Rate of the simplified tax system “Income”
The tax rate shows how much percent of income the state will have to pay. In most cases it is 6%. But there are regions that have reduced the rate.
In Crimea and Sevastopol the rate is 4%. In Sevastopol, you can pay even less - 3%, if you run a business from the list of preferential activities. In the Chechen Republic, the tax rate depends on the number of employees and ranges from 1% to 6%.
In Moscow, St. Petersburg and Yekaterinburg, the simplified taxation system rate is standard - 6%.
Find out on the tax website in the section “Features of regional legislation” what rate is valid in your region.
If your annual income exceeds 150 million or there are more than 100 employees, then the rate for any region will increase to 8%.
The role of the simplified tax system in enterprise accounting
Businesses are generally required to maintain accounting and tax records. When using the simplified tax system in activities, the reporting procedure is somewhat simplified. Guided by specific regulations, individual entrepreneurs and simplified organizations may not keep accounting records at all. Law No. 129-FZ of 1996 speaks about this.
However, commercial units are not exempt from preparing primary documentation. In practice, this means that it is mandatory to keep records of intangible assets and fixed assets. Accounting is necessary solely to determine the possibility of applying the simplified tax system. That is, the right to use this regime is lost as soon as the amount of fixed assets and assets exceeds a total of 100 million rubles. Accounting also becomes mandatory in the case of combining regimes, for example, UTII and “simplified”.
Depending on the chosen tax payment scheme by the base, the following may happen:
- profit - income;
- profit – income minus expenses.
When taxing income, profit is considered to be:
- revenue from the sale of goods or services;
- non-operating income.
Revenue recognition for tax purposes is carried out on a cash basis in some cases. Receipt of money into the cash register is recorded according to KUDiR. Certain types of profit are not taken into account (Article 251 of the Tax Code).
Not considered profit (for tax purposes):
- contributions to the authorized capital;
- pledge (deposit) in monetary or property form;
- earthly means;
- the value of property received for sale under an intermediary agreement.
When using the “income minus expenses” scheme, it is necessary to take into account material expenses. It is most often done by valuing the purchased item at unit price, average price, or first purchase (FIFO).
Costs in this case:
- salary;
- depreciation of fixed assets;
- material needs;
- social needs and so on.
What is considered income under the simplified tax system?
Income under the simplified tax system is everything you earn from your business. Basically, this is income from the sale of goods or services. For example, you developed a website and received 100 thousand rubles for the work. Record the same amount in the income of the simplified tax system and pay tax on it.
There are also non-operating incomes that are not directly related to the business, but they also need to be taken into account. These include:
- interest on current account balance
- fines and penalties from partners for violated terms of the agreement
- compensation for damages from the insurance company
- exchange rate difference when buying or selling currency at a rate that is more favorable than that of the central bank
- gifts and other free property received
- other income from Art. 250 Tax Code.
Most often, you receive income in cash. But there are non-monetary incomes, for example, with barter and mutual offsets, when you exchange one product for another. Such income also needs to be taken into account - in rubles at the market value of a similar product.
Convert income in foreign currency into rubles at the central bank exchange rate in effect on the day you receive the money. We talked about this in more detail in the article “How to pay taxes when making payments in foreign currency.”
Submit reports in three clicks
Elba is suitable for individual entrepreneurs and LLCs on the simplified tax system. The service will prepare a tax return, calculate the tax and reduce it by insurance premiums. Try 30 days free.
Try 30 days free Gift for new entrepreneurs The promotion is valid for individual entrepreneurs under 3 months old
Which subaccount 99 account to use for penalties and fines
1C free 1C-Reporting 1C:ERP Enterprise management 1C:Free 1C:Accounting 8 1C:Accounting 8 CORP 1C:Accounting of an autonomous institution 1C:Accounting of a state institution 1C:Municipal budget 1C:Settlement budget 1C:Clothing allowance 1C:Money 1 C: Document flow 1C: Salaries and personnel of a budgetary institution 1C: Salaries and personnel of a government institution 1C: Salaries and personnel management 1C: Salaries and personnel management CORP 1C: Integrated automation 8 1C: Lecture hall 1C: Enterprise 1C: Enterprise 7.7 1C: Enterprise 8 1C: Retail 1C: Management of our company 1C: Management of a manufacturing enterprise 1C: Trade management 1 Enterprise 8
Which subaccount 99 of the account should be used to calculate penalties and fines on profits, VAT, Pension Fund and Compulsory Medical Insurance if the accounting policy does not use PBU 18/02 On the forums they write 99.01.1 and on the ITS disk 99.02.3 is indicated, but the accounting analysis complains about it because it is a subaccount intended only for PBU18/02
We recommend reading: Which okved to take for clothing trading
What income does not need to be taken into account in the simplified tax system?
