What is accounting policy
The accounting regulations explain: in the accounting policy, the accountant and director record the methods of accounting in their organization.
The issue requires a serious approach, because the order of formation of taxable objects depends on the elements of accounting policy, and all this affects the company’s finances. Approve the document no later than 90 days after registration of the company. To formulate an accounting policy (AP), an organization chooses methods of maintaining accounting and tax records from several standard options or develops accounting procedures itself based on the requirements of laws and regulations.
If the company's activities do not change for years, there is no need to change the accounting policies. But when new types of activities are opened, when the tax regime changes, or when laws are updated, the UE will have to be adjusted.
Materiality criteria
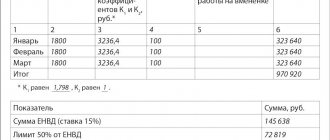
The degree of information disclosure depends on the level of materiality. For example, you can set the materiality level to 5% of the balance sheet currency. Then an indicator of more than 5% will have to be disclosed.
The level of materiality of the accounting error is also established. It is expressed as a percentage or rubles. The level of materiality affects the correction of errors. A high level simplifies this procedure, but may lead to unreliable reporting. Low makes it more difficult. It's important to find a balance. It is recommended to set different materiality levels for different categories. For example, 3% for material assets, 5% for fixed assets, and so on.
Significant accounting policies
To build a management program, follow the basic principles of accounting. Some of them are contained in the second section of PBU 1/98, others are enshrined in various documents in the field of accounting - they are derived from the theory and practice of accounting.
1. Principle of integrity: accounting data should form a unified system that helps manage the company's activities.
2. The principle of property separation: the organization’s funds, liabilities and assets must be accounted for separately from the funds of its founders and the funds of other companies if they are transferred to your company for use.
3. The principle of continuity: accounting must be carried out continuously - from the registration of a company to its liquidation or reorganization. The company must base its actions on the intention to continue operations, and therefore plan to repay obligations to individuals and legal entities.
4. The principle of completeness, or complete registration: operations and inventory results must be registered in the accounting department on time and without omissions or withdrawals.
5. Documentation principle: business facts must be confirmed by primary documents; only on the basis of primary documents, transactions are taken into account.
6. Accrual principle: business transactions must be reflected in the accounting department in the same tax period in which they occurred, even if the transaction was paid earlier or later.
7. The principle of quantitative measurement: all business transactions must be measured in money, pieces and other units.
Keep records of exports and imports in the Kontur.Accounting web service. Simple accounting, payroll and reporting in one service.
8. Principle of information control: it must be possible to verify all business transactions.
9. The principle of consistency: the information in analytical accounting and the information on balances and turnover in synthetic accounting on the last day of each month must coincide.
10. The principle of separating current and capital costs: consider separately the current costs of production or services and capital investments.
11. The principle of interpretability: information in accounting must be clear so that third parties can also interpret and analyze it.
12. Principle of prudence: the organization must be ready to recognize liabilities and expenses, assets and income in accounting without the formation of hidden reserves.
13. The principle of priority of content over form: an organization must recognize the facts of economic activity, based primarily on their economic content, and not on their legal form.
14. The principle of rationality: accounting should be carried out rationally, in accordance with the scale and conditions of economic activity and the size of the organization.
15. The principle of consistency of application: if an organization has adopted an accounting policy, it must be applied from year to year, changing only in established cases (change of the main type of activity, changes in the composition of the founders, etc.).
Research journal
Yulia Viktorovna Roshchina, Akime Enverovna Ablyametova 1. Ph.D. in Economics, Associate Professor 2. Student in the direction of 04/38/01 “Economics” Institute of Economics and Management (structural unit) of the Crimean Federal University named after V.I. Vernadsky" Roshina Juliya, Ablyametova Akime 1. PhD in Economics, Associate Professor of Accounting and Auditing 2. Student in the Direction 04/38/01 "Economy" Institute of Economics and Management of Federal State Educational Institution of Higher Education "VI Vernadsky Crimean Federal University ", Simferopol
Abstract: This article analyzes the interpretation of the term “accounting policies” in the scientific economic literature, reveals the role and significance of accounting policies in the activities of an organization, and substantiates recommendations for its formation. economic literature, reveals the role and significance of accounting policies in the organization, grounded recommendations for the formation of
Key words: accounting policy, tax accounting, accounting, chief accountant, financial result. Keywords: accounting policy, tax accounting, accounting, chief accountant, financial result.
