Hello!
Having paid dividends to an employee, and part-time to a member of the company, I would not be surprised if the accountant asks the question: are they not the employee’s income and, accordingly, an expense of the organization? After all, by its nature, it is, like a salary, income received from the organization.
But in the field of taxation, not everything is so simple. Expenses, dividends, Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - what point unites these concepts? Or maybe labor costs have nothing to do with it at all? I put everything on the shelves.
Briefly about Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation contains all possible types of expenses that are taken into account when calculating income tax. One of them is wages.
The paragraphs of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation list the employer’s expenses when paying employees on the basis of labor contracts and collective agreements.
The list of costs covers almost all cases of life, from paid amounts of official salaries and revenues to payment for employee rest and reimbursement of costs (interest) for the purchase of housing.
Legislators left the list of expenses open, limiting the employer only to labor agreements that regulate wages. The last paragraph of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation tells us this.
Are sick leave payments paid at the expense of the employer subject to insurance premiums?
According to Art.
3 of the Federal Law of July 16, 1999 No. 165-FZ “On the Basics of Compulsory Social Insurance”, security for compulsory social insurance (insurance coverage) is the fulfillment by the insurer, and in some cases also by the policyholder, of its obligations to the insured person upon the occurrence of an insured event through insurance payments or other types of security established by federal laws on specific types of compulsory social insurance. In accordance with paragraphs. 1 clause 1 art. 9 of the Federal Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ “On insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation, the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund and the Territorial Compulsory Medical Insurance Funds” are not subject to insurance premiums for state organizations benefits paid in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, legislative acts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, decisions of representative bodies of local government, including unemployment benefits, as well as benefits and other types of compulsory insurance coverage for compulsory social insurance.”
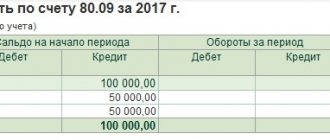
Accounting entries for dividend payments
In accounting, dividend payments are recorded by postings on the date when the participants’ decision to pay them was made.
The recipient and the payer have accounting entries reflected in different accounts.
Accounting of transactions for recipients is documented by the date of the decision - Dt76 Kt91, and upon payment - Dt51 Kt76.
The payer's postings are indicated depending on whether the recipient has an employment relationship with the company, and whether NP or personal income tax is due.
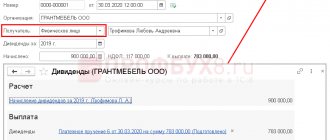
Calculation of dividends in 1C:Accounting 8
To enter information about dividends into the 1C: Accounting 8 program, a basis is required. This is the decision of the founders adopted at the general meeting or the sole decision of the sole participant.
Postings from the payer are made on different accounts based on the status of the founder:
- for a participant who is not in an employment relationship with the company - Dt84 Kt75;
- for an employee – Dt84 Kt70.
Accordingly, depending on whether the recipient works for the payer or not, the postings are also broken down.
For accrued and withheld taxes: Dt75 Kt68 - for non-working shareholders and Dt70 Kt68 - for employees.
For the listed dividends: for non-workers - Dt75 Kt51, for employees - Dt70 Kt51.
Paid taxes are indicated on Dt68 and Kt51.
How to record the accrual and payment of dividends in accounting
To reflect accruals in 1C, on the “Operations” tab, select “Accrual of dividends”, where they indicate all the information about the operation being carried out:
- date;
- name of the payer and recipient;
- accrual period;
- sum;
- necessary explanations.
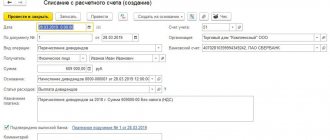
To reflect the transaction in accounting, all you have to do is select “Record” and “Post”.
The payment is reflected using the same operation. To create a payment document, you must click “Create based on” and select the appropriate method: “Cash withdrawal” or “Payment order”.
