details of transfer and acceptance acts, contracts for this asset;
- signature of the manager or duly authorized person;
- date and signature in familiarization with the order of the materially responsible person.
Meaning of the order
A document confirming the acceptance of a fixed asset on the company’s balance sheet is necessary not only for the preparation of financial statements. Only after its issuance, the assets received by the organization can actually be put into production on the basis of the Certificate of Putting this Property into Operation. The Act must reflect:
- characteristics of the property;
- appearance and technical condition of the means of production;
- Full name of the persons responsible for the use of the property;
- degree of equipment readiness for use.
The act is signed by a commission consisting of the manager, chief accountant and specialists in whose jurisdiction the property will be used.
Deadlines for drawing up an order
The accounting legislation does not contain deadlines for placing property on the balance sheet after its acquisition. However, it is not beneficial for the organization to delay issuing such an order. Companies can reduce their tax payments by the amount of depreciation on capital equipment. Accrual of depreciation is possible only after the property is accepted on the balance sheet and put into operation.
Errors when drawing up an order
Frequent mistakes when drawing up an order to accept fixed assets onto the balance sheet are:
- Lack of evidence to support the original cost of the asset. The basis for registering property is the documents that accompany the appearance of a means of production at the enterprise (for example, a purchase and sale agreement, lease, donation, etc.). It is at the value indicated in them that the property must be assessed. These documents must be presented during the tax audit.
- Incorrect classification of an object as a fixed asset. When forming the category of “fixed assets”, it is necessary to understand which means of production will contribute to the performance of the main function of the company, and which simply organize the life of workers. For example, even if a coffee machine has been used for more than a year and will not be disposed of by the enterprise, it is not an operating system, since it is not related to the needs of the enterprise itself.
- Accounting for parts of property as independent fixed assets. If the object is used comprehensively and the service life of the parts is not much different, it cannot be taken into account in parts.
Shelf life
In accordance with the Accounting Regulations, all primary accounting documentation must be stored for at least 5 years from the date of its preparation. This category includes acts of acceptance and transfer of fixed assets, contracts confirming its acquisition. In accordance with Order of the Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation No. 558 dated August 25, 2010, all documents on the approval of fixed assets must be stored in organizations permanently.
Purchase of fixed assets and their receipt
Acceptance of fixed assets for accounting in 1C 8 begins with the fact that the fixed asset, ready for use and operation, is registered immediately after purchase in 1C 8.3 in the “Receipt of fixed assets”, accessible from the section “Fixed assets and intangible assets” of the main menu of the 1C: Accounting system "
Fig.2 Receipt of fixed assets
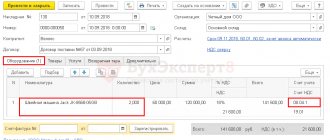
Required to fill in the header:
- Supplier invoice number and date – entered manually;
- Name of the supplier contractor – selected from the directory, can be added directly through the document;
- Agreement between the organization and the counterparty - selected from the directory, can be added directly through the document;
- The method for displaying depreciation expenses is created automatically in the document and can be changed by the user;
- The location of the OS, as a division of the organization, is selected from the directory;
- The financially responsible person, as an individual receiving OS, is selected from the directory;
- Accounting group – selected from the proposed predefined list.
Fig.3 Filling out the header
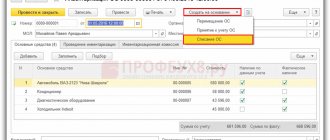
A line indicating the OS is added to the tabular section. The line is added using the “Add” button.
Fig.4 A line indicating the OS is added to the table section
In this line, you must fill in the fixed asset object by selecting or creating it in the 1C: Accounting directory of the same name.
Fig.5 Filling in a fixed asset object
To correctly calculate depreciation, you must fill in the accounting group, code of the All-Russian Classifier of Fixed Assets (OKOF) and depreciation group on the card. OKOF must be pre-loaded into the 1C: Accounting system from an external file that comes with the configuration installation package.
The tabular part is completed by indicating the cost of the fixed asset, the VAT rate, and the useful life.
The invoice number and date must be indicated in the footer.
Fig.6 Invoice number and date
The document in question provides for the registration of the receipt of a non-current asset as fixed assets, its registration and commissioning, as well as the formation of transactions:
Fig.7 Formation of transactions
So, the OS was accepted for accounting in 1C 8.3! If the receipt of fixed assets has raised any questions for you, please contact our 1C user support service, we will be happy to help you.