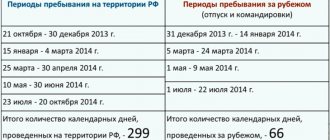
How much is spent on patients with rare diseases?
In 2021, it is planned to spend about 10 billion rubles from regional budgets to provide care for all patients with life-threatening orphan (rare) diseases, and the federal program provides for expenses of about 35 billion rubles, the head of the project office “Rare (orphan) diseases” of the National Research Institute told RBC public health ON THE. Semashko Elena Krasilnikova. In addition, there are patients with rare diseases that are not included in any of the federal registers, but they are partially provided with disability benefits from regional budgets. It is difficult to say how much is spent on such groups of patients with rare diseases, the expert noted, adding that the epidemiological list of orphan diseases includes about 260 diseases, but only 28 are programmatically designed and funded on the basis of orphan diseases.
Of the announced initiatives, the decision on personal income tax is the most striking and significant in the long term, believes political scientist Alexander Pozhalov. “This is, albeit still quite neat, but a clear step from a flat to a progressive scale and thereby a response to the growing demand of a society that has become victorious in recent years for social justice, a step towards leftist forces,” he adds. High salaries of top management of state corporations irritate the majority of Russian residents, and this decision is addressed specifically to them, notes political scientist Dmitry Fetisov. The change in the personal income tax scale for wealthy Russians is driven more by public demand for social justice rather than by fiscal considerations (60 billion rubles is too small an amount in terms of the budget), the NKR rating agency said earlier in a commentary.
Read on RBC Pro
Hiring with a demotion: is it worth hiring a former manager for a line position? Founder of VkusVill: if the employee is not mistaken, he should be fired RBC Pro: run, be patient, look for profit. How to work with a toxic manager Prices for new Moscow buildings are almost at their peak. What should investors do?
Kudrin called personal income tax adjustments accurate Economics
Sources from Forbes and RBC reported on the discussion of raising the personal income tax rate for wealthy Russians last week. A source close to the presidential administration told RBC that now “the ideal sanctions-pandemic situation” for increasing the personal income tax rate on high salaries. According to him, the idea of increasing the personal income tax rate was promoted by the former Minister of Economic Development and presidential aide Maxim Oreshkin. The issue of increasing personal income tax was discussed with Prime Minister Mikhail Mishustin and the economic bloc of the government, a government source told RBC. “The first option [of the annual income threshold] was 3 million rubles,” noted RBC’s interlocutor. According to him, Mishustin was initially against it. Earlier in the State Duma, the prime minister spoke out against the progressive scale of personal income tax. “But, given that the amount is quite high and this was the president’s initiative, we settled on the amount of 5 million, or more precisely, more than 5 million,” the RBC source said.
Another source close to the government told RBC that the idea of an increased personal income tax for high-income Russians was worked out at the end of last year during the preparation of the President’s January address to the Federal Assembly. Another RBC interlocutor close to the government said that the topic of increasing personal income tax was discussed a year ago during the work of Dmitry Medvedev’s cabinet, but then the matter did not come to a decision.
Two years ago, Vladimir Putin said that from the introduction of a progressive personal income tax scale, “the fiscal result is almost zero, but there is a lot of noise.” In February 2021, Finance Minister Anton Siluanov, in an interview with RBC, assured that until 2024, taxation principles will remain unchanged, and the issue of progression of personal income tax can be returned in four years.
The other day, the president returned to the campaign agenda for voting on amendments to the Constitution (scheduled for July 1) the topic of “Tereshkova’s amendment” (on zeroing out presidential terms) and did not rule out the possibility of running again if the amendments are approved, Pozhalov recalled. Against this background, an injection of social optimism should increase both voter turnout and support for the amendments, returning to the president some of the voters who had hesitated amid the crisis, the political scientist noted.