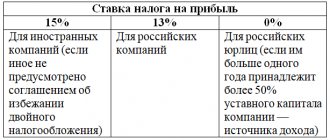
How can a tax agent calculate personal income tax at a rate of 13 percent?
The rate of 13% applies to individuals – residents of Russia. The calculation of personal income tax is influenced by whether the tax agent himself received income from participation in the activities of another legal entity. If not, then the tax is calculated as dividends accrued to an individual × 13 percent.
If the tax agent received income from participation in the activities of another organization in the past or present year, then it is necessary to establish whether such income was taken into account when making payments to its founders. If yes, then personal income tax is calculated as in the first paragraph.
Otherwise, first calculate the personal income tax deduction using the formula:
Resident dividends / Total amount of dividends for all participants × Payments received by the payer
Now the tax is calculated at a rate of 13%:
(resident dividends – deduction) × 13%.
How can a tax agent calculate personal income tax at a rate of 15 percent?
The personal income tax rate of 15% is established for non-residents of the Russian Federation, unless otherwise approved by an international treaty (clause 3 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In this case, the tax for non-residents is calculated using the same formula as for residents of Russia, only with a corresponding coefficient of 15%.
When must a tax agent withhold and transfer personal income tax?
For each type of organizational form of a company, tax legislation establishes different terms for withholding and transferring personal income tax:
- If the payer is a joint-stock company, then personal income tax must be transferred within one month after the payment of dividends (subclause 3 of clause 9 of Article 226.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- If it is an LLC, then the deadline for transferring the tax is one day, not counting the day when dividends are paid (clause 6 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Are sick leave insurance premiums paid?
There is another situation when the employer will have to pay social insurance from sick leave - the Social Insurance Fund did not accept for deduction the amount of benefits calculated and paid to the employee. Officials emphasize that if the company has not received compensation from the social insurance fund, then the payment cannot be considered a benefit exempt from contributions. And in other cases, when receiving income, it is necessary to “share” with the state.
To the question “Is sick leave subject to insurance contributions?” both colleagues and management should respond negatively. Because temporary disability benefits, including those provided in connection with the upcoming birth, are considered a state payment, which, by virtue of social insurance in case of illness, should not be subject to any taxation. For such payments there is no need to accrue funds for pensions, medical care, or even less so for social insurance against industrial accidents.
Payments for temporary disability depend on the employee’s length of service – the so-called insurance period. When filling out the sheet, both insurance and non-insurance periods for sick leave are taken into account - a separate column is provided for non-insurance periods.
A sick leave certificate is an official form that is filled out in the hospital and confirmed with his signature and seal by the doctor to whom the sick employee of the enterprise contacted. This document provides a legal basis not to go to work during the period of treatment, and after recovery to receive monetary compensation for missed work days.
In what cases is temporary disability benefits paid?
The calculation and, accordingly, payment of temporary disability benefits is carried out on the basis of the submitted sick leave certificate, which is issued in accordance with Federal Law No. 255-FZ of December 29, 2006 “On compulsory insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity” to employees unable to perform their job duties due to a number of reasons:
- employee illness or injury, including medical termination of pregnancy and in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedure;
- caring for a sick family member;
- quarantine of an employee or a child under 7 years of age attending a preschool educational organization, or another family member recognized by law as incompetent;
- implementation of prosthetics in an inpatient specialized medical institution;
- rehabilitation in sanatorium-resort institutions on the territory of the Russian Federation after inpatient treatment.
In other words, if a person is working, he can count on being provided with sick leave.
Remuneration under civil law contracts
Let's consider the situation. Let’s assume that an LLC has signed a contract with a citizen to carry out commissioning activities on production equipment. Is it possible to include the remuneration paid to him as salary expenses under Art. 255? In this case, you should refer to paragraph 21 of this article. It says that the costs can take into account payments to individuals who are not on the staff of the enterprise if they perform work under a contract. At the same time, the conditions established in Art. 252. In particular, these expenses must be supported by documents and be aimed at generating income from the company’s commercial activities. The contract itself must comply with the requirements of the Civil Code. When performing work by an individual, the rental and use of equipment is excluded. If there are costs for this, then they are classified as “Other costs”.
