Basic criteria for scheduling work
In modern personnel records management, work scheduling has been simplified by the introduction of electronic forms. The work schedule corresponds to the form provided by the 1C: Salary and Personnel program. This form is unique. It is designed taking into account the individual characteristics of any enterprise. The HR officer’s task is to correctly draw up the internals of the proposed form, namely the content, which consists of distributing personnel according to the work schedule. The internal content is designed taking into account the convenience of work not only for employees, but also for accounting calculations. Working with the 1C program reduces the time spent by the clerk on drawing up work schedules.
The program takes into account the features of different lengths of working weeks:
- 40 hour;
- 36 hour;
- 30 hour;
- 24 hour and others.
The preparation of the work schedule is based on:
- on the operating mode (the operating time of the enterprise;
- on labor legislation.
The operating mode of an organization (institution, enterprise) is the fixed time of production. The worker (specialist) spends time preparing the work area and performs certain procedures at the end of the working day. Starting work requires a minimum 10-minute deviation from the opening of the organization.
For example. The kindergarten operates on a 12-hour schedule - from 7.00 to 19.00. Kindergarten teachers should start their day at 6:50 a.m. and end at 7:10 p.m. The working hours of teachers do not duplicate the work of the preschool organization. Compliance with legal requirements is strictly observed: i.e. The time required for the teacher to perform work duties (8 hours, 7.2 hours) is strictly observed. An individual employee is obliged to fulfill the hourly rate established for his workplace.
It is better to plan rest breaks by studying the sanitary standards and rules established in production. Lunch rest varies in different organizations, mainly within time limits - 12.00-15.00.
The schedule reflects how the institution operates on established holidays and on weekends (shops, factories with non-stop production, etc.).
A well-constructed schedule will eliminate cases of shortcomings, overwork, underfunding, or, conversely, exceeding the estimated wage calculations. An error-free schedule will help optimize the work process.
With whom to agree on the schedule and when to familiarize employees with it
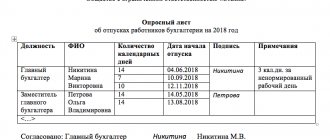
According to the general rules, work schedules must be coordinated with the trade union body and employees must be familiarized with it against signature no less than 30 days before the schedule comes into effect.
However, for the “in three days” schedule, these requirements are not applicable. Coordination with the trade union and written familiarization with the schedule at least 30 days in advance are required when drawing up a shift schedule - when employees work in two, three or four shifts and replace each other at the workplace during the day (Article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
With a “every three days” schedule, no one replaces the employee during the working day, that is, work in this mode is not considered shift work. This means that the employer has no obligation to agree on the schedule and comply with the deadlines for familiarizing employees with it. Although it is in the employer’s interests to comply with these requirements.
The employer has the right to set the period for familiarization of employees with the “every three days” schedule at its discretion, recording it in the PVTR or other local act. This will help to promptly resolve issues related to their workload with employees and avoid unnecessary proceedings.
Kinds
There are three types of work schedules: shift, rotating, weekly. All schedules have both advantages and disadvantages, but their type is necessary to meet the specifics of the work of a particular institution.
The shift schedule is used mainly by organizations with a 24-hour work system. In addition, in those organizations (the majority of them), the schedule assumes that employees work in succession. Sometimes charts calculate the period of joint work of two or more specialties at one workplace; this is mainly found in education, culture and healthcare. Shift work allows for non-stop production. The definition of the shift work schedule is given in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 103.
The law identifies 2 cases of using a shift schedule:
- Non-stop (continuity) of the production process. The working hours exceed the daily production norm - 7.2 hours (women), 8 hours - men.
- Efficiency of the equipment used (stopping the operation of units, or constant switching on/off leads to production losses).
Shift work schedules are compiled according to the forms offered by the electronic version of the program. Shifts, their number, time period are determined, and then the data is entered into the program. Most often, the shift schedule is made for a month in order to change employees in shifts within a month (1,2, night). If shifts are arranged correctly, there will be no overtime for one employee and shortcomings for another.
