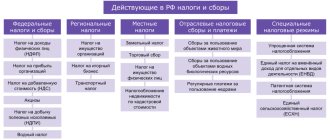
Who “rents” for VAT?
The obligation to submit a VAT return lies with (clause 5 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- Individual entrepreneurs and companies using OSNO (general taxation system), except for those exempt from VAT under Art. 145-145.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- VAT tax agents (including freight forwarders, developers, etc.);
- special regimes and merchants exempt from duties as VAT payers (if they have issued an invoice with VAT).
The VAT return is submitted quarterly, almost always in electronic form (with rare exceptions). The procedure for filling it out, the form and electronic format were approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 29, 2014 No. MV-7-3/ (as amended on December 20, 2016). The declaration form is expected to be updated in the near future.
Composition of the report
The declaration consists of a title page and 12 sections. Its composition is indicated in the table:
| Section number of the VAT declaration | Purpose of the section |
| 1 | Summary section containing the total VAT amount |
| 2 | Designed to determine the amount of tax paid by tax agents |
| 3 | Contains information that allows you to calculate VAT on transactions that are taxed at rates of 10%, 18% or calculated rates |
| 4 | To be completed in case of transactions taxed at 0% rates |
| 7 | Included in the declaration if there were transactions not subject to VAT under Art. 149 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| 8-9 | The data specified in the purchase book and sales book are reflected. |
| 10-11 | Prepared by tax agents (contain information from the invoice journal) |
| 12 | To be completed by taxpayers who are exempt from VAT but have issued VAT invoices |
However, it is not necessary to include all of these sections in the declaration. Let us explain why with an example.
Etude LLC uses OSNO. In the 1st quarter of 2021 the company:
- sold goods in the amount of 3,788,133 rubles. (including VAT = RUB 577,851);
- received invoices from suppliers, the total amount of VAT on which was 355,021 rubles.
The VAT return for the 1st quarter will include a title page, sections 1 and 3. In addition, you will need to upload information from the purchase book and sales book (sections 8 and 9) into the declaration preparation program.
This composition is explained by the fact that, in addition to the sale of goods at a rate of 18%, the company did not carry out other operations (taxed at a rate of 10% or 0%), did not act as a tax agent, etc.
The computer program with which the declaration is drawn up will itself calculate the VAT (payable or refundable) using the simplest formula:
VAT = 577,851 ─ 355,021 = 222,830 rubles.
How to fill out a VAT return for the example considered, see the sample.
The "five percent rule" has changed
If during a quarter a product is used in both taxable and non-VAT-taxable transactions, the proportion must be calculated. This proportion allows you to determine the part of the input VAT that needs to be deducted, and the part that will have to be taken into account in the cost of goods.
But the proportion could not be observed if during the quarter expenses for preferential transactions were less than 5% of the total amount of expenses. At the same time, organizations could not keep separate records.
But according to the new rules, in order to apply the “five percent rule”, you will have to keep separate records. Only in this case, the entire input VAT on goods that were used in both taxable and non-taxable transactions can be deducted.
Conclusion - for goods involved only in transactions not subject to VAT, the deduction cannot be applied.
What calculations will be needed to fill out the VAT return?
Before the figures for calculating the tax are included in the declaration, it is necessary to carry out preliminary actions:
- Check the accounting data with the information reflected in the accounting registers. You will need account information:
- 19 (amounts of deductions);
- 60, 62 and 76 (correspondence of the amounts of advances and related VAT);
- 90, 91 (sales volumes);
- 68 (participating in the calculation of the tax amount and the final result of the declaration).
- Conduct a preliminary analysis of deductions:
- calculate the total amount of deductions (DC) that you are entitled to claim based on the results of the 1st quarter;
- compare it with the safe share of deductions (SDR), determined by tax authorities by region;
- assess the possible risks and consequences of reflecting the calculated amount of deductions in the declaration if B > BDV.
The Federal Tax Service recently once again updated data on BFV (as of 02/01/2018). By region, the spread ranges from 50.9 (Baikonur) to 125.7 (Nenets Autonomous Okrug).
If deductions exceed the BDV, do not forget about your right to partially include VAT in the deduction (clause 1.1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation): VAT on goods, works and services can be deducted in parts for 3 years. However, this rule does not apply to VAT deductions on fixed assets, intangible assets and equipment for installation - the deduction for them is made in full after registration (clause 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Typical errors in the VAT return that tax authorities identify
As part of control activities, inspectors most often identify the following errors in VAT returns:
1. Incorrect transaction code for the sale of goods (work, services) to VAT payers.
In section 9 “Information from the sales book” of the declaration, taxpayers-sellers reflect transactions of the sale of goods (work, services) to buyers - VAT payers, using transaction type code 26 (“Sales of goods (work, services) to persons who are not VAT payers”). Invoices with code 26 do not participate in the process of comparing invoices from section 8 “Information from the purchase book” of the buyer’s declaration and invoices from section 9 of the seller, as a result of which auto claims are generated to taxpayers for identified discrepancies.
2. Errors when deducting VAT in parts
The right to deduction can be used within 3 years from the date of its occurrence, and the amount of tax on the invoice can be declared in installments over several tax periods (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 18, 2015 No. 03-07-RZ/28263). At the same time, taxpayers, when deducting VAT in parts, incorrectly fill out column 15 of the purchase book (cost of purchases according to the invoice) (line 170 of section 8).
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137 established that when accepting invoices for deduction in parts, column 16 of the purchase book (VAT amount on the invoice) (line 180 of the section reflects the part of the total tax amount that is accepted for deduction in the current quarter. And in column 15 of the purchase book (line 170 of the section)
reflects the part of the total tax amount that is accepted for deduction in the current quarter. And in column 15 of the purchase book (line 170 of the section) the cost of goods (work, services) is always indicated, indicated in column 9 on the line “Total payable” of the invoice, without dividing into parts.
the cost of goods (work, services) is always indicated, indicated in column 9 on the line “Total payable” of the invoice, without dividing into parts.