When are insurance premiums for temporary disability benefits calculated?
An explanation on the issue of calculating insurance premiums for amounts paid as insurance coverage in case of temporary disability was provided by the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation in letter dated February 26, 2016 No. 17-3/B-76. The legislation of the Russian Federation provides for the right of citizens to receive insurance coverage only if certain conditions are met and the necessary documents are available, properly executed. The paid amounts cannot be insurance coverage if the employer pays insurance coverage in case of temporary disability:
- in violation of the requirements of laws and other regulations;
- in the absence of relevant documents;
- on the basis of documents that were incorrectly executed or issued in violation of the established procedure.
Thus, these amounts do not relate to payments not subject to insurance premiums. In this case, the amounts of payments accrued to the employee are not accepted for credit by the territorial body of the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation, and, therefore, these payments are subject to insurance contributions to state extra-budgetary funds on a general basis.
Example:
ABC LLC made a payment in the amount of 12,200 rubles in case of temporary disability. The territorial body of the Social Insurance Fund refused to reimburse the amount of payment due to an incorrectly issued certificate of incapacity for work.
Calculation of dividends in 1C Accounting 8
In the standard configuration of 1C Enterprise 8.1, the calculation of dividends to employees of organizations is not automated, but it can be reflected in such a way that all reporting submitted for employees is correctly reflected.
1. In the list of accruals of organizations (menu Salary - Accruals of organizations) we create a new type of accrual "Dividends", the fields will be filled in as follows: - "Reflection in accounting" - with the value "Do not reflect in accounting" - "Unified Social Tax" - "Not object of taxation" - "FSS (insurance against accidents)" - Not taxed - "Type of accrual under Article 255 of the Tax Code" - do not fill out - "May relate to types of activities subject to UTII" - the checkbox is cleared 2. After auto-filling the document “Payroll” (menu Salary - Payroll for employees of organizations) you must manually add lines with dividends.
Filling out: Accrual-Dividends; Do not fill in personal income tax code-1010, deduction code and deduction amount.
3. Using a manual operation, we generate the following transactions: Dt 70 Kt 68.01 Personal Income Tax at a rate of 9% 4. To generate correct reports (payslips, 2-personal income tax, etc.), we create a document “Adjustment of register entries”, in which we indicate in “Setting the composition of registers” the following accumulation registers: — mutual settlements with employees of organizations On the register tab “Mutual settlements with employees of organizations” we create a record: Type of movement - Expense; Activity - check the box; indicate the individual, organization, period of mutual settlements; In the cell for the amount of mutual settlements, we enter the amount of personal income tax on dividends at a rate of 9%. On the register tab “Personal income tax settlements with the budget” we create two records: Similar to the first except: Type of movement - Expense; Line view-Hold; Calculated from salary - do not check the box.
Financial assistance for the rest period
The LLC pays financial aid for employee vacations based on incoming applications. Can such costs be taken into account in salary expenses? According to paragraph 23 of Art. 270 of the Tax Code, the company has no grounds for such inclusion. However, the Ministry of Finance provided clarification on this matter. According to the Ministry, these expenses cannot be taken into account only if they do not relate to the fulfillment of labor obligations. The letter explains that financial assistance is interconnected with the implementation of professional activities. However, for accounting the following conditions must be met:
- Financial assistance must be specified in a collective or employment agreement.
- Payments must be tied to salary.
- Material assistance should be related to compliance with labor discipline.
Are uniform costs included in labor costs?
Let's look at another example.
plans to buy uniforms for employees and give them to them free of charge. How to factor this into labor costs?
