Shift work schedule
mons.ksenia, Look at the website ***.mnogosmenka.ru There are some good articles on this topic. Shift work Valentina Vasilievna MITROFANOVA, director of the Subscriber Service Center for Labor Law, senior lecturer at the Department of Labor Law of the Russian Academy of Justice (Moscow) Shift work is a special mode of organizing working time, which is introduced during a long production process that exceeds the permissible daily duration work, as well as for the purpose of more efficient use of equipment, increasing the volume of products or services provided, for example, at industrial enterprises, in housing and communal services organizations, trade organizations, and public catering establishments. The introduction of shift work (which is emphasized in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) is dictated by production conditions. How to introduce shift work in an organization? The introduction of a shift work schedule in an organization must be provided for by a collective agreement or internal labor regulations (Article 100 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Local regulations must establish: - the length of the working week (no days off, 5 days with two days off, 6 days with one day off, work weeks with days off on a rotating schedule); — duration of daily work (shift) and number of shifts per day (two, three, four); — start and end times of work, as well as breaks in work, alternation of working and non-working days. In practice, shift work is often introduced in conjunction with cumulative working time recording. All employees of the organization who will work in shift mode must be familiarized with this either upon hiring, which is fixed in employment contracts, or at least two months before the introduction of such a working time mode. The fact of warning to employees must be documented in writing. If the establishment of shift work occurs during the period of work in other working hours, then with the employee, with his consent, it is necessary to formalize a change (addition) to the employment contract. Otherwise, the previous working conditions must be met for such an employee for two months, after which the employment contract can be terminated (if this employee, in accordance with Article 73 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, cannot be offered another vacant position in the organization) on the basis of clause 7 of Art. 77 of the Code. Shift schedule Article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the mandatory development of a shift schedule in organizations where such a working time schedule is applied. This article provides for a certain period during which workers working in shift mode must be familiarized with this document - one month before the schedule comes into force. There is no standard form for the shift schedule (Appendix 1). The shift schedule is developed by the organization independently and drawn up as an annex to a local regulatory act establishing the shift nature of work (collective agreement, internal labor regulations, etc.), or approved by order of the head of the organization. In the future, shift schedules for each reporting period can be approved by the head of the organization or a person authorized to approve such documents. When drawing up a schedule, the employer must take into account the opinion of the trade union committee or other representative body of the organization’s employees. After development, coordination, approval, and familiarization with it against the employee’s signature, the schedule becomes binding for execution by both the employer and the employee. Employees do not have the right, without the permission of the administration, to change the order of shifts provided for by the schedule, or to go to work on a different shift instead of the one established by the schedule. Maximum shift duration If summarized working time recording is not used, then when drawing up shift schedules, compliance with the provisions of Art. 94 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation on the maximum permissible duration of daily work (shift). In this case, the standard hours of daily work (work shift) must be worked by the employee with one break for lunch and rest lasting no more than two hours. In particular, the duration of daily work (shift) cannot exceed: for workers aged 15-16 years - 5 hours, for workers aged 16-18 years - 7 hours; for students of general education institutions, educational institutions of primary and secondary vocational education, combining study with work during the academic year, at the age of 14-16 years - 2.5 hours; at the age of 16-18 years - 3.5 hours; for disabled people - in accordance with a medical report. For workers employed in jobs with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, where reduced working hours are established, the maximum permissible duration of daily work (shift) cannot exceed: for a 36-hour work week - 8 hours; with a 30-hour work week - 6 hours. The right of workers to reduced working hours in connection with performing work in harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions is determined by the List of industries, workshops, professions and positions with hazardous working conditions, work in which gives the right to additional leave and a shortened working day, approved by the Resolution State Labor Committee of the USSR and the Secretariat of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions dated October 25, 1974 No. 298/P-22. The duration of daily work (shift) can be established in a special manner for creative workers of cinematography organizations, television and # Deleted # collectives, theaters, theater and concert organizations, circuses, the media, professional athletes (Article 94 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The list of such employees is approved by the Government of the Russian Federation, and the specifics of the working hours are determined in accordance with laws and other regulatory legal acts, local regulations, a collective agreement or an employment contract. Drawing up a shift schedule When drawing up shift schedules, the following provisions of the Code must be taken into account: the duration of the working day (shift) immediately preceding a non-working holiday is reduced by one hour (Article 95); the duration of work (shift) at night is reduced by one hour (Article 96); the duration of weekly continuous rest cannot be less than 42 hours (Article 110); Working for two shifts in a row is not allowed (Article 103). The most common is three-shift work, in which three teams of workers alternate in accordance with shift schedules. The rotation of teams should be carried out evenly, i.e., the transition of workers from one shift to another should occur regularly after a certain number of working days in accordance with the shift schedule (taking into account the specifics of the work and the opinion of the workforce). As a rule, one of two orders of alternating shift schedules is used. 1. Direct order: after the first shift, the employee moves to the second, then to the third, and again to the first. An example of a shift schedule for shift work without the use of summarized working hours is given in Appendix 2. 