Not all money received is your income. When calculating the simplified tax system, you do not need to take into account:
- loan repayment;
- obtaining a loan;
- replenishing your account with personal money;
- security deposit or pledge;
- refund from the supplier;
- erroneous receipts from a counterparty or bank - Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 7, 2006 N 03-11-04/2/231;
- money received by an agent under an agency agreement, except for agency fees;
- grants;
- income from business on a different taxation system, if you combine the simplified tax system with UTII or a patent;
- other income from Art. 251 NK.
Individual entrepreneurs have income that is not taken into account in the simplified tax system, but personal income tax is withheld from them at a rate of 35%:
- The cost of winnings and prizes from participation in incentive competitions that are held to advertise products. Personal income tax must be paid on that part of the winnings whose value is above 4,000 rubles. Personal income tax is transferred not by the individual entrepreneur himself, but by the organizer of the competition.
- Saving on interest when receiving a loan at a rate below ⅔ of the refinancing rate. The bank itself will calculate and pay personal income tax to the tax office.
Penalties for non-payment of advance payments under the simplified tax system
It turns out that if the company did not pay advances at all under the simplified tax system, then penalties must be calculated for the period from the date on which the deadline for making advance payments expired until the day on which the tax for the year was paid. At the same time, with the object “income” there is no possibility to adjust the amount of penalties.
The delay in payment of advance payments was: for six months - three days, and for nine months - seven days. Penalties are calculated based on 1/300 of the refinancing rate of the Bank of Russia (clause 4 of article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). During the period under review, the rate was 8.25%.
We recommend reading: What greenery looks like for an apartment
When to take into account income of the simplified tax system
It's important to record earnings on the correct date because it determines when you pay tax on that money.
Earnings are recorded on the day you receive them. This is called the cash method of revenue recognition. If the income is cash, take it into account on the day the money arrives in your bank account or cash register. Prepayment must also be taken into account on the day of receipt.
In some situations, income must be taken into account before you receive the money. For example, you sell through a courier who receives payment and transfers it to you. In this situation, income is taken into account on the day the client paid the courier, despite the fact that you have not yet received the money.
If the income is non-monetary, for example, offsetting mutual obligations with a client, take it into account on the day when you signed the act of offset or other document.
For example, you developed a website for a furniture showroom, and he supplied you with office furniture. The counterparty must pay 100,000 rubles for the website, and you must pay him the same amount for the furniture. In order not to transfer money from account to account, you agreed on a mutual settlement, after which no one owes anyone. To formalize the agreement, you sign an act of offset. On the same day, you need to take into account 100,000 rubles in the income of the simplified tax system.
To which accounting account is the penalty tax accrued?
Each fact of the company’s economic life must be recorded in its own way. This will allow you to create an impeccable balance sheet. If the company was nevertheless charged with penalties under the simplified tax system, transactions in such a case are drawn up in the same way as in the situation with VAT, that is, according to Debit account 99, sub-account “penalties” and Credit 68, using the sub-account, designed to reflect
We recommend reading: How to get family capital for 3 children in the Samara region
But in practice, many entrepreneurs prefer to follow the canons of accounting. Dear readers! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique.
How to reduce the simplified tax system 6%
One of the advantages of the simplified tax system “Income” is that the tax can be reduced on insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs and employees. To do this without errors, remember two rules:
- Individual entrepreneurs without employees reduce the tax on contributions completely, and individual entrepreneurs with employees and LLCs - by half.
For example, you have no employees, and the simplified tax system for the first quarter was 10 thousand rubles. In the same quarter you paid 8,000 rubles in insurance premiums. You subtract this amount from the simplified tax system and pay 2,000 instead of 10 thousand rubles.Another situation: you hired employees and paid 20 thousand rubles in insurance premiums for them and for individual entrepreneurs during the first quarter. The simplified tax system for the first quarter is 15,000 rubles. Since you have employees, you only reduce the simplified tax system by half. It turns out that the simplified tax system for the first quarter cannot be lower than 7,500 rubles. As a result, you pay 7,500 rubles instead of 15 thousand rubles in tax.
- You can deduct from tax only those contributions that you paid in the same period for which you are calculating tax. For example, on March 1 you paid 15,000 rubles in insurance premiums. You can deduct this amount from the simplified tax system for the first quarter. We wrote a separate article about the rules for reducing taxes, “How to reduce the amount of tax on the simplified tax system.”
