In accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 149 of the Tax Code of Russia, a number of business transactions are not subject to VAT. These transactions are exempt from tax by default, that is, companies and entrepreneurs do not have the obligation to notify the Federal Tax Service of the application of preferential taxation. At the same time, the law provides for the conditions and procedure for refusing this tax exemption. This means that the taxpayer, at his own discretion, can calculate and pay VAT on these transactions in the general manner. At the same time, he, like other taxpayers, has the right to declare the amount of “input” VAT for deduction. The advantage of refusing preferential VAT taxation is that there is no need to maintain separate tax records for taxable and non-taxable transactions.
Who can be exempt from value added tax
The legislation provides that firms and individual entrepreneurs may not charge or pay VAT if over the last 3 months their revenue from the sale of products, services or work excluding tax was less than 2 million rubles. To achieve this right, they are required to provide the tax office with the appropriate notice in writing and documents confirming their right to avoid paying VAT. They must be submitted no later than the 20th day of the month from which the company or entrepreneur wants to exercise the right to tax exemption.
Those. The law provides for the possibility of a notification procedure for the implementation of the right discussed in this article. It is entirely determined by the desire of the taxpayer himself. Fiscal authorities cannot prevent this in any way unless the established revenue limit is exceeded. However, arbitration courts believe that exemption from VAT leads to a reduction in the tax burden on businessmen engaged in small-scale sales of goods subject to VAT.
Important!
To be exempt from VAT, the most important thing is that the revenue does not exceed the maximum level. The cancellation of the payment itself depends on the implementation of transactions, due to the insignificant volume of which are unimportant for the collection of tax.
The submission of the above notification in itself is a normal formality, as the Arbitration Court of the West Siberian District decided in 2021. For this reason, violation of the regulations for notifying tax employees of the exemption does not prevent it. Of course, if the business representative does not abuse it.
In the case considered by this AC, a number of mandatory conditions were violated:
- submitting notifications and documents to the tax office;
- compliance of the revenue volume with the maximum amount.
The taxpayer did not submit the required application either during the tax audit or when filing a complaint with higher tax authorities. Moreover, he did not provide it during the consideration of his case in the court of 1st instance. As a result, the decision to charge additional VAT was recognized by the court as legal.
If old benefits were canceled or new ones were introduced
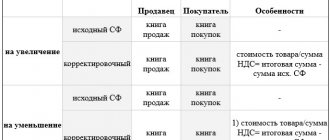
It may turn out that legislation abolishes old ones or establishes new benefits. In this case, the tax is calculated in the order that was in effect at the time the goods were shipped. The date of payment by the buyer does not matter (clause 8 of Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The old product benefit has been cancelled.
Let's say that when the goods were shipped, the benefit for them was canceled.
Then the company must pay VAT, even if the buyer paid for these goods when the exemption was still in effect. EXAMPLE 3. After the goods were shipped, the VAT benefit was for the sale of goods that were not subject to VAT.
The goods were paid for by the buyer on June 10, and shipped to him on July 5. Let’s assume that on July 1, changes to the Tax Code came into force, canceling the benefit for these goods. For goods shipped on July 5, Radar must pay VAT, since at the time of their shipment the exemption was no longer in effect. If the buyer made an advance payment before the changes canceling the benefit came into force, the seller needs to issue an invoice already including VAT and require the buyer to pay an additional amount of tax.
EXAMPLE 4. The seller received an advance for goods before the abolition of the VAT exemption.
Kosmos LLC sells goods not subject to VAT. On December 20 of this year, the buyer transferred an advance to Kosmos to pay for the goods in the amount of 50,000 rubles.
(without VAT). From January 1 of the following year, the benefit for these goods was canceled, and they began to be subject to VAT at a rate of 10%. Cosmos shipped the goods to the buyer on January 10. The Cosmos accountant must make the following entries: December 20 DEBIT 51 CREDIT 62 SUBACCOUNT “ADVANCES RECEIVED”
— 50,000 rub.