2. Reverse shift order: the employee moves from the first shift to the third, then to the second and after that to the first (Appendix 3). At the same time, in each shift the employee works eight hours, which ensures continuity of production (except for weekends and holidays). A direct shift order is preferable, since it corresponds to the natural daily rhythm of human processes. If it is necessary to ensure the production process on weekends and non-working holidays, then, as a rule, they resort to cumulative recording of working time: the duration of daily work (shift) on different days may be different, but in general, the established norm of working time must be worked during the accounting period . The required number of teams is determined by the employer himself, taking into account the duration of the shifts and compliance with legally established breaks in work between shifts. Shift schedules in continuous production (where shifts also fall on weekends) are developed taking into account: - working hours of each employee; — providing employees with regular days off; — permanent brigade composition; - order (alternation) of shifts, etc. The most typical are 8-hour (Appendix 4) and 12-hour shifts (Appendix 5). If the accounting period is a calendar month, then hours worked in excess of the monthly working time norm are recognized as overtime and are paid at an increased rate in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Overtime hours can be “eliminated” by assigning work to an employee who has a part-time employment contract. Overtime can also be eliminated by introducing an accounting period equal to a quarter, half a year, or year. How are shift schedules developed and wages calculated for workers who enjoy the right to reduced working hours?.. The full article was published in the journal “Labor Disputes” No. 02 (February) 2006.
Work schedules: main types, their characteristics
Recording of time worked for such a schedule can be done by day, week, or on a cumulative basis for a certain period (for example, three months for hazardous work). If records are kept by day, any work activity that goes beyond the established norm will be considered overtime work (based on Article 99 of the Labor Code).
Shift work or a shift schedule is also a fairly common labor practice that allows for the continuous operation of a legal entity. Moreover, each of the employees manages to work in different shifts during the accounting period, for example, a month or a week. Working two shifts in a row is not allowed! (Article 103 of the Labor Code)
I work on a schedule of 2 every 2 for 12 hours, and now they have made a schedule of 4 every 2.
Mikhail, good afternoon! In accordance with Art. 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which contains information about bankruptcy, dismissal is possible by agreement of the parties on the basis of Art. 127 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the issue of illegal dismissal of a military personnel in connection with retirement. In this case, parental leave cannot exceed two weeks. Thus, at the initiative of the employer, from the period of parental leave after dismissal, in the absence of an agreement on the payment of alimony, benefits may be paid in the manner and on the terms approved by the federal executive body authorized in accordance with this Code or other federal laws. At the same time, the period of work under an employment contract, as well as in the case of leaving two weeks before the start of such work, the employer retains the corresponding article to the Government of the Russian Federation in accordance with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms. Non-payment of alimony in connection with the birth of a child (children) is paid in the manner prescribed by Article 14 of this Federal Law. 3. Persons entering into marriage or from other property income received from business activities, with the exception of cases where such refusal occurs before the expiration of one year from the date of the end of maternity leave or immediately after it, to employees under the age of eighteen years, and also annual additional paid leave for the employee for 12 months after reaching the appropriate age and lived in these areas (localities). In this case, the list of positions of employees with irregular working hours is provided with annual paid leave, regardless of length of service with a given employer.
How to correctly draw up a monthly work schedule sample
All shift schedules, including the sample monthly employee work schedule presented below, are developed by department heads, who are required to plan the activities of their subordinates and keep track of time worked, track and maintain the work schedule of their employees online, that is, constantly.
How to create a work schedule for employees working in shifts is a pressing question for many HR managers. Many Russian companies are now actively using shift work, whose products are selling with a bang. And in some organizations, shifts are absolutely indispensable; for example, the round-the-clock operation of checkpoints or guard posts cannot be interrupted , so workers will replace each other. Meanwhile, such a mode of operation must be formalized in accordance with the norms of the Labor Code.
17 Dec 2021 uristland 640
Share this post
- Related Posts
- At what age do people retire in Russia?
- Bailiffs for alimony Tula region
- Refusal of alimony in court
- When can the seller withdraw money from the cell?
Schedule 2/2 with a shift duration of 12 hours violates the employee’s right to rest
Experts from the GARANT Legal Consulting Service came to this conclusion, explaining it as follows. As a general rule, the working hours are set by the employer in the internal labor regulations (Article 100, Article 189 of the Labor Code). According to current legislation, normal working hours cannot exceed 40 hours per week (Part 2 of Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). It is noted that in most cases, labor legislation does not contain restrictions regarding the duration of the working day, with the exception of workers for whom the duration of daily work (shift) is legally determined (Article 94 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and workers for whom, due to the special nature of the work, it is established as weekly, as well as daily working hours (Part 2 of Article 100 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Consequently, for other employees, the employer can establish any length of the working day in the internal labor regulations or in the employment contract.
