Accounts receivable. Competent control, planning and management
The flip side of increased sales is almost always an increase in accounts receivable. In the modern post-crisis situation, increasing production and sales is no longer a key factor in the development of the company. The main indicator of stability is competent control, planning and management of receivables.
At the stage of making a decision to provide a loan to a buyer, the following are of primary importance:
- the validity period of the contract for deferred payment (as a rule, standard contracts with a predetermined loan period are used);
- the level of solvency and reliability of the client, while special attention when collecting information is paid not only to open sources, but also to unofficial ones (for example, personal connections in regulatory and law enforcement agencies);
- creating a system of reserves in case of bad debts. The most reliable and honest client, on the basis of any standard contract, is exempt from liability in the event of force majeure circumstances, and although force majeure circumstances are rarely the real reason for non-payments, they should not be discounted;
- creation of a reliable mechanism for working with problem payers. As a rule, this responsibility is assigned to the enterprise security service. In addition, financial instruments are used, such as charging a penalty for each day of delay, including the day of payment, revising the terms of the contract as a whole;
- providing a discount, the size of which is inversely proportional to the loan term. Thus, the client becomes interested in repaying the debt as quickly as possible.
However, as practice shows, the most advanced filtering system for customers purchasing goods on contractual terms is not capable of providing a 100% result.
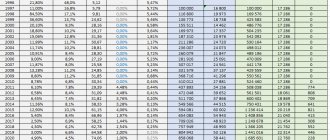
Accounts receivable in itself are not an evil for the company, although it is necessary to know exactly what size, quality and period of debt are acceptable or unacceptable for the supplier. A certain mechanism has been developed for this. First, the level and dynamics of debt in the previous period are analyzed using the formula:
Kdz = Z/A,
where Kdz is a coefficient showing the level of involvement of working capital in accounts receivable;
Z – amount of debt;
A is the total amount of working capital.
An important indicator of the quality of receivables is the turnover rate of working capital invested in debt, which is calculated using the following formula:
KO = OR/Z,
where KO is the number of rotations of the remote control in the period under review;
OR – the amount of turnover in the period under review;
Z – the amount of debt in the period under review.
After this, the level of bad debt is determined using the formula:
Kpr = Zpr/Z,
where Kpr is a coefficient expressing the level of overdue debt;
ZPR – debt not paid under the contract in the period under review;
Z – the amount of debt in the period under review.
Then the efficiency ratio of investing working capital in accounts receivable is determined:
Edz = Pdz - Zdz - Pdz,
where Edz is the efficiency ratio of invested funds in receivables;
Pdz – profit received due to sales on contractual terms;
Zdz – costs associated with lending (verification, work with debtors, etc.);
Pdz – the amount of financial losses from non-repayment of debts.
Next, we determine the required amount of working capital invested in accounts receivable using the formula:
Sdz = Or + Ks x (Pdn + Ppr),
where Sdz is the amount of funds invested in accounts receivable;
Or – planned sales volume on credit;
Kc – the ratio of cost and product price;
Pdn – weighted average of the number of days for which goods are shipped on credit;
Pdr – period of late payments, days.
When a company cannot invest the necessary funds in accounts receivable, it is necessary to make adjustments to the planned revenue and profit received from sales on debt.
One of the new methods of debt management is the refinancing of receivables, the main forms of which are factoring, forfaiting, and bill accounting.
Of particular interest to the company is factoring as a tool that covers a significant amount of supplier risks. In addition, the capital turnover period increases; for a relatively small percentage, the company optimizes its financial structure and does not incur additional costs for working with problem customers.
One of the key conditions for granting a loan is determining the duration of the agreement. Due to an increase in the duration of the contract, sales volume and revenue increase, but the amount of funds that need to be invested in accounts receivable increases, and the company’s financial cycle increases. When setting the limit of a loan agreement, it is necessary to take into account all the stated points.
Determining for itself the importance of each factor, weighing all potential risks, the company builds its credit policy, which determines the credit limit for each individual period.
In combination with the period for which the loan is provided, its cost is of particular importance. Determined by a system of price discounts for immediate payments for the supply of products. Based on these indicators, the interest rate for the loan provided is calculated:
Pg = Cs x 360/Sp,
where Pg is the interest rate on the loan provided;
Tss – discount for immediate payment without deferment;
SP – validity period of the loan agreement.
A special feature of establishing this norm is that it is linked to the interest rate on a bank loan. In any situation, it should be lower than in financial institutions. Otherwise, it is more profitable for the counterparty to take out a loan from a bank and pay for the delivery on an advance payment basis.
Based on the experience of domestic companies, it is possible to create an algorithm showing the degree of responsibility of each employee in the process of managing accounts receivable. As a rule, the commercial division of the company (sales department) oversees sales and cash flow issues, while the financial service is responsible for information and analytical work. The legal service is responsible for the impeccable state of document flow for problematic shipments (a necessary condition in the event of litigation). If the debt becomes problematic, the company’s security service gets involved.