The increase in income tax will affect a small share of Russians, but has great potential for expansion in the future, believes Anton Tabakh, chief economist of the Expert RA rating agency. “As with the tax on deposits, mechanisms are probably being worked out to launch a full-fledged progressive tax,” he believes. After “training” on a small group of taxpayers, in a year or a year and a half, it is possible that the personal income tax rate will increase and the income level will be lowered, Tabakh expects. In addition, federalization of part of the personal income tax is being worked out, all income from which now goes to regional budgets. Personal income tax is a regional tax (85% goes to the budget of the subject, 15% to the municipality). However, from the words of the president it follows that an additional tax on wealthy citizens in the amount of 2 percentage points. will be centralized at the federal budget level, from where it will be redirected for the treatment of children.
Briefly about personal income tax
It is important to understand that personal income tax is paid at the expense of the employee, not the employer. as a tax agent for personal income tax in relation to the hired persons . This means that he must calculate, withhold this tax from the employee’s income and transfer it to the budget.
Income of individuals is taxed at several rates. The standard rate applicable to employers is 13% for employees who are residents of Russia, and 30% for non-residents.
Chapter 23 of the Tax Code is devoted to personal . When calculating the tax base, there are quite a few features that depend on the type of income. However, employers calculate tax only on those payments that they themselves make in favor of the taxpayer. The most common types of payments to employees are wages, vacation pay, bonuses, disability benefits, and financial assistance. Below we will look at examples of how they are subject to personal income tax.
Submitting a 2-NDFL certificate: how to calculate the tax amount for the year
So, the first type of personal income tax reporting for the year is certificate 2-NDFL. The last change in the 2-NDFL form occurred with the publication of the Federal Tax Service order No. ED-7-11/ [email protected] It cancels the certificate as an independent document and makes it part of the 6-NDFL calculation submitted at the end of the year.
Read more about changes to 2-NDFL in the analytical Review from ConsultantPlus experts. Trial access to the legal system is free.
However, the new procedure will only apply to information about income for 2021. The form for 2021 was approved by order of the Federal Tax Service dated October 2, 2018 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected]
In it, the tax agent reflects the income of individuals (for each recipient), which the agent actually:
- accrued;
- paid and recognized as income from which personal income tax can be withheld.
Both criteria must be met. That is, the certificate does not indicate:
- amounts of arrears of wages and other payments that have already been assigned, but have not yet been transferred (for example, deposited wages are the amount of wages temporarily stored in the cash register, which was not received by the employee on time due to personal circumstances, but can be handed over to him at any time in within 3 years from the date of deposit);
- amounts of salary advances before the end of the billing month, from which personal income tax cannot be withheld (since salaries are recognized as income only at the end of the month).
The amounts indicated in 2-NDFL are divided into two types:
- those from whom it was possible to withhold tax;
- those from which personal income tax was not withheld, although there was taxable income.
For the first category of payments, a certificate with attribute 1 is drawn up, the second - with attribute 2. From 2021, both types of certificates are submitted to the tax office within the same deadline - no later than March 1 of the year following the reporting year. Certificates for 2021 must be submitted by 03/01/2021.
Important! Tip from ConsultantPlus If in the past year you did not pay income to an individual from which personal income tax had to be withheld, then a zero certificate 2-NDFL... See K+ for more details, having received a free trial access.
Please note that Order No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected] contains two forms of certificate: one of them is intended for submission to the Federal Tax Service, and the second for issuance to the employee.
2-NDFL and see a sample of filling out here.
Salary
Let's say an employee's salary is 50,000 rubles . He is a resident of Russia, therefore the personal income tax rate of 13% applies. Its amount is calculated as follows: 50,000 / 100 * 13 = 6,500 rubles.
Thus, the situation with wages and personal income tax for this employee is as follows:
- he is awarded a salary in the amount of 50,000 rubles;
- from this amount personal income tax is withheld in the amount of 6,500 rubles ;
- the employee receives 43,500 rubles (50,00 - 6,500).
The situation changes if the employee has children under 18 years of age. In this case, he has the right to a standard personal income tax deduction in the amount of 1,400 rubles for each child . The deduction is applied to the tax base, that is, wages reduced by the deduction amounts will be subject to personal income tax. For example, if there are two children, the tax will be calculated as follows: (50,000 - 2 * 1,400) / 100 * 13 = 6,136 rubles.
The result is the following:
- the employee is paid a salary of 50,000 rubles;
- the amount of personal income tax taking into account the standard deduction is 6,136 rubles ;
- the employee receives 43,864 rubles.
Transfer of personal income tax to the budget from income in the form of wages is made no later than the day following its payment.
Personal income tax rates for residents in 2021: table
A tax resident is a person who, on the date of receipt of income, has been in the Russian Federation for at least 183 calendar days for 12 consecutive months.
| Type of income | Bet size |
| 1. The cost of winnings, prizes received in competitions, games, and other events for the purpose of advertising goods (works, services). Only income over 4,000 rubles is taxed. Income within the specified limit is exempt from tax | 35% |
2. Interest on deposits in banks in Russia and interest (coupon) on circulating bonds of Russian organizations. In this case, only part of the interest is taxed:
Interest within the specified limits is exempt from tax.
| |
| 3. Material benefits from saving on interest for using borrowed funds in two cases. Firstly, if the loan was received from an interdependent organization (IP) or employer. And secondly, if savings on interest are actually material assistance or a form of counter-fulfillment of an obligation to the taxpayer. Tax is imposed on the difference between the amount of interest calculated on the basis of the terms of the contract and the amount of interest calculated on the basis of:
The exception is material benefits received:
| |
| 4. Payment for the use of funds of members (shareholders) of consumer credit cooperatives, as well as interest on loans issued to agricultural credit consumer cooperatives by their members (associate members). The tax is imposed on the difference between the amount of income calculated on the basis of the terms of the contract and the amount of income calculated on the basis of the refinancing rate increased by 5 percentage points, valid during the period for which the specified income was accrued. Income in the form of fees for the use of funds of members (shareholders) is exempt from tax if the following conditions are simultaneously met:
| |
| 5. Interest on mortgage-backed bonds issued before January 1, 2007 | 9% |
| 6. Income of the founders of trust management of mortgage coverage received on the basis of the acquisition of mortgage participation certificates. Provided that these certificates were issued by mortgage coverage managers before January 1, 2007 | |
| 7. Income from securities of Russian organizations (except for income in the form of dividends), the rights for which are recorded in securities accounts of foreign holders (depository programs), if such income is paid to persons whose information has not been provided to the tax agent in accordance with Article 214.6 of the Tax Code | 30% |
| 8. All other types of income received by tax residents from sources in the Russian Federation and abroad (including dividends) | 13% |
Vacation pay
Vacation pay is subject to personal income tax at standard rates - 13% and 30% (for non-residents).
It happens that an employee quits before he has time to go on vacation. In this case, he is paid compensation for unused vacation days. This compensation is also subject to personal income tax.
The deadline for paying personal income tax on vacation pay or compensation is set differently than for wages. The tax amount must be transferred to the budget in the month in which the payment was made. The deadline is the last day of this month.
For example, an employee goes on vacation on July 1 . According to current legislation, vacation pay must be paid no later than 3 days before the vacation. Accordingly, payment will be made in June. This means that personal income tax must be transferred to the budget no later than June 30.
Let's look at the calculation of personal income tax on vacation pay using an example, the data for which is given in the following table.
Table. Data for calculating vacation pay and personal income tax
| Index | Meaning |
| Vacation day | July 1 |
| Employee salary amount | 50,000 rubles |
| Billing period | July 2021 - June 2021 (12 months) |
| Amount of payments for the billing period | 50,000 * 12 = 600,000 rubles |
| Number of vacation days | 28 |
| Personal income tax rate | 13% |
Vacation pay is calculated based on average daily earnings and the number of vacation days. Average earnings for calculating vacation pay are calculated using the formula: From the amount of payments for the billing period / 12 months / 29.3 (average number of days in a month). In our example, the average daily earnings will be: 600,000 / 12 / 29.3 = 1,706.48 rubles.
Let's calculate vacation pay: 1,706.48 * 28 = 47,781.44 rubles.
Let's calculate the amount of personal income tax on vacation pay: 47,781.44 / 100 * 13 = 6,211.59 rubles.
Before the vacation, the employee will receive: 47,781.44 - 6,211.59 = 41,569.85 rubles.