– advance payment has been received from the buyer; January 10 DEBIT 62 SUBACCOUNT “PAYMENTS WITH CUSTOMERS” CREDIT 90-1
- 55,000 rubles.
(RUB 50,000 + RUB 50,000 × 10%) – revenue from the sale of goods is reflected (including VAT); DEBIT 62 SUB-ACCOUNT “ADVANCES RECEIVED” CREDIT 62 SUB-ACCOUNT “PAYMENTS WITH CUSTOMERS”
- 50,000 rubles.
– prepayment is credited; DEBIT 90-3 CREDIT 68 SUBACCOUNT “VAT CALCULATIONS”
- 5000 rub.
(RUB 55,000 × 10%: 110%) - VAT is charged. As a result of these transactions, the buyer incurred a debt in the amount of RUB 5,000. When the buyer pays off the debt, an entry must be made in the accounting: DEBIT 51 CREDIT 62 SUB-ACCOUNT “SALEMENTS WITH BUYERS”
— 5000 rub. - money has been received from the buyer.
A new product benefit has been established
If at the time of shipment the benefit is not yet in effect (that is, changes adopted in the legislation have not yet entered into force), you will have to pay VAT.
Even if the money arrives at a time when the benefit is already in effect. EXAMPLE 5. If at the time of shipment there is a VAT benefit,
Radar LLC sold goods that were subject to VAT. The goods were shipped to the buyer on June 10 and paid for on July 5. Let us assume that on July 1, changes to the Tax Code came into force, allowing a company not to pay VAT when selling these goods. Despite the fact that the money was received on July 5, for goods shipped on June 10, Radar must pay VAT, since at the time of their shipment, the benefit was not yet in effect.
The greatest difficulties will arise if the buyer transferred money for the goods in advance, including tax, and before the goods were shipped, the law established a new benefit.
In this case, if on the date of shipment the goods are no longer subject to VAT, the accountant needs to deduct the VAT paid on the advance payment and return the tax amount to the buyer.
EXAMPLE 6. What to do if payment was received for a preferential product, including VAT.
Cosmos LLC sold products of its own production, subject to VAT.
To pay for the products, the company received an advance in the amount of 120,000 rubles. (including VAT - 20,000 rubles). The advance payment was received on June 25. Let’s assume that on August 1, changes to the Tax Code came into force, allowing the company to use the benefit. Starting from this time, Kosmos products are not subject to VAT. The goods were shipped to the buyer on August 10. The Kosmos accountant must make the following entries: June 25 DEBIT 51 CREDIT 62 SUB-ACCOUNT “ADVANCES RECEIVED”
- 120,000 rubles.
– advance payment received from the buyer; DEBIT 62 SUB-ACCOUNT “ADVANCES RECEIVED” CREDIT 68 SUB-ACCOUNT “VAT CALCULATIONS”
- 20,000 rubles.
(RUB 120,000 × 20%: 120%) – VAT is charged on the advance; until July 25, August 25, September 25 DEBIT 68 SUBACCOUNT “VAT CALCULATIONS” CREDIT 51
- 6667 rub.
– VAT was paid to the budget based on the results of the tax period (according to the declaration for the second quarter); August 10 DEBIT 62 SUBACCOUNT “PAYMENTS WITH CUSTOMERS” CREDIT 90-1
- 100,000 rubles.
(120,000 − 20,000) – revenue from the sale of products is reflected (excluding VAT); DEBIT 68 SUB-ACCOUNT “VAT CALCULATIONS” CREDIT 62 SUB-ACCOUNT “ADVANCES RECEIVED”
- 20,000 rubles.
– VAT accrued on the advance payment is accepted for deduction; DEBIT 62 SUB-ACCOUNT “ADVANCES RECEIVED” CREDIT 62 SUB-ACCOUNT “PAYMENTS WITH CUSTOMERS”
- 100,000 rubles.