Online calculator for calculating the simplified tax system (6%, 15%, penalties)
In order for the online simplified tax system calculator to make the correct calculations, you will need to indicate the current rate in the region, as well as the quarterly amount of income received, expenses and the amount of tax advances paid.
You will need to indicate the amount of income for each quarter, the amount of insurance premiums paid (including for voluntary insurance), sick leave benefits and advance payments for the single tax. If necessary, it is possible to reflect payment of the trade fee.
We recommend reading: Where to go to check out of an apartment
Reporting on the simplified tax system “Income” in 2021
Tax on the simplified tax system is paid quarterly, and the declaration is submitted once at the end of the year - this is the most important thing that entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system need to remember. Quarterly payments are called advance payments because you pay them in advance for the whole year.
Every quarter you need to pay tax:
- until March 31, 2021 for LLCs, until April 30, 2021 for individual entrepreneurs - final calculation of the simplified tax system for 2021.
- until April 26 - for the 1st quarter of 2021,
- until July 26 - for the first half of 2021,
- until October 25 - for 9 months of 2021.
Submit your simplified taxation tax return once a year. For 2021, LLCs report until March 31, 2021, and individual entrepreneurs - until April 30, 2021.
In addition, keep a book of income accounting. Record all business income and insurance premiums paid there. This book does not need to be handed over to the tax office until it asks.
Article “How to keep a book of income and expenses.”
Accounting entries for accrual of penalties for taxes in 2021
Otherwise, a penalty will be charged at the initiative of the Federal Tax Service. A fine is not a tax penalty, but is related to tax obligations. Therefore, accountants often have a question about how to correctly reflect penalties in accounting.
We recommend reading: How many photos do you need for a health book?
In addition, the same article states that the mentioned expenses are taken into account if they comply with the parameters given in paragraph 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which states the possibility of reducing income by the amount of expenses other than those listed in Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Calculation of simplified tax system 6% of income: postings
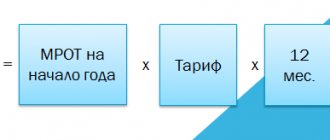
The tax base (TB) under the special simplified tax regime of 6% is the total amount of income recorded in the accounting records. To determine the NB for the tax period, income is calculated quarterly with a cumulative total. At the end of the year, the total income result is summed up. The marginal tax rate is 6%, but regional authorities are given the right to set the rate from 1 to 6%. Advance tax is calculated using the formula:
In this case, the amount of the advance payment can be reduced by the amount of insurance premiums paid in the reporting period (for contributions of individual entrepreneurs without employees “for themselves”, the tax can be reduced in full, insurance premiums of companies and individual entrepreneurs with employees can reduce the amount of calculated tax by 50%), as well as trade tax. When calculating the tax for the year by intra-annual periods, the amounts of previously transferred advances are also deducted from the calculated tax amount.
At the end of the year, at the final tax calculation, either an additional payment or an overpayment may arise, which is counted against future payments or returned to the company’s account. The decrease in the final tax amount is recorded by posting: D/t account. 68 – K/t count. 99.
Individual entrepreneur Ivanov P.T. who has no employees. applies the simplified tax system “income” and maintains accounting. In 2021, he earned 296,000 rubles:
in the 1st quarter – 60,000 rub.,
in the 2nd quarter – 120,000 rub.,
Tax calculation first quarter
Tax calculation is performed at the end of the month. Since the simplified tax system is calculated quarterly, at the end of the quarter the line “Calculation of the simplified tax system” will appear in the assistant.
Let's look at the transaction transactions.
Accounting is maintained in account 68.12 “Tax under the simplified taxation system.”
How is the calculation done? To check, in the assistant window, click on the operation and select the “Calculation of simplified tax system” item.
A detailed explanation of the calculation will open.
It works like this:
- We consider the amount of income as a cumulative total: 35,000 rubles.
- We consider the amount of expenses as a cumulative total: 24,000 rubles.
- We calculate the difference between income and expenses: 35,000 - 24,000 = 11,000 rubles.
- We multiply the resulting difference by the tax rate of 15%: 11,000 * 15% = 1,650 rubles.
- We determine the amount of the minimum tax. This is a mandatory tax of 1% of income. It is paid if the difference between income and expenses is zero or negative. That is, we pay 15% of the difference, or 1% of income. It turns out 35,000 * 1% = 350 rubles.
- We compare the amounts in steps 4 and 5 and take the largest. 11,000 > 350 - this amount is then taken into account.
- We subtract the amount of advance payments from the previous period from the tax amount. In this example, there are no advance payments, so the final tax amount will be 1,650 rubles.