Introduction . The main purpose of accounting and financial reporting is to provide users with complete, truthful and impartial information about the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the enterprise. An important component of the rational organization of accounting in an organization is the accounting policy, the development of which must take into account external and internal factors, as well as the specifics of the enterprise’s economic activities. Therefore, we can consider accounting policy as a reflection of the financial and economic activities of enterprises and as one of the main factors influencing it.
The purpose and objectives of the research are to study the significance of accounting policies in the economic activities of an organization.
Research methodology. The study was carried out using methods of analysis of scientific literature and the existing legislative framework on cash accounting issues in the Russian Federation, as well as generalization of the results obtained.
Research results, their brief analysis. In Russia, the concept of “accounting policy” appeared in 1992 after the approval of the state program for Russia’s transition to the accounting and statistics system accepted in international practice in accordance with the requirements of the development of a market economy.
In Art. 8 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ (as amended on May 23, 2016) “On Accounting” it is noted that accounting policy is a set of ways for an economic entity to conduct accounting [1]. In addition, the concept of accounting policy for tax accounting purposes is given in Article 11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which states that “accounting policy for tax purposes is a set of methods (methods) permitted by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for determining income and (or) expenses, their recognition, and assessment, chosen by the taxpayer. and distribution, as well as accounting for other indicators of the taxpayer’s financial and economic activities necessary for tax purposes)”[2]. As you can see, there are no fundamental differences in the definitions - the only difference is in the adjectives to the word “accounting” (accounting and tax).
International accounting standards in particular IAS 8 “Accounting policies, changes in estimates and errors”, the concept of “accounting policies of an organization” means specific principles, frameworks, agreements, rules and practices applied by an organization for the preparation and presentation of financial statements [3 ].
The scientific economic literature has its own approaches to defining the concept of “accounting policy,” which are presented in Table 1.
Table 1
Approaches to defining the concept of “accounting policy”
| authors | Determination of accounting policies |
| Astakhov V. P. | “A set of methodological techniques, methods and procedures for organizing and maintaining accounting records, selected by an enterprise from generally accepted ones or developed independently, taking into account the specifics of its activities in order to ensure the protection of the rights and interests of the owner (owners, participants)”[4, p.112] |
| Ivashkevich V.B.. | “The system of methods and techniques for organizing and maintaining records at a specific enterprise is enshrined in the relevant internal regulations for a certain period” [5, p. 59] |
| Kovaleva O.V. | “A set of principles, methods and procedures used by an enterprise to prepare financial statements”[6, p.245] |
| Kondrakov N.P. | “A set of forms and methods of accounting at an enterprise” [7, p.58] |
| Belukha N.T. | “The enterprise’s choice of methodological methods for reflecting financial and economic operations in accounting” [8, p.59] |
| Kharkova A.K. | “One of the important issues of organizing accounting, the correct execution of which contributes to the reliable determination of the financial result and contributes to the reliable determination of the financial result” [9, p.63] |
| S. Svirko | “A set of accounting principles, methods, procedures and measures to ensure the continuous flow of information from the stage of primary observation to the general one - reporting” [10, p.79] |
In our opinion, having summarized these interpretations, the most complete and reliable interpretation of this concept is accounting policy - a set of methodological techniques, methods, schemes and procedures for organizing and maintaining accounting records of its current financial and economic activities and reporting, which are chosen by the organization among the generally accepted ones, or is developed independently, based on the characteristics of its activities.
For each organization, the accounting policy is formed individually. This takes into account the organizational and legal form of the enterprise, the type and scale of activity, financial strategy, material base and structure of the organization.