– the received advance is credited; DEBIT 62 SUBACCOUNT “ADVANCES RECEIVED” CREDIT 51
- 20,000 rub. – the amount of VAT is returned to the buyer. Transactions related to writing off the cost and generating the financial result are made in the generally established manner.
If the notice deadline is missed
To be exempt from paying the tax in question, the inspectorate is notified before the 20th day of the month from which this right must be exercised. Sometimes payers send notice much later. From the tax point of view, violation of the deadline may become the basis for additional VAT assessment and denial of exemption from it. Because the law determines the exact time for providing notifications, and it cannot be violated. But the Arbitration Courts do not consider this a significant violation, which was recognized by the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of Russia with a corresponding Resolution in 2014. It explained that the taxpayer only informs the tax authorities about his decision to take advantage of the right to a benefit. Moreover, the consequences of violating the notification time are not defined by law, and this notification can be sent even after the start of using the tax benefit.
That is why those who actually used the right to avoid paying VAT cannot be denied it solely on the basis of a delay in providing a notice to the tax service. The same applies to situations where notifications regarding the extension of the benefit are not sent in a timely manner. At the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court back in 2013, it was stated that the taxpayer can in any case use the right to a benefit that was not used during earlier tax periods by submitting an updated tax return and an application during an on-site audit from the tax office. You can also submit an application to the inspectorate at the time of tax payment according to the appropriate notification.
Notifications based on the results of control checks: practice of Arbitration Courts
The taxpayer can learn that it is necessary to comply with the established notification regulations during a tax event (audit) and based on its results - when specialists found a delay in notification and then assessed additional tax. True, as the practice of Arbitration Courts shows, this does not deprive a company or individual entrepreneur of the right to benefits (Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In 2013, by a resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, a dispute regarding the additional assessment of value added tax due to the incorrect use of UTII by a businessman was considered. It was found that during the on-site inspection he spoke about exemption from VAT under Article 145. At the same time, he provided the documents stated in paragraph 6 of Article 145 of the Tax Code to confirm his right to the benefit.
The Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation points out that in situations where an entrepreneur learns that it is necessary to pay VAT as a result of an audit, the regulations for obtaining the right to VAT exemption are not defined by law. However, this fact does not mean that a businessman will not be able to exercise his right. On this basis, the decision to assess additional tax was declared illegal.
It is possible to submit a notification even after the end of the audit - this is what the Volga District Autonomous District considered in 2021. Then the business representative was denied exemption due to his failure to provide the required notification before completing the tax audit procedure. The court's explanation stated that the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not say how to apply the right to exemption from VAT when the entrepreneur learns that it still needs to be paid as a result of an audit.
This means that failure to submit the required statement during the verification process cannot deprive a businessman of his rights. The court found that the payer fulfilled all the conditions to receive the benefit. Therefore, he can use it even before a higher authority makes a decision on his appeal.
The tax authorities’ arguments about the failure to provide the documents described in paragraphs 3 and 6 of p. 145 of the Tax Code were rejected by the court. He noted that the businessman’s receipt of income of more than 2 million rubles for every 3 subsequent months was not proven during the audit. As a result, the court’s conclusion stated that the tax authority’s decision to assess additional taxes cannot be considered justified.
"Popular" benefits
In practice, VAT benefits are most often used for the provision of medical or educational services. And here there are some peculiarities that must be taken into account in the work.
Medical services
The sale of “...medical services provided by medical organizations, individual entrepreneurs engaged in medical activities, with the exception of cosmetic, veterinary and sanitary-epidemiological services” is not subject to VAT. If veterinary and sanitary-epidemiological services are financed from the budget, then they are also not subject to VAT. This benefit is established by subparagraph 2 of paragraph 2 of Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The benefit can be used by medical organizations and institutions, private individual entrepreneurs - doctors and medical centers on the balance sheet of non-medical companies.
Here is a list of medical services that are not subject to VAT.
1. Services provided under compulsory health insurance. Such services can be provided to both individuals and companies. The list of these services is given in Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated October 4, 2010 No. 782 and Methodological recommendations approved by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation and the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund on August 28, 2001 No. 2510/9257-01, 3159/40-1.