In paragraph 5 of Art. 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that the cost of uniforms given to employees free of charge and remaining for their personal use can be taken into account as part of labor costs for tax purposes. But remember that in this case you will have to pay VAT on the gratuitous transfer, as well as personal income tax (since this will be considered a payment to the employee in kind) and insurance premiums. Agree that these are significant additional costs.
IMPORTANT! To account for uniform costs as part of labor costs, the following conditions must be met:
- issuing uniforms for employees once has an economic justification;
- by uniform you can determine affiliation with the company;
- the issuance of such clothing is provided for by a collective or labor agreement or other local document of the company;
- expenses for the purchase of clothing are documented.
As an alternative, we propose to use the provisions of Art. 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and try to reclassify clothing from uniform to special clothing. To do this, you need to conduct an assessment of working conditions. If it is impossible to classify clothing as special clothing, then it is worth transferring it not into ownership, but only for temporary use, in order to avoid the above-mentioned burdensome additional costs.
Is sick leave subject to personal income tax?
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, temporary disability benefits (including benefits for caring for a sick child) are subject to personal income tax.
According to Art. 15 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity” establishes the period intended for the payment of benefits for temporary disability:
| Payer of temporary disability benefits | Payment deadline |
| Employer | Assignment of benefits within 10 calendar days. Payment of benefits on the next payday date. |
| Territorial body of the FSS | Assignment and payment of benefits within 10 days from the date of receipt of the application. |
Calculation and withholding of personal income tax from temporary disability benefits is made on the day the employee is paid, and tax payment must be made on the last day of the month the benefit is paid.
It should be remembered that the date of receipt of wage income and temporary disability benefits and the date of payment of personal income tax on both payments may not coincide.
Conditions for payment of temporary disability benefits
In accordance with Art. 6 of Federal Law No. 255-FZ of December 29, 2006, in order to pay benefits for temporary disability, a number of conditions must be met regarding the maximum permissible period of disability when assigning payments:
| Category of recipients of temporary disability benefits | Conditions for payment of benefits |
| An employee on sick leave due to illness or injury | Payment of benefits is carried out for the entire period of incapacity until the day of restoration of working capacity or determination of disability. |
| An employee undergoing rehabilitation after inpatient treatment in sanatorium and resort organizations of the Russian Federation | The benefit is paid for no more than 24 days. |
| An employee recognized by law as disabled | Receipt of benefits for no more than 4 consecutive months or 5 months during a calendar year |
| An employee recognized as disabled and sick with tuberculosis | The benefit is paid until the day of restoration of working capacity or until the disability group due to tuberculosis is revised |
| An employee who has entered into a fixed-term employment contract (for a period of up to 6 months) | Payment of benefits for no more than 75 calendar days under this agreement |
| A worker caring for a sick child under 7 years of age | Payment of benefits is carried out: · for the entire period of the child’s illness, but not more than 60 days a year; · in the case of a child receiving a diagnosis specified in the list of diseases in Order No. 84n of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated February 20, 2008, benefits are paid for the entire period of illness, but not more than 90 calendar days a year. |
| A worker caring for a sick child aged 7 to 15 years | Payment of benefits for no more than 15 days for each case of illness and no more than 45 calendar days per year. |
| An employee caring for a sick disabled child under 18 years of age | The entire period of the child’s illness, but no more than 120 days a year |
| A worker caring for a sick HIV-infected child under 18 years of age | The entire period of hospital treatment of the child |
| An employee caring for a sick child under 18 years of age in case of an illness associated with a post-vaccination complication or cancer | The entire period of treatment of the child |
| A worker caring for a sick family member during outpatient treatment | No more than 7 calendar days for each case of illness and no more than 30 days per year |
| Employee subject to quarantine | The entire quarantine period |
| An employee who is with a child under 7 years of age, attending a preschool educational organization, or who is with an incapacitated family member subject to quarantine | The entire quarantine period |
| An employee undergoing prosthetics in a specialized hospital | The entire period of incapacity for work, including travel in both directions |
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |