Many questions and disputes arise about how to choose the right dates for calculating penalties for late payment of taxes.
Don't waste time on calculations. Calculate the amount of penalties using our Penalty Calculator.
He will calculate not only penalties for taxes, contributions and fees, but also for unpaid wages on time and penalties for late payment of utilities. There is an opinion that when calculating tax penalties, the day of payment of the overdue payment is not included (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 07/05/2016 N 03-02-07/2/39318), however, the Federal Tax Service has always thought differently, so our calculator takes into account the point of view of the tax authorities services. Penalties are accrued for each calendar day of delay in fulfilling the obligation to pay a tax or fee, starting from the day following the payment established by law (clause 3 of Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The period begins to run the next day after the calendar date or the occurrence of an event (action) that determines its beginning (clause 2 of article 6.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
An example of the effect of this rule is the resolution of the North-Western District (regulatory Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-West District dated 02/03/2014 No. F07-9669/13 in case No. A05-16543/2012), in which the judges noted that the deadline for a desk audit of a declaration, the beginning of which is determined the date of submission of the declaration, for example February 22, begins to run from February 23, and its end date is May 22.
What should be taken into account when calculating penalties?
Article 330 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation contains comprehensive data on how exactly the penalty for late payment is calculated. In accordance with this, you should focus on the following points:
- It is necessary to determine the amount from which penalties for late payment will be calculated. We can talk about the entire amount under the contract or about the part unpaid by the customer. The clause of the agreement on the responsibility of the parties must certainly contain information that allows you to resolve this issue.
- The interest rate used. It is this indicator that will be the measure of liability for violation of the contract. The percentage is specified in the contract.
- The time that has passed since the terms of the contract were considered violated.
Consequences of debts for housing and communal services
In accordance with Part 1 of Art.
153 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Housing Code of the Russian Federation), rent must be paid in full and on time. The entire amount must be transferred by the 10th day of the current month, unless there is another agreement between the residents and the service organization. Violation of the payment deadline is an illegal action, therefore it may be accompanied by:
- accrual of penalties and fines;
- suspension of services or their complete shutdown;
- eviction.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpressru
Penalties accrued for late payment will become part of the debt, so they must be paid or appealed by presenting reasonable objections. The consequences of what will happen if you do not pay penalties for utilities are identical to the sanctions for non-payment of the principal debt.
The client should pay special attention to the choice of microfinance organization. Even if there is an urgent need for a loan on a card, you should at least analyze several options and read the entire agreement, and especially the conditions for calculating fines.
Today there are more than 100 different microfinance organizations. Some of them operate only online, others have a wide or small network of offices throughout the country. The requirements for borrowers are approximately the same - age of majority and possession of a passport. However, the loan programs themselves may differ significantly in:
- the size of the interest rate;
- return periods;
- possibilities and conditions for extension;
- the amount of penalties in case of late payment.
Most microfinance organizations require repayment of the debt within a short period of time - from 1 week to 1 month. However, there are programs valid for up to 180-365 days. For example, you can borrow up to 50,000 rubles. for up to six months.
Often, clients do not take the agreement with the microfinance organization seriously. They consider it their responsibility to carefully read the loan agreement with the bank, but not with microfinance organizations.
At the same time, it is important to understand that by borrowing funds from any company, the borrower assumes serious obligations, including the payment of fines in connection with possible delay.
You should view the paper version of the document (in the MFO office) or its electronic equivalent (scan of the contract or rules, user agreement) and get answers to all the basic questions:
- is there a penalty for early repayment of the debt (strictly speaking, this is contrary to the law, but such situations are not excluded);
- how exactly the last date for making a payment is determined (down to a specific hour - Moscow or other time);
- how exactly fines are calculated, what types they are (fines, penalties, etc.).
For example, in the following conditions: View reviews about the lender online.
- for each day of delay, interest continues to accrue under the main agreement (2.17% per day) until the amount of interest becomes 2 times the principal debt;
- Along with this, a penalty is also charged at the rate of 20% per annum (on the principal debt); it is added until the amount of interest becomes three times the amount of the principal debt;
- as soon as this happens, the penalty continues to be accrued on a daily basis (0.1% of the principal debt).
They believe that they will definitely be able to return the money on time. However, in practice, unforeseen situations may arise, due to which you will have to pay a significantly larger amount.
As already mentioned, today there are a large number of microfinance organizations operating on the market. Even if a difficult situation arises, almost every borrower has a chance to borrow money from another company in order to repay the previous debt.
For example, if you reborrow the required amount for another 1 month, you can even out the situation, wait for your salary, or get a temporary job. Then there will be no delays. In addition, the client will improve his credit history, which will allow him to borrow larger amounts in the future.
Very often, clients, realizing that they will not be able to return the funds on time, simply turn off the phone or do not answer calls from MFO representatives. As a result, the debt begins to immediately increase, and the borrowers do not make contact, believing that this will somehow relieve them of responsibility.
It is important to understand that microfinance organizations regularly face the fact of non-repayment, so this is a typical situation for them. Representatives of the company also do not strive to file a lawsuit as quickly as possible - it is easier for them to reach an agreement personally with the debtor than to search for him, file a statement of claim, etc.
Therefore, the desired model of behavior in such cases is as follows.
- Realizing that it will not be possible to repay the debt on time, it is advisable for the borrower to notify the company in writing in advance.
- Documents proving a significant deterioration in financial situation can be attached to the application.
- It is often possible to reach a compromise with an MFO and postpone the payment date and reduce the fine, since it is beneficial for the company to receive at least a small amount from the borrower rather than nothing at all.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: The nuances of applying for a CASCO policy when purchasing a used car
Finally, if it becomes clear that in fact the agreement with the microfinance organization is clearly illegal (the annual percentage exceeds the limit established by the regulator), you should contact law enforcement agencies or directly to the court. You should not pay unreasonably high interest rates.
Most companies operate within the law, but there are still dubious MFOs on the market whose actions contain clear signs of fraud. As a rule, they are engaged in aggressive “knocking out” of debts and begin to threaten the borrower and his family members.
You need to react to this situation immediately: call the police, and before their arrival, record by all available means the conversations and actions of representatives of this microfinance organization.
Thus, the very practice of collecting fines for late payments is a normal phenomenon that is observed both in microfinance organizations and in banks and other credit institutions. It is in the client’s interests to eliminate the situation of overdue debt.
However, even in the event of unforeseen circumstances, it is quite possible to solve the problem - the main thing is to act and not shy away from dialogue.
Claim for penalty under contract
How to receive a forfeit and charge late fees?
If controversial situations arise between two parties whose relations are fixed by agreement, you can first try to resolve the issue amicably, without contacting government agencies.
So, to begin with, it is worth drawing up a claim, which should indicate the essence, details of the parties, the calculation of the penalty itself, as well as proposals for its payment with the obligatory designation of the method and date of payment.
If this approach does not lead to the desired result, you may well go to court. But keep in mind that these authorities will certainly require you to submit a claim sent by you to the second party to the contract, which, in fact, is the first step in resolving the conflict.
But with the participation of the judiciary, consideration of the case may take a long time, so first try to come to an agreement with the culprit of the misunderstanding and remember that you can try to resolve any issue peacefully, and if this does not help, only then move on to more active actions and protecting your interests with with the help of government agencies and courts.
USEFUL : watch a video with additional tips on drawing up a claim for penalties, and also order help from our lawyer on the issue
Rules for calculating penalties after the lifting of the moratorium on their calculation
As mentioned earlier, by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 2, 2020 No. 424, a moratorium on the accrual of penalties was introduced from April 6 to December 31, 2021
and bringing debtors to pay for housing and communal services to other types of liability. From January 1, 2021, performers have the right to resume accrual of penalties.
