How to return VAT to an individual
VAT is a value added tax. The tax is paid by the seller on the markup on the goods, but this cost is included in the purchase price. In fact, the buyer pays not only the cost of the product, transportation costs for its delivery and markup to make a profit, but also VAT.
A VAT refund to an individual is not possible, but a citizen who pays taxes to the state treasury has the right to a tax deduction.
There are several options for tax refunds from the budget:
- tax refund for goods purchased outside the state. In each state, there are certain categories of goods for which you can receive a tax deduction; in addition, the amount of VAT in each country sets its own VAT amount;
- receiving a tax deduction in the case of purchasing or constructing housing. A property tax deduction is provided in the amount of two million rubles if housing is being built, or three million rubles if housing was purchased on credit;
- receiving a tax deduction for training, treatment or insurance. This deduction is a social tax deduction and can be paid based on an amount of up to 120 thousand rubles annually.
Who can return VAT
Individual entrepreneurs and organizations have the right to a tax deduction. Individuals do not have the right to return.
Renting non-residential premises - entrepreneurial activity
From January 1, 2021, the VAT rate is 20% and according to Art. 143 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when selling services within the framework of non-entrepreneurial activities, individuals are not considered VAT payers. However, we must pay attention to the definition of entrepreneurial activity. Taxpayers, as a rule, believe that since they did not register an individual entrepreneur, they did not conduct any business activity. But the tax authority thinks differently. What could be the arguments of a tax authority that considers the activity of leasing non-residential premises to be entrepreneurial?
- Non-residential premises are intended for commercial use and are not intended for personal use. How can we explain the use of a depot building, a warm parking lot for tractors, a main production building, a transformer substation, a water tower, an industrial garage, an administrative building, a store, a shopping pavilion, an office space for personal and family purposes?
- The purpose of providing premises for rent is systematic and long-term profit-making.
- The stability of ties is evidenced by the consistency in the choice of counterparties when concluding lease agreements.
- Renting out premises is carried out at your own risk.
- The lessor pays the costs associated with the operation of the property, utility bills, and repairs, which indicates the presence of economic activity in the activities of the individual.
- The lessor bears the risk of accidental loss of property as the owner, as well as risks in the event of a change in the economic situation.
- Lack of registration as an individual entrepreneur does not refute the actual conduct of business activities.
An example from judicial practice
The courts in such a situation support the position of the tax authority. (Definition of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation No. 16-KG18-17 dated July 20, 2018, Definition
RF Armed Forces No. 59-KG15-2 dated 04/08/2015. Determination of the RF Armed Forces No. 306-KG15-11736 dated 09/23/2015).
Let's take a closer look at the situation reflected in the Ruling of the RF Armed Forces dated September 23, 2015 No. 306-KG15-11736. An individual, not being an entrepreneur, rented out non-residential premises located in a residential building for office use. The tenant withheld personal income tax from the rent paid and submitted information to the tax authority in form 2-NDFL. The tax authority, citing the fact that the named premises were used by an individual not for personal purposes, but to make a profit, assessed additional VAT, determining its amount by calculation by allocating the tax amount from the price specified in the lease agreement.
Thus, those who continue to rent out commercial real estate as an individual are at great risk of additional VAT charges.
Conditions and procedure for compensation
In order to return VAT, certain conditions must be met:
- Individual entrepreneurs or organizations must apply the general taxation system; if a different tax regime is applied, it is impossible to receive a refund;
- the amount of liabilities is less than the tax deduction;
- the right to compensation is documented. To do this, you need to contact the Federal Tax Service by submitting a tax return, a book, a book of purchases and sales, invoices, as well as customs declarations and other documents confirming the right to a refund.
If the individual is in good faith, VAT payable must be allocated from the revenue, and not charged on top of it
In a situation where an individual’s operations have been recognized as entrepreneurial activity, an important question arises: what is the formula for calculating VAT payable? There are two options:
- The first is to determine the tax by calculation, applying a rate of 20/120 (or 10/110) to the revenue received. So, if an individual’s revenue is 200,000 rubles, and the corresponding transaction is subject to a VAT rate of 20%, then the VAT payable will be 33,333 rubles (200,000 rubles * 20 / 120).
- The second is to charge VAT on top of the revenue amount. So, if an individual’s revenue is 200,000 rubles, and the corresponding transaction is subject to a 20% rate, then the VAT payable will be 40,000 rubles (200,000 rubles x 20%).
Tax authorities most often practice the second option, that is, they charge VAT on top of the amount of revenue received. But the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation does not support the inspectors. From the definition of December 20, 2018 No. 306-KG18-13128, the following conclusion follows: since the parties to the transaction agreed on the price of a product or service, then increasing the price by the amount of VAT would violate the rights of the buyer. Consequently, the amount of tax payable must be determined by calculation, separating it from the transaction price.
The authors of the commented letter took into account the position of the Supreme Court. But they added that it must be adhered to only if the condition of good faith is met. That is, when, before the start of the inspection, an individual sincerely believed that his activities were not entrepreneurial, and he did not need the status of an individual entrepreneur. It’s another matter if the inspectorate has evidence that a person deliberately evaded paying taxes. This could be similar violations in the past, loss of individual entrepreneur status before concluding a transaction, signing an agreement on behalf of an “ordinary” individual if he has individual entrepreneur status, etc. In such circumstances, VAT should be charged on top of the revenue (clause 5 of the commented letter No. SA-4-7/8614).
Step-by-step procedure for VAT refund upon application
- It is necessary to prepare a VAT return for the reporting period.
- Prepare supporting documents; when exporting, you must submit a customs declaration or contract. If the contract contains information related to state secrets, documents should be submitted in a special order.
- Decide how the funds will be returned. The taxpayer has the right to return the overpayment to the budget or offset it against future payments. However, if there is a debt, these actions are not available.
Background
Since the 90s of the twentieth century, the tax service began to actively campaign citizens, motivating them to pay taxes. The advertising slogan invented in those years: “Pay your taxes and sleep well” is still remembered by many Russians. And such advertising had a very strong response - people registered their income en masse and diligently paid the required 13 percent of personal income tax to the treasury.
One of the most popular types of passive income in our country is renting out residential and non-residential premises . By becoming the owners of such real estate and receiving rentier status, citizens provided themselves with at least some kind of financial stability. They profitably rented out their premises for long periods of time as offices, shops, warehouses and had a constant and reliable income. individuals on the rent received .
Many enlightened people understood that having received the status of private entrepreneurs (later changing their name to individual entrepreneurs or individual entrepreneurs), they would spend less by notifying the tax authorities about the transition from OSNO, where you need to pay VAT , to the “simplified tax” and reducing the tax to 6%. But the bureaucratic “bonus” in the form of constant reporting for all regulatory authorities attracted few people. And the notorious personal income tax was included in the rental price and was not burdensome for the rante itself.
vzimaetsya_li_nds_s_fizicheskih_lic.jpg
Related publications
The topic of this article is interesting in its ambiguity and surprise for a wide range of consumers, which, in fact, are all of us. “Is VAT withheld from individuals?” Ask a similar question to tax department employees, and you will receive a seemingly specific, but in fact a generalized answer that individuals are not included in the list of entities recognized as VAT taxpayers (Article 143 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But is this really so, if you “dig deeper”? Let's try to figure it out.
Is there a choice? No choice!
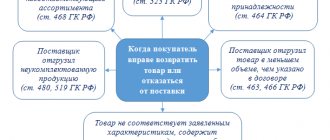
In order to find the answer to the question of whether VAT is actually withheld from individuals, let us turn to the main document - a cash receipt, in which the total amount contains two financial positions:
- actual cost of the goods;
- the amount of VAT included in the cost of goods (services).
Since VAT must be charged on the cost of almost the entire range of production products, goods sold or services provided, business entities include the tax in the final cost of the object of taxation, so to speak, “in addition” to the price, essentially “shifting” the tax obligatory for business entities to buyer's shoulders. This reveals the main feature of VAT: it is an indirect tax that is actually paid by the end consumer.
With this principle of price formation, the individual consumer ultimately has no choice whether to pay VAT or not, because the amount of tax is included in it and is not a separate payment. Accordingly, for every purchase in a store or receipt of various types of services, a citizen will pay VAT, which will be confirmed by a separate line in the receipt issued to him.
When can an individual become a VAT payer?
Author: Anna Arkhipova , Deputy Director of First Rostov Tax Consultation LLC, tax consultant, member of the Chamber of Tax Consultants
Materials from the newspaper “Progressive Accountant”, April 2021.
There are often cases when individuals, having owned non-residential premises, rent them out for offices, shops, beauty salons, and so on, believing that this is not a business activity, but honestly pay personal income tax on the income received. Few people think that there is a risk of additional VAT being charged on the rental amount.
In case of a dispute with the tax authorities
If a dispute with the tax authority already exists, do not forget that with the emergence of the taxpayer’s obligations, rights must also arise, including the right to exemption from VAT under Art. 145 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. But this is only suitable for those who have rental income per quarter of no more than 2 million rubles. Such persons must submit a written notification and attach documents confirming that the revenue does not exceed two million rubles, no later than the 20th day of the month from which they will exercise this right.
If this deadline has long passed, you should submit such a notice now. If the tax authority refuses to apply the benefit, appeal these actions in court. This is exactly what G.A. Pakhalkov did. from the Tyumen region. He submitted notifications, but the tax authority refused him on the grounds that he was not registered as an individual entrepreneur and was late on time. The businessman went to court. In Determination No. 304-KG18-2570 of July 3, 2021, the RF Armed Forces indicated that when interpreting clause 3 of Art. 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, courts should proceed from the fact that the taxpayer only notifies the tax inspectorate of his intention to exercise the right to exemption, while the consequences of missing the deadline for filing a notification with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not defined. And for cases where the taxpayer did not know that he had to pay VAT, and this became known to him as a result of a tax audit, the procedure for exercising the right to exemption is not provided for by law. But the absence of a procedure established by law does not mean that this right cannot be exercised by the taxpayer.
If gaining experience in tax disputes is not the goal of an individual leasing commercial real estate and the tax authority has not yet made a claim, it is advisable to register as an individual entrepreneur and apply a special tax regime: simplified tax system or special taxation system. Quite often, paying tax by an entrepreneur according to the simplified tax system or special tax system and insurance premiums is more economical than paying personal income tax, but the risk of additional VAT charges is completely absent.
Where else is VAT collected from individuals?
“Hidden taxation,” which is actually VAT for individuals, is included not only in the cost of goods purchased in a store.
A careful study of financial documents will reveal that VAT is included in the cost of services of utility and management companies, postal and mobile operators, transport companies involved in cargo and passenger transportation, a number of medical services and products, training in educational institutions, and in other areas of business that provide services to individuals.