2. Services provided to the population according to the list approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated February 20, 2001 No. 132. These include:
- diagnostic, prevention and treatment services directly provided to the population within the framework of outpatient (including pre-medical) medical care, including medical examination;
- diagnostic, prevention and treatment services directly provided to the population as part of inpatient medical care, including medical examination;
- diagnostic, prevention and treatment services directly provided to the population in day hospitals and by the services of general (family) doctors, including medical examinations;
- diagnostic, prevention and treatment services directly provided to the population in sanatorium and resort institutions;
- health education services provided directly to the public.
According to financial officials, if a licensed organization provides the population with medical services mentioned in this list free of charge, then these services are also not subject to VAT (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 13, 2016 No. 03-07-11/21224).
3. Services for collecting blood from the population. A medical organization or private doctor must have an agreement with a medical organization providing medical care in outpatient and inpatient settings.
4. Services provided by medical organizations and private doctors to pregnant women, newborns, disabled people and drug addicts.
5. Emergency medical services.
6. Services for medical personnel on duty at the patient’s bedside.
7. Pathological services.
8. Services of pharmacies for the manufacture of medicines for medical use (the benefit is provided for in subclause 24, clause 2, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
9. Services for the manufacture and repair of spectacle optics (except for sun protection), repair of hearing aids and prosthetic and orthopedic products, services for the provision of prosthetic and orthopedic care (the benefit is provided for in subclause 24, clause 2, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
10. Sanitary, epidemiological and veterinary services financed from budget funds. In this case, the company must have the following documents:
- license;
- contract for the provision of veterinary or sanitary-epidemiological services indicating the source of financing;
- written notification of the customer, to whom funds have been allocated from the federal budget, to the company about the targeted budget funds allocated to him to pay for sanitary-epidemiological and veterinary services;
- a certificate from the financial authority about the opening of financing of veterinary and sanitary-epidemiological services at the expense of the regional or local budget.
Veterinary and sanitary-epidemiological services that are not financed from the budget or are financed on a repayable basis are subject to VAT.
A company or doctor engaged in private practice must have a license to practice medicine.
If there is no such license, then the benefit cannot be applied.
If your company provides medical services that are not subject to VAT, then you cannot refuse this benefit.
But the services of intermediaries in the field of medical services are subject to VAT.
EXAMPLE 7. Intermediary medical services are subject to VAT.
Be Healthy LLC provides paid emergency medical services to the population. At the same time, the company transports patients both within the framework of emergency care and for hospitalization for preventive and diagnostic purposes. Services provided within the framework of emergency care are not subject to VAT. Transportation of patients for hospitalization for preventive or diagnostic purposes, that is, in situations that do not threaten the life and health of people, is subject to VAT, since it is an intermediary service.
Educational services
Sales are not subject to VAT (subclause 14, clause 2, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) “...services in the field of education provided by non-profit educational organizations for the implementation of general education and (or) professional educational programs (main and (or) additional), professional training programs specified in the license, or the educational process, as well as additional educational services corresponding to the level and focus of educational programs specified in the license, with the exception of consulting services, as well as services for leasing premises.”
In other words, services in the field of education are exempt from VAT not only if they are specified in the license. The benefit also applies to additional services that correspond to the educational programs of the organization (for example, classes with a speech therapist in a preschool educational institution). The benefit is provided only to non-profit educational organizations. They do not pay VAT regardless of how the income received from the provision of educational services is distributed.
There are a number of fairly common services of non-profit educational organizations that are subject to VAT. Such services include, in particular:
- consulting services;
- premises rental services;
- sales of goods of own production, manufactured by educational enterprises;
- sale of goods purchased externally.
Services of commercial organizations and individual entrepreneurs in the field of education are taxed in accordance with the generally established procedure.
Classes with children in clubs, sections and studios are not subject to VAT (subclause 4, clause 2, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
EXAMPLE 8. Fees for additional classes at school are not subject to VAT.
The school has a swimming pool on its balance sheet. In addition to the main classes with students, the organization also conducts additional classes for children under 18 years of age on a paid basis. In this case, fees received for additional classes are not subject to VAT.
If your company provides services in the field of education and is entitled to a benefit, then you must definitely apply it. You cannot refuse the benefit.
The services of intermediaries in the field of education are subject to value added tax at a rate of 20 percent.
In general, intermediaries deserve to talk about their taxation in a little more detail.
Other factors
The fact that during a tax audit it was established that the taxpayer had submitted a VAT return does not prevent an exemption from paying VAT. This is what the Arbitration Court of the North-Western District decided in 2015. In this case, the basis for additional tax assessment was the businessman’s application for VAT tax deductions. The tax service did not find any evidence that he was not entitled to a VAT benefit. Also, the documents presented by the business representative showed that he had the right to be released. The inspectorate said that before filing a tax notice, the individual entrepreneur filed VAT returns. In addition, he also used the right to tax deductions.
However, the CA decided that the filing of the VAT return occurred due to its execution of the tax decision. This decision indicated the individual entrepreneur’s failure to fulfill the obligation to submit declarations. In addition, the court noted that Article 145 of the Tax Code of Russia contains a mechanism that helps restore deducted tax amounts. As a result, the CA ruled that the individual entrepreneur legally took advantage of the benefit.
How does the court determine the fact of refusal of benefits?
As mentioned above, even if the application for refusal of preferential taxation was not filed within the prescribed period, the courts may recognize that the refusal of tax exemption nevertheless took place. In this case, the arbitrators rely on the reflection in tax returns of VAT amounts calculated without taking into account benefits, that is, when exempt transactions are taxed in the general manner. In addition, such declarations must be filed within the time limits provided by law for the submission of appropriate reporting. This implies that the taxpayer violated the requirements of paragraph 5 of Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation only formally. After all, by calculating VAT on exempt transactions, he thereby committed implied actions that indicate an actual refusal of preferential taxation.
If no notice of release is provided
Sometimes companies or individual entrepreneurs may not send notifications at all for exemption from the accrual and payment of VAT. This can happen if they mistakenly take advantage of a certain preferential special treatment and think that they do not have to pay VAT. Even in such cases, a court decision may be in their favor: this was confirmed by the Arbitration of the Central District with its Resolution of 2021. The reason for calculating VAT in the situation considered by the court was the entrepreneur’s incorrect use of UTII.
At the same time, the Arbitration found the additional assessment illegal, pointing out that the tax authorities, having established the wrong qualifications for the business activities carried out by the individual entrepreneur, were obliged to explain to him the rights to provide benefits. And also make sure that the individual entrepreneur meets the criteria for giving the benefit, which was not met.
However, the court found that the entrepreneur’s revenue excluding VAT during the disputed periods was not higher than the limit established by Article 145. It turns out that an individual entrepreneur would have the right to a VAT benefit, and it needs to be provided to him. When the time came to confirm his right, a representative of the business community did not think that he had to pay this tax due to the use of UTII. Therefore, he did not submit the required notification to the tax office.
Important!
In similar cases, taxpayers may submit a notice after the stated deadline. However, you will almost inevitably have to prove your case in court.
Is it possible to challenge a refusal to provide a VAT benefit?
When a company or individual entrepreneur submits a notification of its right to VAT exemption, tax representatives can theoretically take advantage of any mistake made to refuse. As you know, a formal cause can also be considered a cause.
Which does not mean that the refusal cannot be challenged in court. On the contrary, in many cases it shares the point of view of taxpayers, and refusals are recognized as illegal. However, it is better to avoid wasting time and energy on lengthy legal proceedings by spending it on completing work tasks. It is much easier, and most importantly, more productive, to comply with the specified deadlines and adhere to all formalities specified in the Tax Code. It's much easier. And, in the end, cheaper.
View 1C catalog