Shift work schedules can be changed or left unchanged. It all depends on the capabilities and characteristics of production.
A sliding work schedule is used in institutions where the traveling nature of work (business trips) is used: employees of railway institutions. In their schedules, the start time of the working day (train crews) and the end of the work shift (freight transportation), for road transport (long-distance trips) and other similar services are unknown. The personnel officer records upon receipt of information that the employee has begun his duties and their completion. From the fact of finishing work, the calculation of time for rest begins, then the start time of work (trip, departure on a flight) is determined again, i.e. Truly, the schedule slides according to the calendar and is individual for each individual employee. The electronic version of the sliding schedule allows you to track the hours worked by each member of the work unit. The weekends here are also sliding, only approximate dates are set, and the fact is revealed during the labor process.
The weekly schedule is used when employees work out the standard hours without being directly at their workplace every day, but only in the sum of the numerical values of the time worked for the week. The departure to work is selected by a specialist and agreed with the head of the department, workshop, etc. individually. This mode is also called flexible working mode. It is considered the most common abroad. There are many benefits to the weekly regimen: increased work efficiency, a decrease in the level of disciplinary violations, and improved psychological health of employees.
Article 102 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation also defines the weekly operating hours. The weekly schedule is used in the following cases:
- Working outside the office (working place at home, coming to the organization to receive a task or to coordinate assignments, handing over completed work), so-called homeworkers.
- Real estate companies where employees are forced to work according to a schedule that is set not by the employer, but by the client. These are, for example, real estate specialists: agents, managers, couriers.
- Accountant. Nowadays it is becoming fashionable to hire one accountant. Small companies, private entrepreneurs, and individual entrepreneurs prefer not to maintain an accounting staff, but to carry out accounting through a separately hired specialist. In this case, the accountant processes documents at home, or in some room, but outside of production. It makes no sense to set him any kind of work schedule other than a weekly one, since he can complete the entire amount of work at a time convenient for him.
The wages of these employees do not depend on the time worked, so the employees themselves control its implementation. The norm for them corresponds to the norm of ordinary workers, but the regime is different. It is difficult to record the work time of a given employee in a specific schedule, so the form is filled out, indicating the approximate standard of hours, rather than tracking the actual value.
The schedule must include time to restore physical strength. Rest time usually divides the working day into two parts of approximately equal time. Most often, this is one lunch break. The actual length of time used for rest and food is not included in working time. According to Art. 108 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, breaks provided to an employee during a working day (shift) can be no more than 2 hours and less than 30 minutes. There are organizations where they choose short technological breaks, they last no more than 15 minutes. If you have been tasked with drawing up a work schedule, then you must first decide on the type of schedule that is most appropriate for your organization (enterprise).
Tabular work schedule
Types of charts
There are quite a large number of types of schedules, but most enterprises have now switched to the same unified forms of the electronic version of personnel programs. They allow you not to waste time on creating your own forms, entering formulas and other tasks that programmers perform. The document specialist selects the type of schedule.
Types of charts:
- tabular;
- program;
- diagrammatic.
Diagrammatic work schedule
Interchangeable modes
Such labor regimes are usually established at enterprises and production organizations. In simple words, when the production cycle (process) requires round-the-clock labor (maintenance, maintenance, manufacturing). It is in this case that the employer is interested in organizing several shifts so that the production cycle does not stop.
This work regime is completely different from the standard five-day week. This could be working two after two, or other ways of alternating shifts. General instructions and current examples are presented in the special material “How to create a shift work schedule.”
Source of the article: https://ppt.ru/forms/rabota/grafik-raboty
The schedule is being drawn up in stages.
The accounting period is selected
It is necessary to set the working time recording period - month, quarter, year. The selected time period directly depends on the nature of production, its specifics, and the characteristics of labor.
Example. College employees must complete an hourly workload from September to May. We distribute the hours of workload for the teacher according to the accounting period. In this case, summer is excluded and included in the vacation period. If the earned vacation time is not enough (for example, vacation is 44 days, the teacher is not involved - 90 days), the teacher is offered rest at his own expense, additional workload or other options. The accounting period in this case is the academic year (not the financial year).
The time fund for servicing a specific workplace is calculated
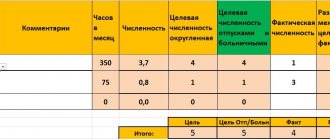
For each workplace, the fund of serviced time is calculated. Loading the workplace. The load for any type of schedule is calculated in hours and minutes.
For example. The workplace of a turner-milling operator functions according to the action of the machine. The machine works for 3 hours non-stop. After three hours, the unit takes 1.5 hours to cool down. Therefore, the operating time of the machine is 15 hours per day. The last rest for the machine is given for 3 hours. During this time, shift changes can be arranged in the work schedule. Men work on these machines - their working hours are 8 hours, so with the right schedule, you can easily assign two staff units to one machine.
If the employee’s place is occupied for 24 hours (power grid manager). This norm is calculated for the accounting period (year) and is evenly distributed over the working time of individual employees.
The hourly rate is determined
The duration of work of individual specialties has a different meaning from that of the entire staff. The schedule assigns a value to each employee if his standard working time differs from the standard of work of others.
Example. Various specialists work in an educational institution. The length of their working week is different, for example, a teacher is required to work 36 hours a week, a music director - 24 hours, a teacher - speech therapist - 20 hours. The maximum operating time per month (production rate) is different for them, it should be reflected in the schedule. The load should not be allowed to exceed the norm, as it will require additional financial investments.
Counting the number of workers
The number of employees per workplace and the total number of staff are calculated. This number of employees must serve the workplace and fulfill the plan. This results in a quantitative staffing structure – staff. Standard indicator of staffing units of an enterprise.
Example. The duty dispatcher of the power grid organizes round-the-clock duty at the control panel. The accounting period of its work is calculated for the financial year. The total service time for the dispatcher's workplace is 8760 hours (365 calendar days × 24 hours). We calculate the number required to service this workplace; it is approximately 4.8 people. In practice, an employer can hire five people, or maybe four, distributing part-time wages among employees.
A schedule is being formed
Job positions are entered into the selected form, then data is filled in for the specialists serving the jobs, and the hourly rate is distributed between them. A production is exhibited that includes all the individual features of each workplace. Weekends and holidays are included. The principle of filling is the principle of uniformity, distribution in approximately equal volumes between specialists.
The number of shifts is calculated and the shifts between employees are recorded.
The main task of creating a schedule is accessibility when perceived by the employee, and simplicity and legibility for calculation by the accounting department. All full-time employees of the enterprise are included in the schedule. The schedule requires daily adjustments (sick leave, business trips, time off). If the basic data is entered in advance, this process is easier than entering data every day.
- Salary. The work schedule is the basis for remuneration; it is transferred to the working time sheet and the employee’s wages are calculated. Therefore, it is important to make a schedule in such a way that there is no possibility of erroneous calculations.
- Payment for overtime is based on payment for hours worked by the employee in excess of the norm. Only correct data entered into the chart will give accurate recycling figures.
- Pay for night work. Night work time is considered to be the period from 22:00 to 6:00. In the schedule, night hours are recorded and counted in a separate column. Their pay is higher than regular hours, 35% of the basic salary, in addition to wages for hours worked. The employer, taking into account the complexity of night work, can establish other increased payment indicators.
What is the purpose
Let’s decide why employee HR is needed? In order to determine the duration of work and rest for each employee separately for a certain period of time. For example, approve shifts for a production workshop for March 2021. This document allows you to solve several problems at once. It is required for:
- determining the work schedule;
- streamlining shifts, duration of work and rest;
- to identify overtime and overtime;
- to determine the amount of remuneration (part-time, substitution, night and evening work),
- for the preparation of statistical reporting.
However, do not confuse the document with a time sheet. GDV is how employees will work, and the time sheet is the hours, shifts and days recorded in fact, that is, already worked. For more details, see the material “Working time schedule, how to draw it up correctly.”