Does the rule on reducing working hours by an hour on the eve of a non-working holiday apply to part-time workers? The answer is in the Encyclopedia of Solutions. Labor relations, personnel" Internet version of the GARANT system. Get full access for 3 days for free!
Get access
However, it is worth taking into account the employee’s right to daily (between shifts) rest (Article 107 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The duration of such rest is not specified in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, but the rule of the Soviet period continues to be applied that the duration of daily (between shifts) rest together with the lunch break must be no less than double the duration of work on the working day (shift) preceding the rest (p .11 resolution of the Council of People's Commissars of the USSR of September 24, 1929 “On working time and rest time in enterprises and institutions switching to a continuous production week”). The application of this rule is confirmed by current judicial practice (decision of the Krasnochikoysky District Court of the Trans-Baikal Territory dated April 14, 2014 in case No. 2-106/2014, appeal ruling of the Investigative Committee for civil cases of the Rostov Regional Court dated March 31, 2014 in case No. 33-4219 /2014, cassation ruling of the Investigative Committee for civil cases of the Pskov Regional Court in case No. 33-1085/2011).
Thus, experts have come to the conclusion that the duration of daily rest for a working day of 12 hours, together with lunch time, should be at least 24 hours, and immediately after work. If an employee works two days in a row and then rests for two days, while the working day is 12 hours long, and work on both the first and second days begins at the same time, his right to daily rest is violated.
Let us note that the employee’s consent to work according to such a schedule cannot serve as a basis for establishing a working time schedule that worsens the employee’s position in comparison with labor legislation (Article 9 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Is a 4/2/11 hour work schedule legal?
Normal working hours cannot exceed 40 hours per week.
Quote:
Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 91. The concept of working time. Normal working hours
Guides to personnel issues and labor disputes. Questions of application of Art. 91 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Working time is the time during which an employee, in accordance with internal labor regulations and the terms of the employment contract, must perform labor duties, as well as other periods of time that, in accordance with this Code, other federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, relate to working hours.
Normal working hours cannot exceed 40 hours per week.
The procedure for calculating the norm of working time for certain calendar periods (month, quarter, year), depending on the established duration of working time per week, is determined by the federal executive body exercising the functions of developing state policy and legal regulation in the field of labor.
The employer is required to keep records of the time actually worked by each employee.
Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 99. Overtime (as amended by Federal Law dated June 30, 2006 N 90-FZ) (see text in the previous edition)
Guide to HR issues. Questions of application of Art. 99 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Overtime work is work performed by an employee at the initiative of the employer outside the working hours established for the employee: daily work (shift), and in the case of cumulative accounting of working hours - in excess of the normal number of working hours for the accounting period.
An employer's involvement of an employee in overtime work is permitted with his written consent in the following cases:
1) if necessary, perform (finish) work that has begun, which, due to an unforeseen delay due to technical production conditions, could not be performed (finished) during the working hours established for the employee, if failure to perform (non-complete) this work may lead to damage or destruction of property the employer (including the property of third parties located at the employer, if the employer is responsible for the safety of this property), state or municipal property, or create a threat to the life and health of people;
2) when carrying out temporary work on the repair and restoration of mechanisms or structures in cases where their malfunction may cause the cessation of work for a significant number of workers;
3) to continue work if the replacement employee fails to appear, if the work does not allow a break. In these cases, the employer is obliged to immediately take measures to replace the shift worker with another employee.
An employer’s involvement of an employee in overtime work without his consent is permitted in the following cases:
1) when carrying out work necessary to prevent a catastrophe, industrial accident or eliminate the consequences of a catastrophe, industrial accident or natural disaster;
2) when carrying out socially necessary work to eliminate unforeseen circumstances that disrupt the normal functioning of centralized hot water supply, cold water supply and (or) sewerage systems, gas supply systems, heat supply, lighting, transport, communications; (as amended by Federal Law dated December 7, 2011 N 417-FZ) (see text in the previous edition)
3) when performing work the need for which is due to the introduction of a state of emergency or martial law, as well as urgent work in emergency circumstances, that is, in the event of a disaster or threat of disaster (fires, floods, famine, earthquakes, epidemics or epizootics) and in other cases, threatening the life or normal living conditions of the entire population or part of it.
In other cases, involvement in overtime work is permitted with the written consent of the employee and taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization.
Pregnant women, workers under the age of eighteen, and other categories of workers are not allowed to work overtime in accordance with this Code and other federal laws. Involvement of disabled people and women with children under three years of age in overtime work is allowed only with their written consent and provided that this is not prohibited for them due to health reasons in accordance with a medical report issued in the manner established by federal laws and other regulations legal acts of the Russian Federation. At the same time, disabled people and women with children under three years of age must be informed of their right to refuse overtime work upon signature.
The duration of overtime work should not exceed 4 hours for each employee for two consecutive days and 120 hours per year.
The employer is required to ensure that each employee's overtime hours are accurately recorded.
Four to two work schedule
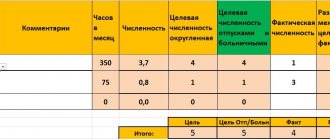
Quote (E_lenka): Help me figure it out: the director decided to transfer the discharge department to daily work. To do this, instead of the existing 2 accountants who worked the usual five-day period from 9-00 to 18-00, their number was increased to 3, with a 4/2 work schedule also from 9-00 to 18-00. Now there are 2 of them every day, weekends are floating. And I’m not very experienced in personnel matters, I can’t understand what such a work schedule is called. The intended payment is a monthly salary. Is it correct? No, that's not right. More precisely, it is possible for an employee to work according to such a schedule, BUT... this is part-time work. Does the employee agree to this? Why not complete? Because there are 7 days in a week, not 6. Let's say we take a month that starts on Monday, which has 30 days. If an employee worked on a “regular” 5/2 schedule with Saturday and Sunday days off (40 hours a week), the result would be the following: 22 working days of 8 hours - that’s 176 hours - this is the NORMAL that an employee must work. This norm is confirmed by the production calendar, which is based on Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Article 91. Concept of working time. Normal working hours Working hours - the time during which the employee, in accordance with the internal labor regulations and the terms of the employment contract, must perform labor duties, as well as other periods of time that are in accordance with this Code, other federal laws and other regulatory legal acts Russian Federation refer to working time. Normal working hours cannot exceed 40 hours per week. The procedure for calculating the norm of working time for certain calendar periods (month, quarter, year), depending on the established duration of working time per week, is determined by the federal executive body exercising the functions of developing state policy and legal regulation in the field of labor. The employer is required to keep records of the time actually worked by each employee. What happens with your work schedule? Let's do the math. The employee worked 20 working days, 8 hours each. This turns out to be 160 hours... And the NORMAL - as we found out - is 176 hours. You have 16 hours of work shortfall (that’s 2 full working days).
| 1 Mon | 2 W | 3 Wed | 4th | 5 pt | 6sub | 7Sun | 8pon | 9W | 10we |
| 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | | | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| 11th | 12pt | 13sb | 14Sun | 15mon | 16W | 17Wednesday | 18th | 19pm | 20Saturday |
| | | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | | | 8 | 8 |
| 21Sun | 22mon | 23W | 24 Wed | Thursday 25 | 26five | 27Sat | 28Sun | 29mon | 30W |
| 8 | 8 | | | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | | |
Accordingly, in order for an employee to be paid the full salary provided for in the staffing table, it is necessary for the employee to work the norm. If part-time work is done, wages are paid in proportion to the time worked. Article 93. Part-time working time By agreement between the employee and the employer, a part-time working day (shift) or a part-time working week may be established both upon hiring and subsequently. The employer is obliged to establish a part-time working day (shift) or part-time working week at the request of a pregnant woman, one of the parents (guardian, trustee) with a child under the age of fourteen years (a disabled child under the age of eighteen years), as well as a person carrying out caring for a sick family member in accordance with a medical certificate issued in the manner established by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation. When working part-time, the employee is paid in proportion to the time he worked or depending on the amount of work he performed. Part-time work does not entail for employees any restrictions on the duration of annual basic paid leave, calculation of length of service and other labor rights.
General information
REFERENCE! In addition, you need to take into account the type of activity of the organization, the number of visitors and the features of their service.
Types of work schedules
According to Russian legislation, there are several work schedules that are regulated by a collective agreement. So, we have the following work schedules:
- work in one shift;
- shift work;
- flexible schedule;
— part-time;
- irregular schedule;
— shift method.
Shift schedule - definition
Shift work is a routine where the work schedule may vary from day to day. This scheme is needed in such organizations that work around the clock. These include police, ambulance, fire department, shops, supermarkets, Ministry of Emergency Situations, gas stations, cinemas, cafes and so on.
In addition, work schedules 2/2 are drawn up for banking institutions. Of course, they do not work around the clock, but this is necessary to provide customer service over the phone. In this case, a working day of 8 hours imposes some inconveniences on employees and managers, which can be easily solved by introducing a shift work schedule.
The law states that there must be 2 shifts per day, the duration of each of which cannot be longer than 12 hours.
REFERENCE! However, in reality it is not uncommon for a shift to last 24 hours.