It should also be noted that accounting is an instrument of government regulation. It is thanks to the regulation of the methodological and methodological foundations of accounting for all business entities that the state establishes the substantive aspects of the information infrastructure of the national economy. The main reasons that determine the formation of the accounting policy of an enterprise in Russia are:
- General accounting rules established at the international and federal levels, which should optimally combine state regulation with the principles of a market economy.
- Alternative options for organizing accounting in many areas of economic activity.
- The need for comparability and interpretation of financial statements by external users and auditors.
- Knowledge of market needs and the state of the external environment in which the enterprise operates.
- Promoting the development of market relations and increasing the number of users of financial information.
The great importance of accounting policy is expressed in the fact that the current legislation in the field of accounting allows the choice of one of several methods of organizing accounting, which involves reducing the labor intensity of accounting.
Accounting plays an important role in the effective management of a company; it is a separate management function, without which the use of other management functions, such as control, analysis and others, is impossible. At the same time, accounting policy is the basis of the entire accounting system. At the same time, regulating accounting in an organization, it is at the same time one of the tools for managing the organization. With the help of accounting policies, you can influence both the information processing process and the cost of production, the amount of profit, and the amount of tax payments.
A skillfully formed accounting policy contributes to the effective management of the organization’s economic activities, and also allows you to formulate a strategy for its development for the long term. In this case, accounting policy acts as a tool:
- cost and financial performance management;
- strategic and tactical planning;
- managing the amount of accrued taxes;
- practical resolution of contradictions in accounting regulations;
- unification of accounting procedures and reduction of their labor intensity;
- implementation of IFRS principles.
The accounting policy is formed for a long period and contributes to the development of a certain ideology of the enterprise’s economy, allows for strengthening accounting and analytical functions in enterprise management, facilitates a prompt response to changes that occur in the production process, allows for the effective adaptation of the production system to environmental conditions, and also reduces the economic risk and achieve success in competition.
The chosen accounting policy has a significant impact on the value of indicators of production costs, profits, income taxes, and indicators of the financial condition of the organization. The significant impact of accounting policies on the financial result of an organization is due to the fact that the choice of method and recognition of expenses and income of an organization can increase or decrease the final financial result.
The method that was chosen in the accounting policy for recognizing income (expense) (accrual or cash) significantly affects both the amount of sales revenue and the financial result of the organization. Thus, when reflecting costs associated with the production and sale of products (works, services), only in terms of paid costs, the cash method helps to increase the financial result by reducing costs.
Accounting policy has a much greater impact on the financial result when choosing a cost accounting method, which is due to the fact that the variability of cost accounting is much greater, and also because the cost estimate can vary significantly depending on the options used by the organization for accounting for cost elements.
Accounting policy as a specific element of the accounting system should create an organizational and methodological environment for achieving the following results: rational use of the owner’s property; provision of a variety of formal and informal management information, constant monitoring of the performance of management personnel, creation of an independent and subordinate internal control service; providing the owner with information about the financial results of the enterprise; organization of management accounting subsystems.
At the same time, accounting policies can be formed in the organization taking into account other goals not related to the interests of the owners. In this case, the accounting policy is formed in such a way as to ensure the least labor intensive accounting procedures.
The analysis showed that both the accounting strategy focused on the interests of the organization’s owners and the accounting strategy focused on reducing the labor intensity of accounting have disadvantages:
- An accounting strategy focused on the interests of the organization's owners is more labor-intensive, which contributes to the formation of a large number of errors and leads to a decrease in the control capabilities of accounting. As a result, all this increases the risk of penalties from tax authorities and, accordingly, reduces the overall efficiency of the business entity.
- An accounting strategy aimed at reducing the labor intensity of accounting contributes to the conscious underestimation by the administration of the financial results of the organization’s activities, since the most harmonization of accounting and tax accounting is achieved by choosing “slow” accounting methods [12, p.251].