In addition, it is important that the functions of performers when working with a client are not duplicated. Otherwise, there is inconsistency between departments, leading to a decrease in operational efficiency. Therefore, it is necessary not only to clearly distribute functions between departments, but also to clearly describe their actions at all stages of working with a problem client (see table).
Distribution of functions of performers when working with clients
| Accounts receivable management stage | Actions of departments for managing receivables | Responsible department |
| Establishing a payment period within the scope of the contract | Signing the contract | Financial Director |
| Issuing an invoice for payment | Sales department | |
| Shipment of goods and support of shipment (issuing invoices, receiving confirmation from the client that the goods have been received in the proper quantity and quality) | Sales department | |
| Reminder of the payment date (three working days before the end of the contract) | Sales department | |
| Control of overdue payments up to 7 working days | Finding out the reasons for the delay in payment | Sales department |
| Coordination of a repayment schedule for overdue debts | Financial department | |
| Stopping further shipments | Commercial Director | |
| Written notification of the commencement of application of penalties | Financial Director | |
| from 7 to 30 working days | Calculation of a fine | Financial Director |
| Daily calls reminding you to pay | Sales department | |
| Personal meeting with the director or owner of the debtor company | Commercial Director, Sales Department | |
| Written notice of preparation for trial | Legal service | |
| from 30 to 60 working days | Repeated personal meeting with the manager or owner of the debtor’s company, taking all possible measures to find a compromise solution | Head of Security Service, Sales Department |
| Official complaint (written) | Legal service | |
| more than 60 working days | Filing a claim in court | Legal service |
An additional incentive that can reduce the number of bad debts is such an unpopular measure as establishing a relationship between bonus payments to sales employees and the state of the company's total accounts receivable.
Despite the fact that all divisions of the company, without exception, take part in the process of assessing the solvency of a potential client, his reliability, it is the sales department specialists who are the first link in the chain of starting contractual relations, they always have more reliable and timely information about the state of the market, the solvency of certain counterparties. It is on the basis of information transmitted by the sales department to other divisions of the company that decisions are made to sign or not to sign contracts for deferred payment. No less responsible is the financial department of the company, whose responsibilities include conducting an error-free analysis of the state of total accounts receivable for the company as a whole. System errors that can be made in this case are no less dangerous for the company’s activities than the occurrence of bad debts due to the collection of incorrect information about potential clients.
Accounting and timely analysis of the status of accounts receivable is currently impossible without the use of special computer programs and automation of cash receipts accounting. This is due to an increase in shipment volumes, the number of invoices issued and deferred payment agreements. At the same time, it is possible to perform an analysis not only by counterparties and periods, but also to identify for which product groups and in which price segment bad and problem debts most often arise. This, in turn, allows you to more accurately assess risks when deciding whether to sign an agreement with a particular buyer.
In conclusion, we would like to add that in the process of managing accounts receivable, professionalism and a high degree of motivation of the personnel involved in this process are of great importance. The preparation of all necessary documents confirming the fact of shipment and the imposition of obligations on the counterparty must be completed exactly on time and in the proper manner. Practice knows many examples when the debtor was released from payments during the trial due to the fact that the plaintiff did not submit all the necessary, correctly executed documents confirming the fact of shipment and the provision of a loan.
Question about filling out section 5 of the Explanations (form 0710005)
The form of Explanations to the Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss Statement (0710005) contains indicators that organizations are required to disclose in the annual financial statements in accordance with the requirements established by the accounting regulations (PBU).
According to clause 27 of PBU 4/99 27 (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 6, 1999 No. 43n), explanations to the balance sheet and profit and loss account must disclose the following additional data:
— the presence of certain types of receivables at the beginning and end of the reporting period;
— the existence of certain types of accounts payable at the beginning and end of the reporting period.
Thus, the regulatory document does not require disclosure of information about debt that arose and was repaid during the reporting year. In this regard, in Section 5 of the Explanations to the columns “Changes for the period: arrivals/departures” the following links are made:
— “Data is disclosed minus accounts receivable received and repaid (written off) in one reporting period”;
— “Data is disclosed minus accounts payable received and repaid (written off) in one reporting period.”
However, as follows from paragraph 7 of PBU 4/99, if, when preparing financial statements based on the rules of the specified PBU, an organization reveals insufficient data to form a complete picture of the financial position of the organization, the financial results of its activities and changes in its financial position, then the accounting The organization's reporting includes relevant additional indicators and explanations.
According to clause 4 of the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n, the form of Explanations (0710005) is given as an example and, accordingly, is advisory in nature. The organization has the right to independently determine the type and content of the Explanations.
Thus, if the organization believes that information about the turnover of accounts receivable and payable that arose and repaid in the reporting year is useful for users of financial statements, as well as in the case of direct indication of participants (shareholders, founders), the organization has the right to accounting policy, approve its form in Section 5 of the Explanations. In this form of Section 5, in references to the relevant columns, it should be indicated that they reflect the full turnover for the reporting year without any exceptions.