In addition, in column 13b of the sales book (invoice value of sales) (line 160 of section 9) and in column 14 of the invoice journal (cost of goods) (line 160 of section 10) it is also necessary to reflect the total cost of sales according to the invoice - invoice without division.
3. Incorrect recording of import transactions
Taxpayers in the purchase book and section 8 of the declaration incorrectly reflect import transactions from EAEU member countries (transaction type code 19) and from other countries (transaction type code 20).
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137 established that when reflecting in the purchase book a transaction for the import of goods from the EAEU, in column 3 “Number and date of the seller’s invoice” of the purchase book, the registration number of the application for the import of goods from the territories of the EAEU states, assigned tax authority, and the date of registration of the application for the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes.
When reflecting in the purchase book a transaction for the import of goods from other countries not included in the EAEU, in column 3 “Number and date of the seller’s invoice” of the purchase book the number and date of the customs declaration are indicated.
4. Incorrect completion of the title page of the declaration if it is submitted by the legal successor
When submitting a declaration for another organization as a legal successor, in the title page in the column “Code of the place of submission,” code 215 (“At the location of the legal successor who is not the largest taxpayer”) or 216 (“At the place of registration of the legal successor who is the largest taxpayer”) is indicated with indicating the code of the reorganization form, TIN and KPP of the reorganized company in the appropriate columns. If in this situation, on the title page in the column “Code of the place of submission” you indicate code 213 (“At the place of registration as the largest taxpayer”) or 214 (“At the location of the Russian organization that is not the largest taxpayer”), the declaration will be considered submitted for oneself . As a result, the previously submitted form receives the status “irrelevant”.
Thus, as a result of these errors, discrepancies arise, leading to increased paperwork and an undesirable burden on both the taxpayers themselves who committed violations and their counterparties.
Letter from the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation for the Moscow Region dated December 9, 2016 No. 21-26/ [email protected] “About typical errors when filling out a VAT return.”
As part of a desk audit, if contradictions are discovered, tax officials have the right to request clarification. If a company has an obligation to submit a VAT return in electronic form, then explanations to it are submitted in the same form. In this regard, Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated December 16, 2016 No. ММВ-7-15 / [email protected] approved the electronic format for submitting the specified explanations to the VAT return.
Thus, explanations on paper are not considered submitted. A fine in the amount of 5 thousand rubles is collected in case of failure to submit (untimely submission) explanations to the tax authority when the updated tax return is not submitted on time (clause 1 of Article 129.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In case of repeated violation - 20 thousand rubles.
What to pay attention to
It is important to pay special attention to deductions - even before sending the VAT return to the Federal Tax Service. It should not include data from “dangerous” invoices (containing errors, received from dubious counterparties, etc.). Thanks to the ASK VAT system, controllers identify any discrepancies in accrued tax and deductions. With this system:
- unscrupulous taxpayers are identified;
- illegal VAT deductions are excluded.
Thanks to the connection of ASK VAT to the banking system:
- the search for merchants dependent on each other is made easier;
- the movement of amounts withdrawn from taxation is monitored.
Inconsistencies identified by the system in the declaration will entail:
- submission of explanations to the Federal Tax Service (they also need to be transmitted to controllers via electronic communication channels, like VAT);
- submission of an updated declaration.
Another equally important issue when preparing a declaration is the correct indication of codes for types of transactions. If the code is used incorrectly or is not reflected at all, the declaration will not pass format-logical control, resulting in:
- it will be considered not accepted by the controllers;
- a fine may follow (if you do not have time to correct the erroneous declaration before the reporting deadline);
- you can provoke an unscheduled tax audit;
- VAT deduction may be denied.
Transaction codes are replenished and updated from time to time, so it is necessary to regularly monitor their relevance (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated January 16, 2018 No. SD-4-3/).
Before sending the declaration to the inspectorate, check it for errors. Use the control ratios for this (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated March 23, 2015 No. GD-4-3/). It is also necessary to monitor their relevance - their last update was in the letter of the Federal Tax Service dated 04/06/2017 No. SD-4-3/
Declaration and changes in legislation
The latest legislative innovations also need to be taken into account when preparing the VAT return for the 1st quarter. For example, from 01/01/2018, buyers of raw animal skins (as well as scrap, waste of ferrous and non-ferrous metals, secondary aluminum and its alloys) have an obligation to reflect the corresponding amount of VAT in the declaration and pay it to the budget. That is, in this situation, the buyer is obliged to perform the functions of a tax agent (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated January 16, 2018 No. SD-4-3/):
- determine the amount of VAT using the calculation method;
- indicate on line 060 of section 2 of the VAT return the total amount of tax (taking into account possible deductions for transactions with raw hides and scrap, and amounts of restored VAT);
- transfer taxes to the budget.
Legislators periodically supplement and adjust VAT legislation, so it is important to regularly monitor such changes and take them into account when filling out the declaration.
In what time frame must the budget obligation be fulfilled?
In Art. 174 of the Tax Code states that, as a general rule, VAT is paid in three equal shares of the total amount over three months from the end of the reporting quarter. The deadline for transfer is the 25th. If it falls on a weekend, it is transferred to the next weekday.
Based on the above rule, the deadline for paying VAT for the 1st quarter of 2021 for each of the three months occurs:
- 25.04.18;
- 25.05.18;
- 25.06.18.
None of the listed dates falls on a weekend, so no transfers are provided.