Based on the study of the theoretical foundations and existing accounting practices, we have identified the following principles that must be adhered to when developing accounting policies:
- legality - the methodological techniques and procedures chosen by the organization should not contradict current legislation and regulations;
- adequacy - the organization’s accounting policies must correspond to the specific conditions of its activities;
- materiality - one of the criteria for the need to disclose information in financial statements about the choice of one method or another, the absence of which in financial statements can significantly affect the economic decisions of users;
- professional judgment - is a condition for choosing one of the alternative options provided for by current legislation or developing one or another method of the organization’s accounting policy;
- unity - the accounting policy must be uniform for the organization, regardless of the number of its divisions, branches or subsidiaries. This means that the principles, methods and procedures provided for by the organization’s accounting policies must be categorically applied by all its branches, representative offices, divisions and other separate divisions.
The organization's accounting policy must ensure the reliability and information content of reporting data, the balance of interests of various groups of reporting users, the timely generation of management information necessary for making management decisions, while minimizing the level of taxation. In other words, accounting policy is one of the main tools for control and management of an economic entity.
Conclusions. The conducted research allows us to conclude that the formation of accounting policies should be carried out in such a way that it contributes to the effective functioning of an economic entity in the long term and thereby meets the objectives of monitoring financial results. This should include the choice of accounting methods that would ensure the investment attractiveness of the organization and satisfy the interests of the owners, on the other hand, would not increase the complexity of accounting procedures.
Bibliography
1. Federal Law “On Accounting” dated November 21, 1996 No. 129-FZ (as amended by Federal Law No. 261-FZ dated November 23, 2009) 2. Tax Code of the Russian Federation, part one dated July 31, 1998 N 146 -FZ and part two of August 5, 2000 N 117-FZ (as amended on July 28, 2012) 3. International Financial Reporting Standard (IAS) 8 “Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors” (as amended and additions). GARANT system: https://base.garant.ru/70107829/#ixzz4Xuho8i1W 4. Astakhov V. P. Accounting (financial) accounting: Textbook. 5th edition, revised and expanded./ V. P. Astakhov – M.: ICC “MarT”; Rostov n/d: Publishing house, 2011. – 960 p. 5. Ivashkevich V.B. Management accounting: Textbook for universities./ V.B. Ivashkevich - M.: Yurist, 2010. - 618 p. 6. Kovaleva O.V., Konstantinov Yu.P. Audit: Textbook / Ed. O.V. Kovaleva. – M.: “Prior-izdat”, 2011. – 320 p. 7. Kondrakov N.P. Accounting: Textbook./ N.P. Kondrakov – M.: INFRA-M, 2010. – 292 p. 8. Podolsky V.I. Audit: Textbook for universities / Ed. prof. IN AND. Podolsky. – M.: UNITA-DANA, 2011. – 583 p. 9. Suglobov A.E. Accounting and audit: Textbook for universities / A.E. Suglobov, B.T. Zharyglasova. – M.: KnoRus, 2011. – 496 p. 10. Tumasyan R.Z. Accounting: Textbook./ R.Z Tumasyan. – M.: NITAR ALLIANCE LLC, 2010. – 799 p. 11. Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 6, 2008 No. 106n (as amended on March 11, 2009) “On approval of accounting regulations” (together with the “Accounting Regulations “Accounting Policy of the Organization” (PBU 1/2008)" (Registered in Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation 10.27.2008 No. 12522) 12. Makalskaya M.L., Feldman I.A. Accounting: Textbook for universities / M.L. Makalskaya, I.A. Feldman - M.: Higher education, 2010. - 433 pp.
Selecting an Accounting Policy
The choice of an enterprise’s accounting policy and the justification of its provisions depend on many conditions:
- tax regime and list of applicable taxes and rates;
- organizational and legal form;
- main type of activity (services, trade - wholesale and retail, construction, production);
- scale and structure of the organization, number of employees;
- development strategy, direction of investment;
- material resources: premises, fixed assets, equipment, software;
- accountant qualification.
It is not easy to develop a management program that would meet all the principles and would not cause complaints from tax authorities. The accounting policy should cover all important issues and at the same time be concise and have a good structure.
The accounting web service Kontur.Accounting already has developed accounting policy options for different tax regimes that fully meet the requirements of the law. Register and view them. Work in our service: keep records, pay salaries, easily submit reports via the Internet and use the ready-made version of the software. The first two weeks in the service are free for all newbies.