According to the current legislation, the employer is held liable for the improper fulfillment of obligations towards employees. Most often they are held accountable for violating the work of the personnel department.
There are quite a few types of liability, each of which has its own dimensions and is punishable administratively or criminally, depending on the specific violation. Major changes to the Labor Code and the Criminal Code have occurred recently and the amendments have come into force in 2015.
It is worth mentioning separately that in the event of a fine being imposed, payment of the fine does not relieve one from the obligation to eliminate violations. That is why it is necessary to restore personnel records when eliminating violations for the identified periods.
Administrative
The most common type of liability. More than 80% of employer engagements constitute an administrative offense.
Fines
According to statistics, most often employers are brought to administrative liability under Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
According to the law, the following fines are applied to the offender:
- For admission to production of an employee without establishing legal relations with him in the form of an employment contract - up to 5,000 rubles. for individuals, up to 20,000 for responsible persons.
- For the absence of a correctly executed employment contract, only officials are held accountable, the fine is up to 20,000.
- For other violations, grounds for which are not contained in Article 5.21.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, up to 5,000 for an official and up to 50,000 for a legal entity.
This article also provides for additional liability for individuals and organizations that are subject to penalties not for the first time.
Another article regulating the administrative responsibility of the employer is Article 18.15 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, which controls the use of hired labor from foreign countries.
The article provides for the following sanctions:
- In the case of involving persons who do not have official permission in the work - up to 5,000 rubles for individuals, for officials - up to 50,000 rubles, and for organizations - up to 800,000. Also, the activities of the violating company can be stopped for a period of 3 months.
- If the law requires permission to attract foreign citizens, but it is not available at the time of hiring, a similar punishment will apply.
- The same measures apply to an employer who has not notified the FMS that the contract with a foreign employee has been terminated. This must be done within three days after termination.
- If the above offenses were committed in the so-called cities of federal significance, that is, in Moscow or St. Petersburg or in settlements located on the territory of the Leningrad or Moscow regions, then the liability increases - up to 7,000 for individuals, up to 70,000 for officials and up to a million rubles for organizations.
The legislation provides for many violations, but those described above make up a large proportion, while others are much less common. But it is worth remembering that this list does not contain all attraction items. Today, new amendments are being actively developed that could further tighten the employer’s liability.
Changes since 2015
From the first day of 2015, amendments and changes to federal legislation came into force.
Significant changes:
- Firstly, the period for bringing to justice for administrative offenses has been significantly increased, now it is 1 year.
- Secondly, some subtypes of offenses are identified as independent - these are violations relating to the procedure for drawing up an employment contract.
- Thirdly, a new article has appeared in the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, which provides for responsibility for assessing working conditions and monitoring them. Now the employer is responsible for the timely completion of professional examinations by employees, as well as for increasing their level of qualifications in the field of knowledge about labor protection.
- The amount of fines imposed has been significantly increased.
These changes indicate that the federal authorities are increasing the importance of compliance with legislation regarding workers' rights.
Administrative responsibility for organizations conducting SOUT
It should be noted that all innovations were considered for a long time, and entrepreneurs were given the opportunity to prepare for the amendments to enter into legal force. A special transition period was established, which ended with the onset of 2015.
Responsibility for administrative offenses for organizations involved in carrying out special assessments has also been tightened. More details about this are indicated in Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
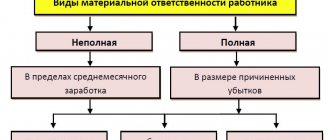
Material
Most often, employers are subject to prosecution after refusing to pay for labor in the agreed manner. Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation contains instructions on the recruitment process and lists all the grounds for starting the process.
It establishes that in the event of a violation of payments (payments include wages, vacation contributions, and payments upon dismissal, as well as any other provided by an official document or legislation) in terms of time or amount, the person held accountable is obliged to pay not only the withheld funds, but also compensation.
The procedure for calculating compensation has changed. The amount of compensation cannot be less than three hundredth of the current national bank rate on the withheld amount, the percentage is calculated for all days of delay. The first day is considered to be the one following the established payment date, and the last day is the one when the calculation is made. If a collective or employment agreement provides for increased compensation, the employee receives the maximum possible amount.
Types of fines
According to the same article, the Labor Code obliges the employer to reimburse the employee for all illegally withheld funds, as well as funds that the employee did not receive when he was deprived of the opportunity to work without good reason.
Such cases include:
- transfer to another position without consent, illegal dismissal, as well as groundless removal of an employee from his duties;
- failure to comply with the decision of the body or person responsible for labor disputes;
- refusal to reinstate or otherwise satisfy the employee’s legal requirements;
- refusal to issue a work book or filling it out improperly with false information;
Changes since 2015
Significant changes have also occurred in the articles defining financial responsibility. Most of all, Article 419 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation has undergone changes.