However, there are certain nuances in this situation. If, before March 2020 inclusive, the homeowner had already accumulated a debt and was accrued a penalty, then in this case the penalty will be accrued already in the payment for January, which will arrive in February.
But with the debt that has arisen since March, everything is a little more complicated
. A moratorium is a ban on holding debtors accountable, not a deferment. That is, this period of non-payment should be completely removed when calculating the period of delay. If the homeowner did not pay bills for utility services provided for February and March 2021, then he still had 10 days to pay the bill. Only after this date will the debt period begin to be calculated. Since the moratorium was already in effect on April 10, 2021, the debt period began to count only from January 2021.
The penalty is accrued only from the 31st day of debt, that is, from February 2021.
The first payment, which will indicate a penalty if the homeowner has not paid the debt, will arrive only in March.
That is, if a subscriber has not paid utility bills for February and March 2021, and in January 2021 he still owes this debt, then in January of this year the homeowner will not be charged a penalty. In February and March 2021 it will be charged in the amount of 1/300 of the refinancing rate
, and from April – 1/130 of the refinancing rate.
Calculation of penalties under the contract
Formula for calculating penalties: how to charge penalties under a contract?
There is a special formula that answers the question of how to calculate the penalty for each day of delay. It looks like this:
contract amount × percentage rate × period of delay
How to find all this data was written above. By the way, the other party may make a demand to reduce the penalty, which is quite legal if one is guided by Art. 333 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation with reference to excessive penalties (read about reducing penalties at the link).
The procedure for collecting penalties under an agreement in court
To collect penalties under a contract in court, compliance with pre-trial procedure is mandatory. So, in order to collect penalties in court, follow these steps:
- Prepare a written claim to the counterparty with a calculation of the amount of the penalty and an offer to pay the penalty on a voluntary basis
- Send or hand over the claim to the counterparty against signature
- Wait for the period for responding to the claim established by the contract or 30 days after sending the claim
- In the absence of voluntary payment, prepare a claim in court to collect penalties under the contract
ATTENTION : taking into account the amount of claims, it may be necessary to prepare not a claim, but an application for the issuance of a court order
- Send one copy of the claim to the defendant in the case, another copy of the claim, attaching copies of supporting documents and documents stating that the claim procedure has been followed, file or send it to court
- If the court appoints the case under a summary procedure, then monitor the receipt of feedback from the defendant and, if necessary, provide objections. If the case is assigned to trial, take part in the process and justify your requirements
- Wait for the court's decision. If the decision is positive for you, wait until it comes into force
- After the court decision comes into force, obtain a writ of execution and submit it to the bailiffs to initiate enforcement proceedings or to the bank
Refinance a microloan at 0%
Sort by default by reviews by rating by approval by amount by rate
| Name, organization | Bid | Amount, up to | Deadline, until | Age, up to |
| With a bad KIA automatic | Age Application verification: Automatically without operator calls Identification: Selfie with passport, video With any credit history. Money in 8 minutes. Application verification - 4 minutes (by robot). Any microfinance organization can refuse, send your application to 1-2 more companies Get on the Seimer website Compare | |||
| Application verification: Automatically without operator calls Identification: Selfie with passport, video With any credit history. Money in 8 minutes. Application verification - 4 minutes (by robot). | ||||
| Application in 5 minutes The first one is free Application in 5 minutes | Age A simple form - a minimum of fields and documents. Application in 5 minutes. Only by passport. Any microfinance organization can refuse, send your application to 1-2 more companies Get on the Kiva website Compare | |||
| A simple form - a minimum of fields and documents. Application in 5 minutes. Only by passport. | ||||
| The first one without commission | Age Money in 15 minutes. Only by passport. Any microfinance organization can refuse, send your application to 1-2 more companies Get on the CreditStar website Compare | |||
| Money in 15 minutes. Only by passport. | ||||
Deadline for payment of penalties under the contract
Payment of penalties under the agreement can be made voluntarily, in several amounts, taking into account the period for which penalties are accrued.
The payment deadline may be established in the claim of the party to the contract. If payment is not made within the specified period, then the party may file a lawsuit.
However, there are statutes of limitations, including for the payment of penalties under the contract. What time period is this? The statute of limitations for penalties under the contract is 3 years, also called the statute of limitations. The corresponding period is calculated for each day, i.e. Penalties are accrued, as a rule, for each day, for example, late payment of payments; then, accordingly, days exceeding 3 years are subtracted from the statute of limitations, and calculations are made for the days that are included in this period.
Moreover, even if the statute of limitations expires, no one prohibits the debtor from fulfilling the claimant’s demand. The expiration of the limitation period can only affect the legal defense of the claimant, i.e. is grounds for refusal of a claim.
Restriction or suspension of utility services
The management company or resource supplier has the right to limit or suspend the provision of utility services
in accordance with paragraph 32 of the Rules approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2016 No. 354. The concepts and rules for suspending or limiting the provision are spelled out in Chapter XI of the above Rules.
A restriction is understood as a temporary reduction in the volume of utility services provided or the determination of a schedule for the provision of services in full during the day. For example, from 10:00 to 16:00 and from 23:00 to 07:00 the service will not be provided
, and at other times it turns out to be in full. Suspension is a complete cessation of the supply of a certain housing and communal services with the sealing of the corresponding equipment. Most often, the supply of electricity is suspended in case of non-payment of services for 3 months, or gas in case of non-payment for approximately six months.
If the restriction or suspension of utility services is made due to late and incomplete payment, then the housing department, management company, homeowners association or other executor is obliged to notify the homeowner of the decision in writing against signature or send a registered letter to the subscriber. Another warning can be entered into the payment document (invoice) or reported by phone (with the answerer’s ID and a call recording). The obligation to notify is specified in paragraphs 117 and 119 of the Rules, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2016 No. 354.
The notice of restriction or suspension of the provision of utility services to the homeowner sets a period of 20 calendar days
for voluntary repayment of debt.
If the debt has not been paid within 20 days, the contractor limits the provision of services if possible. If, 10 days after the introduction of the restriction, the homeowner also has not paid the entire debt, then the provision of the service may be completely suspended. Moreover, in these cases, the contract for the provision of housing and communal services is not terminated.
Subparagraph “c” of paragraph 119 of the Rules approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 26
.
12
.
2016 No. 354, a ban was established on the suspension of heating services, and in apartment buildings, cold water supply
.
The service will be resumed within 2 calendar days.
, and for gas – 5 calendar days, after full payment of the debt. Additionally, you need to pay the contractor’s expenses for suspending or limiting the provision of services. The amount of such expenses cannot exceed 3 thousand rubles in accordance with paragraph 121(1) of the above Rules.
Limitation on the amount of penalties under the contract
The contract may limit the amount of the penalty. How can penalties be limited under a contract?
The contract may stipulate that penalties cannot exceed the contract price. Thus, if the amount of the penalty exceeds the contract price, then in any case only penalties in the amount of the contract price will be subject to collection.
Also, the amount of penalties can be limited by setting a certain percentage of the amount of debt. For example, 5% of the outstanding amount due.
The contract can stipulate in what percentage the penalty will be charged and set an upper limit, for example, 0.1% for each day of delay, but not more than 10% of the cost of the goods not delivered.
It is also possible to provide for some other option for limiting the amount of penalties under the contract.
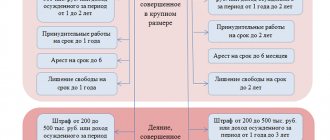
Types of fines and penalties for overdue debts
If a delay occurs, MFOs always apply certain sanctions against the debtor. They may have different names and imply different overpayments:
- the fine can be of any size;
- penalty (one-time, one-time fine) – maximum 20% per annum of the principal debt;
- interest on overdue debt – set by the MFO;
- commission/additional commission – established by the MFO;
- penalty - determined by the MFO;
- penalty – maximum 0.1% of the principal debt.
In addition, the company often applies several types of these measures at once - for example, penalty interest and also penalties are charged on the debt. At the same time, it is important to understand that “ordinary” interest continues to accrue on the entire amount of the debt. Thus, even a few days of delay lead to the fact that the amount of debt increases significantly.
However, sometimes companies impose additional fines for early refunds, which is illegal. If the contract contains such a clause, you should not even consider such an MFO. It’s easy to find another company online or on the street.
Thus, the company may use various enforcement measures in an attempt to induce the debtor to return the funds. In addition, it can apply various types of fines.
- The most common option is the actual late fee (usually charged daily).
- For termination of the contract - let’s assume that the client submitted an application yesterday, it was approved, and the contract was signed today. But tomorrow the borrower finds out that he no longer needs the funds. He immediately terminates the contract, but for this there is a small penalty.
- Fine for lack of income certificate. Let's assume that the borrower borrows a fairly large amount and undertakes to bring a 2-NDFL certificate. It then turns out that he cannot provide this document, but the MFO has already accepted the application and has incurred certain costs. It is for this that she can demand a penalty.
- Penalty for failure to provide/late provision of information about changes in personal data. Some agreements stipulate that the borrower must always notify the microfinance organization about changes in address, full name, telephone number and other previously transmitted information. Subsequently, evading this obligation may also result in the payment of a small fine.
Execution of the decision to collect penalties
A court decision to collect penalties can be executed voluntarily by the debtor, or the amounts under the decision can be collected forcibly.
The compulsory procedure consists of submitting a writ of execution to the bank in which the debtor’s account is opened. The bank will be obliged to recover funds or seize the account, taking into account the claimant’s application.
The writ of execution can be presented to bailiffs, who have the right to carry out a certain set of measures aimed at collecting debt from the debtor, including seizing accounts, requesting information about the debtor’s property, calling the debtor to give explanations, etc.
However, the claimant must constantly interact with the bailiffs, otherwise, enforcement proceedings, after carrying out certain activities at the initial stage, may simply lie on the shelf and will be remembered closer to the end of the year in order to stop.
The legislative framework
First of all, the borrower should pay attention to the current version of the law “On microfinance activities and microfinance organizations.” Since the beginning of 2021, amendments have been adopted according to which the maximum amount of accrued interest cannot exceed the amount of the principal debt by more than 3 times.
For example, a client borrowed 10,000 rubles. The maximum amount of an online loan to be repaid will be 40,000 rubles. (10,000 rubles of principal and no more than 30,000 rubles of interest). However, this rule comes with two important caveats:
- The loan was issued after January 1, 2021.
- The agreement was signed for a period of no more than 1 year.
In addition, it should be understood that we are talking about “ordinary” interest on the amount of debt, and not about fines, penalties, etc. With regard to sanctions for overdue debt, MFOs still have virtually unlimited freedom of action. However, it is indirectly limited by Article 179 of the Civil Code.
It states that the court can cancel a transaction if it was made by a person who finds himself in a clearly difficult life situation, and the other party took advantage of the circumstances and offered clearly unfavorable conditions. Such an agreement is considered enslaving, on the basis of which the judge has the right to declare it invalid.
However, legal proceedings take quite a long time (several months or even years). Moreover, there are no specific guarantees of victory. Accordingly, it is better for the borrower not to get into a situation where late payments are possible.
But even if a problem arises, you should try to solve it. For example, you can re-borrow funds or sign an additional agreement with the microfinance organization to the agreement on postponing the payment date.
In addition, it is advisable to go to court only in cases where all other ways to solve the problem have been exhausted, and the creditor organization does not meet the borrower halfway. It is important to correctly assess your chances and determine the costs. In the absence of relevant experience, it is advisable to seek help from a professional lawyer.