Results
The tax agent submits 2-NDFL certificates and 6-NDFL calculations to the Federal Tax Service within the established time frame. These documents are compiled using the same accounting registers, but have different purposes and differ greatly in terms of algorithms for reflecting the amounts of payments and taxes.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 2, 2018 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected]
- Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 14, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected]
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Financial assistance, bonuses, other payments
Let's start with bonuses . There are no preferences regarding the taxation of premiums with income tax. They are subject to a standard rate of 13%. If the bonus is included in the wages (that is, salary = Salary + Bonus), then personal income tax on this payment is already included in the tax calculated on wages. If the bonus is paid separately from the salary, for example, for an anniversary or based on the results of work for the year, it is included in the employee’s income on the date of receipt. In this case, the employer must calculate and withhold personal income tax on the day when it issues the bonus to the employee, and transfer it to the budget no later than the next day.
As for material assistance , it is not subject to personal income tax in the amount of up to 4,000 rubles per year . Anything above this amount is taxed at 13%. In addition, amounts of one-time financial assistance issued to an employee in special cases are not subject to personal income tax. For example, to pay for treatment, in connection with the death of a family member, in connection with the birth of a child, and others. These amounts are completely excluded from the base when calculating personal income tax.
Temporary disability benefits are included in the employee's income, which is subject to taxation. It is necessary to withhold personal income tax from sick leave immediately when it is paid, and transfer it to the budget no later than the last day of the month in which this benefit was paid.
Personal income tax rates for non-residents in 2021: table
A non-resident is a person who, on the date of receipt of income, has been in the Russian Federation for less than 183 calendar days for 12 consecutive months.
| 1. Dividends from Russian organizations | 15% |
| 2. Income from labor activities of foreigners who are recognized as highly qualified specialists | 13% |
| 3. Income from employment activities based on a patent issued in accordance with Article 13.3 of Law No. 115-FZ of July 25, 2002 | |
| 4. Income from the performance of labor duties by crew members of ships flying the State Flag of Russia | |
| 5. Income from the labor activities of participants in the State program to assist the voluntary resettlement to Russia of compatriots living abroad, as well as members of their families who have moved together for permanent residence in Russia | |
| 6. Income from labor activities of foreigners who are recognized as refugees or have received temporary asylum in Russia* | |
| 7. Income from securities of Russian organizations, the rights for which are recorded in securities accounts of foreign holders (depository programs), if such income is paid to persons whose information has not been provided to the tax agent in accordance with Article 214.6 of the Tax Code | 30% |
| 8. All other income except as provided for by international agreements for the avoidance of double taxation | 30% |
Will individual entrepreneurs be subject to the tax on the rich?
The President said nothing about the application of the 15% personal income tax rate to the income of individual entrepreneurs.
Most likely, the new procedure for calculating personal income tax will affect individual entrepreneurs on OSNO, which, according to the current rules, pay 13% personal income tax on income received. Earning more than 5 million rubles. per year, entrepreneurs with such a taxation system will have to pay an increased amount of personal income tax to the treasury.
In order to save money, such businessmen may decide to change the traditional taxation system to one of the special regimes (STS or PSN).
“Taxpayer” to track changes in personal income tax
You can find out what changes in personal income tax occurred in 2021 using the specialized software package “Taxpayer PRO”. The system is intended for generating, testing and sending certificates and reports to regulatory government agencies (tax inspectorate, pension and insurance funds, statistical authorities).
The modern service has a wide range of useful functionality. Among the main advantages of the accounting program:
- Protection of business documents from loss and damage . A reliable service stores and organizes data. An employee of the accounting department can always print out the necessary documents or enter new data into the database.
- Protection against document forgery . Financial accounting information is signed with an electronic digital signature of the head of the organization or individual entrepreneur.
- Full compliance with current legislation . The program is updated regularly. That is why users of the Taxpayer PRO PC always use only current document formats.
- Information support . If there are questions about how to use the program, the client can clarify the points of interest in the detailed instructions or contact a professional consultant.
- Availability of reliable control protocols for complete testing of generated reports and elimination of errors.
- Efficiency of performing multi-base operations . The program allows you to perform complex manipulations, fill out reports and send declarations for verification in just a few clicks. This greatly simplifies the work of an accountant and allows you to avoid delays in submitting reports to regulatory authorities.
0000