The size of sanctions and the maximum amounts of payments in favor of employees have increased. The procedure for making decisions on controversial issues has not changed. More stringent decisions are provided for when repeated violations are detected.
Employer's liability in case of injury at work
In the event of an injury at work, what should you do first after providing assistance? It is necessary to determine whether the injury is work-related or not. The concept of industrial injury is also given in Art. 227 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Art. 3 of Federal Law No. 125-FZ of July 24, 1998 “On compulsory social insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases.” This is an injury that occurred to an employee while he was performing his job functions. Such injuries include: Having determined that the injury is still work-related, the employer must create a commission that will investigate and register the work-related injury. The employer must cooperate in every possible way with the investigation. In addition, he must take measures that will protect other people from accidents. Based on the results of the investigation, the commission draws up an act, which must be signed by all its members, certified by the employer’s signature and seal, and registered in the Accident Register.
21 Dec 2021 marketur 343
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Where in Tula they film beatings address
- Do I need to fill out the form if there is an online cash register?
- List of documents required for registration of property rights
- What to do if your child's travel card is lost?
Civil liability
According to article number 56 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, organizations and legal entities are responsible for the fulfillment of obligations with all the property they own. If the employee suffered non-material damage, that is, damage to health or moral suffering, then Article 151 contains instructions on the procedure for compensation for damage in monetary terms. The same applies to violations of personal rights, as well as any other actions specified in the law.
It is important that the employer does not have the right to establish rules for its employees that would violate their rights given by the Constitution of the Russian Federation.
Is the employer responsible for the actions of the employee?
There is an exception to the above rule: if the employee committed an offense in the course of performing work, but acted for his own personal purposes, and not for the purposes of the employer, the employer is not responsible for his actions. There are a number of other cases when the employer will not be held liable for the employee’s actions, we will consider them. 1) An employer’s ban on performing an action - if such a ban was brought to the attention of the victim, the employer is not liable for harm due to the principle of “putting oneself in danger.” So, for example, in the case of road transportation, the employer forbade the employee to travel for some reason , and the carrier’s client knew about this, but, nevertheless, agreed to go and, as a result, suffered. The employer will not be held liable in this case. Employers - individuals are individuals registered in the prescribed manner as individual entrepreneurs and carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity, as well as private notaries, lawyers who have established law offices, and other persons whose professional activities are in accordance with federal laws subject to state registration and (or) licensing, having entered into labor relations with employees in order to carry out the specified activities. Individuals who, in violation of the requirements of federal laws, carry out the specified activities without state registration and (or) licensing, who have entered into labor relations with employees for the purpose of carrying out this activity, are not exempt from fulfilling the obligations assigned to employers - individual entrepreneurs.
Please note => Time sheet form sample filling
Criminal liability
This type of liability is also provided for employers.
Thus, an unjustified refusal to employ an employee on maternity leave or a nursing woman, according to Article 145 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, is punishable. The employer is sentenced to either a fine or compulsory work. Violation is subject to investigation as a criminal offense.
Changes since 2015
Article 145 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation has undergone changes (it determines the procedure for making payments both under an employment contract and payments to social groups).
Now the responsibility for the first paragraph of this article is as follows:
- If payments were made partially and the debt amounted to more than 3 months, the punishment was increased to imprisonment for a period of a year, and the damage can also be compensated by fines in favor of the victim, especially severe punishment is provided if the responsible person committed the crime for personal gain.
- In case of complete refusal to pay for more than 2 months, as well as in case of payment of an amount that is less than the minimum wage established in the region, imprisonment for a term of up to three years is provided. Likewise, severe punishment is provided for persons who commit a crime out of self-interest, hostility or other personal motives.
- If the crimes provided for in this article lead to serious consequences, the term of imprisonment can be up to 5 years. The employer is also obliged to compensate for the damage; the fine can reach half a million rubles.
Employer's liability in case of an employee's accident
When using a vehicle, the employer is required to take out a compulsory motor liability insurance policy. If damage occurs as a result of an accident, the amount is covered by the insurance company, unless the circumstances of a violation of the contract are proven. The insurance company determines the conditions under which the insurance amount is not provided. When determining the amount of damage in an amount exceeding the losses caused, the difference is covered by the enterprise (the culprit). Compensation to the employer for losses in full (exceeding the average monthly earnings) may be established by a decision of a court or other body that has the right to impose administrative penalties. If coverage of losses is established in court, the employee has the opportunity to reduce the amount by presenting evidence of a difficult financial situation and the presence of dependents.
Please note => Buying an apartment from a developer with a mortgage procedure